(Press-News.org) Cancer cells are gluttons. We have long known that they monopolize large amounts of sugar. More recently, it became clear that some tumor cells are also characterized by a series of features such as mobility or unlikeliness to join in an ordered set. Researchers are calling this behavior "mesenchymal," and they suspect it promotes metastasis.
At EPFL, Etienne Meylan's research team was able to demonstrate that the two observations – appetite for sugar and mesenchymal behavior – result from the same mechanism, at least in "non-small cell lung cancer." They also showed that the intensity of the phenomenon significantly influenced the chances of patient survival. Published in Cancer & Metabolism, this discovery opens up new potential targets for future therapies.
A useful mechanism, but put to work by cancer
Mesenchymal behavior is not in itself an anomaly. During embryonic development, some cells acquire these characteristics. In adults, a few cells retain this disposition.
"Mesenchymal behavior is a quite useful feature, but is abnormally reactivated in non-small cell lung cancer, which we studied," says Etienne Meylan.
The mesenchymal cancer cells studied by the researchers produce a protein called GLUT3. The latter serves the function of capturing glucose to activate various growth processes. This is the protein responsible for meeting the cell's need for sugar.
By artificially inducing mesenchymal behavior in cancer cells, the researchers found that the cells spontaneously produced GLUT3. This observation clearly shows that the same mechanism is at work. "This shift from one behavior to another, called epithelial-mesenchymal transition, is a highly debated issue. We have clearly established a cause and effect relationship between this transition and the glucose consumption of cancer cells," explains Mark Masin, lead author and PhD student at EPFL.
A case study confirms the results
Lung tumor cells produce widely varying amounts of GLUT3. This is because the gene is itself regulated by an element called ZEB1, and the amount of the latter is a function of many causes.
These variations in the amounts of GLUT3 seem to be a strong indicator of the aggressiveness of the tumor. By analyzing data from 450 patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, researchers were able to show that the larger the quantity of GLUT3, the lower the chances of survival.
Patients were diagnosed relatively early and were followed for several years. Depending on whether they produced high or low amounts of GLUT3, their survival rates over seven years spanned almost 20%. "Our data don't permit us to conclude that the mechanism promotes metastasis, but it reinforces the assumption," says Mark Masin.
The discovery identifies a potential target for future medications. Etienne Meylan imagines, for example, a toxic molecule that could be specifically incorporated by GLUT3 to destroy the cell from within. "Protected by the blood-brain barrier, neurons that also produce GLUT3 would not be affected," says the researcher.
INFORMATION:
Cancer: Tumors absorb sugar for mobility
Some cancer cells are characterized by both high sugar intake and high mobility; researchers at EPFL show that these 2 phenomena are related
2014-07-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study suggests both high physical activity and less sitting in leisure time may be required to substantially reduce risk of obesity
2014-07-29
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) suggests that both higher levels of physical activity and lower levels of sitting in leisure time may be required to substantially reduce the risk of obesity. The research is by Joshua Bell and colleagues, Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, UCL (University College London), UK.
Physical activity and sitting time (or 'sedentariness') are two common lifestyle-related behaviours associated with obesity and metabolic health, as well as with chronic diseases ...
First controlled malaria infection trial in Africa paves way for drug and vaccine development
2014-07-29
Deerfield, Ill. (July 28, 2014) – An international research team today reports the first-ever clinical trial demonstrating controlled malaria infection in an African nation in the modern era. The study, published online in the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (AJTMH) represents a significant milestone in the search for new malaria drugs and vaccines.
The study establishes that in controlled laboratory conditions in Africa, a new product containing frozen, preserved whole sporozoites, an infectious stage of the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum, ...
News from Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet July 29, 2014
2014-07-29
1. Early menopausal hormone therapy shows no effect on atherosclerosis progression
Early initiation of menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) improves some markers of cardiovascular disease (CVD) but does not affect the progression of atherosclerosis, according to a study being published in Annals of Internal Medicine. CVD is the leading cause of death in women and incidence increases after menopause. Research suggests that cardiovascular benefits of MHT may be limited to women who begin treatment at a younger age, closer to menopause, or both. Researchers conducted a randomized ...
ACS NSQIP database helps hospital identify and curb its surgical risk
2014-07-29
NEW YORK (Monday, July 28 – 5 p.m. ET): Surgical patients who are placed in contact isolation after their operations are at a particularly high risk for developing life-threatening blood clots, but ensuring they move around has helped curb the occurrence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in one hospital. This case study on how one surgical team prevented VTEs in their patients placed in isolation was presented today by researchers from the department of surgery at Carilion Clinic Roanoke Memorial Hospital, Roanoke, VA at the American College of Surgeons National Surgical ...
