(Press-News.org) COLUMBIA, Mo. – The child care industry has grown significantly in recent years, contributing considerably to the national economy through job creation and increased opportunities for parents to work. However, little knowledge exists of the size and economic impact of child care, especially informal child care, on rural economies. Now, University of Missouri researchers have studied the child care sector in Kansas, particularly in rural areas, and have found that informal child care services create a large economic impact in the state.
Tom Johnson, a professor in the MU Truman School of Public Affairs, found that the informal child care industry created more than 128,000 jobs and added about $971.5 million in total value to the state of Kansas in 2005. Informal child care services include unlicensed facilities, unreported day care services run from homes, and child care performed for trade rather than money. Johnson says the scale of the informal child care industry reveals the importance of child care to the economy, particularly economies in rural areas.
"In general, child care is much more expensive in rural areas than in urban areas," Johnson said. "This is because people in rural areas often have to travel long distances to find child care services. Add the cost of travel to the potential wages many parents do not earn because they spend so much time travelling to and from child care facilities, and the total cost creates a large impediment to working parents."
Johnson says that due to these high costs of child care in rural areas, policymakers would be advised to facilitate increased access to child care services in rural areas.
"Increased access to child care in rural areas, whether it is informal services or formal services from licensed providers, has the potential to create a large, positive impact on rural economies," Johnson said. "Parents with affordable child care will have more opportunities to work, generating more income for families and creating a more diverse economy."
Johnson says that rural economies do not exist in a vacuum, and anything that is positive for rural economies should be reflected back to urban economies in a positive manner as well.
INFORMATION:
Johnson also is the Frank Miller Professor of Agricultural and Applied Economics in the MU College of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources. This study was co-authored by Eun-Young Choi, a former doctoral student at MU, and will be published in the Journal of Regional Analysis and Policy.
Informal child care significantly impacts rural economies, MU study finds
Policymakers can help economy by facilitating increased access to child care in rural areas
2014-07-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Malaria vaccine shows continued protection during 18 months of follow-up
2014-07-29
A vaccine previously shown to reduce malaria in young infants and children reduces larger numbers of malaria cases in areas of higher malaria transmission, according to results from an ongoing clinical trial published in PLOS Medicine. The effect of vaccination diminished over time, but protection against clinical malaria remained evident 18 months after vaccination.
In the new report, the RTS,S Clinical Trials Partnership* update estimates of vaccine efficacy (the reduction in the risk of malaria in participants who received the vaccine compared to those who received ...
Small increases in Ugandan urbanicity tied to CVD risk factors
2014-07-29
Urban dwellers tend to have higher risk for cardiovascular diseases than people living in more rural locations. In a new study published in PLOS Medicine, Johanna Riha and colleagues, researchers from the University of Cambridge and the MRC/UVRI Research Unit in Uganda, have found that even within rural communities in Uganda that all lacked paved roads and running water, people living in villages with relatively more urban features—such as schools and health facilities –were more likely to have risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as physical inactivity, lower ...
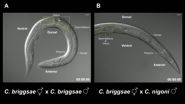
'Killer sperm' prevents mating between worm species
2014-07-29
VIDEO:
These are time-lapse videos of Caenorhabditis hermaphrodites that were (A) mated with the same species and (B) mated with a different species. Male sperm were fluorescently labeled and appear as...
Click here for more information.
The classic definition of a biological species is the ability to breed within its group, and the inability to breed outside it. For instance, breeding a horse and a donkey may result in a live mule offspring, but mules are nearly always sterile ...
Urbanization of rural Africa associated with increased risk of heart disease and diabetes
2014-07-29
The increasing urbanisation of rural areas in sub-Saharan Africa could lead to an explosion in incidences of heart disease and diabetes, according to a new study carried out in Uganda which found that even small changes towards more urban lifestyles was associated with increased risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Over 530 million people live in rural areas of sub-Saharan Africa, where rates of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases tend to be much lower than in urban areas. However, many of these areas are becoming increasingly urbanised, with people living ...
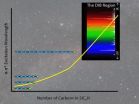
Mysterious molecules in space
2014-07-29
WASHINGTON D.C., July 29, 2014 – Over the vast, empty reaches of interstellar space, countless small molecules tumble quietly though the cold vacuum. Forged in the fusion furnaces of ancient stars and ejected into space when those stars exploded, these lonely molecules account for a significant amount of all the carbon, hydrogen, silicon and other atoms in the universe. In fact, some 20 percent of all the carbon in the universe is thought to exist as some form of interstellar molecule.
Many astronomers hypothesize that these interstellar molecules are also responsible ...
This week from AGU: Cell tower rain gauges, lightning channels, North Sea storm surge
2014-07-29
This Week From AGU: Cell phone tower rain gauges, lightning channels, North Sea storm surge
From AGU's blogs: Dropped cell phone calls become rain gauges in West Africa
A shaky cell phone connection during a rainstorm can be an annoying nuisance. But now scientists are showing that these weakened signals can be used to monitor rainfall in West Africa, a technique that could help cities in the region better prepare for floods and combat weather-related diseases, according to a new study accepted for publication in Geophysical Research Letters, a journal of the American ...
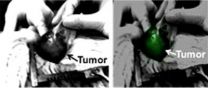
Penn team makes cancer glow to improve surgical outcomes
2014-07-29
The best way to cure most cases of cancer is to surgically remove the tumor. The Achilles heel of this approach, however, is that the surgeon may fail to extract the entire tumor, leading to a local recurrence.
With a new technique, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have established a new strategy to help surgeons see the entire tumor in the patient, increasing the likelihood of a positive outcome. This approach relies on an injectable dye that accumulates in cancerous tissues much more so than normal tissues. When the surgeon shines an infrared light on the ...
Huge waves measured for first time in Arctic Ocean
2014-07-29
As the climate warms and sea ice retreats, the North is changing. An ice-covered expanse now has a season of increasingly open water which is predicted to extend across the whole Arctic Ocean before the middle of this century. Storms thus have the potential to create Arctic swell – huge waves that could add a new and unpredictable element to the region.
A University of Washington researcher made the first study of waves in the middle of the Arctic Ocean, and detected house-sized waves during a September 2012 storm. The results were recently published in Geophysical Research ...
Underwater elephants
2014-07-29
In the high-tech world of science, researchers sometimes need to get back to basics. UC Santa Barbara's Douglas McCauley did just that to study the impacts of the bumphead parrotfish (Bolbometopon muricatum) on coral reef ecosystems at two remote locations in the central Pacific Ocean.
Using direct observation, animal tracking and computer simulation, McCauley, an assistant professor in the Department of Ecology, Evolution and Marine Biology, and his colleagues sought to understand whether the world's largest parrotfish is necessary for positively shaping the structure ...
Vision-correcting display makes reading glasses so yesterday
2014-07-29
BERKELEY — What if computer screens had glasses instead of the people staring at the monitors? That concept is not too far afield from technology being developed by computer and vision scientists at the University of California, Berkeley.
The researchers are developing computer algorithms to compensate for an individual's visual impairment, and creating vision-correcting displays that enable users to see text and images clearly without wearing eyeglasses or contact lenses. The technology could potentially help hundreds of millions of people who currently need corrective ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
[Press-News.org] Informal child care significantly impacts rural economies, MU study findsPolicymakers can help economy by facilitating increased access to child care in rural areas