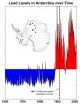
Lead pollution beat explorers to South Pole, persists today
2014-07-29
Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen reached the South Pole in 1911, but new research shows that industrial air pollution arrived long before any human.
Using data from 16 ice cores collected from widely spaced locations around the Antarctic continent, including the South Pole, a group led by Joe McConnell of the Desert Research Institute (DRI) in Reno, Nevada, created the most accurate and precise reconstruction to date of lead pollution over Earth's southernmost continent. The new record, described in an article published today in the online edition of the Nature Publishing ...
Generating a genome to feed the world: UA-led team sequences African rice
2014-07-29
An international team of researchers led by the University of Arizona has sequenced the complete genome of African rice.
The genetic information will enhance scientists' and agriculturalists' understanding of the growing patterns of African rice, as well as enable the development of new rice varieties that are better able to cope with increasing environmental stressors to help solve global hunger challenges.
The paper, "The genome sequence of African rice (Oryza glaberrima) and evidence for independent domestication," was published online in Nature Genetics on Sunday.
The ...
Research letter examines pacemaker use in patients with cognitive impairment
2014-07-28
Dr. Nicole R. Fowler and her fellow reserachers have found that patients with dementia were more likely to receive a pacemaker then patients without cognitive impairment.
Older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia can have co-existing cardiac illnesses and that makes them eligible for therapy with devices to correct rhythm abnormalities. But the risks and benefits need to be weighed carefully with patients, families and clinicians.
The authors examined data from the National Alzheimer Coordinating Center Uniform Data Set gathered from 33 Alzheimer ...
Electronic screening tool to triage teenagers and risk of substance misuse
2014-07-28
Bottom Line: An electronic screening tool that starts with a single question to assess the frequency of substance misuse appears to be an easy way to screen teenagers who visited a physician for routine medical care.
Author: Sharon Levy, M.D., M.P.H., of Boston Children's Hospital, and colleagues.
Background: Substance use can cause illness and death in adolescents. Screening adolescents and intervening if there is substance use can reduce the burden of addiction. The American Academy of Pediatrics and other professional organizations recommend that primary care physicians ...
Dementia patients more likely to get implanted pacemakers, says Pitt study
2014-07-28
PITTSBURGH, July 28, 2014 -- People with dementia are more likely to get implanted pacemakers for heart rhythm irregularities, such as atrial fibrillation, than people who don't have cognitive difficulties, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. In a research letter published online today in JAMA Internal Medicine, the researchers noted the finding runs counter to expectations that less aggressive interventions are the norm for patients with the incurable and disabling illness.
To look at the relationships between cognitive status ...
Non-endoscopic migraine surgery provides significant symptom relief
2014-07-28
A revised version of a surgical procedure to treat severe chronic migraine headaches led to significant symptom relief more than 90 percent of the time in patients treated at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). Physicians from the MGH Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery report that more than half of 35 patients treated with the non-endoscopic procedure – all of whom had headaches associated with compression of craniofacial nerves – reported complete symptom relief a year later. The team's paper has received advance online publication in the journal Plastic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New “lock-and-key” chemistry
Benzodiazepine use declines across the U.S., led by reductions in older adults
How recycled sewage could make the moon or Mars suitable for growing crops
Don’t Panic: ‘Humanity’s Last Exam’ has begun
A robust new telecom qubit in silicon
Vertebrate paleontology has a numbers problem. Computer vision can help
Reinforced enzyme expression drives high production of durable lactate-based polyester
In Rett syndrome, leaky brain blood vessels traced to microRNA
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
The Frontiers of Knowledge Award goes to Charles Manski for incorporating uncertainty into economic research and its application to public policy analysis
Walter Koroshetz joins Dana Foundation as senior advisor
Next-generation CAR-T designs that could transform cancer treatment
As health care goes digital, patients are being left behind
A clinicopathologic analysis of 740 endometrial polyps: risk of premalignant changes and malignancy
Gibson Oncology, NIH to begin Phase 2 trials of LMP744 for treatment of first-time recurrent glioblastoma
Researchers develop a high-efficiency photocatalyst using iron instead of rare metals
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
New system tracks blockchain money laundering faster and more accurately
In vitro antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Tithonia diversifolia (asteraceae) and Solanum torvum (solanaceae) against selected shigella species
Qiliang (Andy) Ding, PhD, named recipient of the 2026 ACMG Foundation Rising Scholar Trainee Award
Heat-free gas sensing: LED-driven electronic nose technology enhances multi-gas detection
[Press-News.org] Cancer: Tumors absorb sugar for mobilitySome cancer cells are characterized by both high sugar intake and high mobility; researchers at EPFL show that these 2 phenomena are related