(Press-News.org) 7/29/2014, Seattle, WA. Research to be presented at the Annual Meeting of the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior (SSIB), the foremost society for research into all aspects of eating and drinking behavior, finds that daily consumption of beverages sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup or sucrose can impair the ability to learn and remember information, particularly when consumption occurs during adolescence. Both adult and adolescent rats were given daily access to sugar-sweetened beverages that mirror sugar concentrations found in common soft drinks. Adult rats that consumed the sugar-sweetened beverages for one month performed normally in tests of cognitive function; however, when consumption occurred during adolescence the rats were impaired in tests of learning and memory capability.
The lead author, Dr. Scott Kanoski from the University of Southern California, says, "It's no secret that refined carbohydrates, particularly when consumed in soft drinks and other beverages, can lead to metabolic disturbances. However, our findings reveal that consuming sugar-sweetened drinks is also interfering with our brain's ability to function normally and remember critical information about our environment, at least when consumed in excess before adulthood". In addition to causing memory impairment, adolescent sugar-sweetened beverage consumption also produced inflammation in the hippocampus, an area of the brain that controls many learning and memory functions. "The hippocampus is such a critical brain region for memory function", says Kanoski. "In many ways this region is a canary in the coal mine, as it is particularly sensitive to insult by various environmental factors, including eating foods that are high in saturated fat and processed sugar."
INFORMATION:
Drinking sugar-sweetened beverages during adolescence impairs memory
2014-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Secular and longitudinal trends in dieting strategies in young adult women from 1982 to 2012
2014-07-30
7/29/2014, Seattle, WA. Research to be presented at the Annual Meeting of the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior (SSIB), the foremost society for research into all aspects of eating and drinking behaviors, finds that the younger a woman is when she goes on her first diet, the more likely she is to experience several negative health outcomes later in life.
Dieting is very common among girls and young women; however, people often fail to consider the long-term consequences of weight-loss diets, particularly in those who begin dieting at a young age. A team led ...
Striatal dopamine transporter binding correlates with body composition and visual attention bias for food cues in healthy young men
2014-07-30
7/29/2014, Seattle, WA. Research to be presented at the Annual Meeting of the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior (SSIB), the foremost society for research into all aspects of eating and drinking behavior, describes a way that brain chemistry may make some people notice food more easily, which can tempt overeating even in people who are not overweight. Dopamine activity in the striatum, an area of the brain sensitive to food reward, was linked to how quickly men noticed a food picture hidden among neutral pictures. In turn, the men who quickly noticed food pictures ...
Parents' reported food preparation time is inversely associated with energy density
2014-07-30
7/29/2014, Seatle, WA. Research to be presented at the Annual Meeting of the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior (SSIB), the foremost society for research into all aspects of eating and drinking behavior, suggests that the amount time parents spend on food preparation at home influences children's food intake decisions made in the laboratory without parental supervision.
"In general, research shows that children tend to eat inadequate amounts of nutrient-rich foods while eating large amounts of sugary and fatty foods," Shehan said. "It's encouraging to see that ...
Research shows impact of soft drinks in meal planning
2014-07-30
Seattle, WA. 7/29/20134. New research by academics in the University of Bristol's Nutrition and Behaviour Unit (NBU) has looked into whether we take liquid calories into account when planning meals.
The research, to be presented at the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior Conference (SSIB 2014) in Seattle, USA this week [29 July to 2 August], argues that we do.
The team was led by Professor Jeff Brunstrom, and is based in the School of Experimental Psychology.
As part of a Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) grant, the researchers looked ...
Time of arrival at hospital impacts time to treatment and survival of heart attack patients
2014-07-29
Going to the hospital for a heart attack during evenings, weekends and holidays increases your risk of dying 13 percent compared with people arriving during workday hours, according to new research in the American Heart Association journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Every year, more than 250,000 people experience an ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), the most severe type of heart attack caused by a complete blockage of blood flow to the heart. To prevent death, it's critical to restore blood flow as quickly as possible by surgically opening ...
Reducing kidney injury using a quality improvement method
2014-07-29
LEBANON, NH (July 29, 2014) – Using quality improvement measures in eight of the 10 hospitals in the Northern New England Cardiovascular Disease Study Group, researchers have found a way to reduce kidney injury in patients undergoing a procedure with contrast dye.
Currently, 7-15 percent of these patients who undergo a coronary stent procedure with contrast-dye end up with kidney injury, which can result in death or rapid decline in kidney function leading to temporary or permanent dialysis, says a study published in the July issue of Circulation Cardiovascular Quality ...
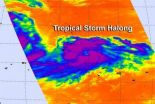
NASA sees developing Tropical Storm Halong causing warning
2014-07-29
NASA infrared satellite data revealed that Tropical Storm Halong is surrounded by strong thunderstorms and an eye appears to be developing.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Halong on July 29 at 03:29 UTC (July 28 at 11:29 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument captured data on the cloud cover. The infrared data showed very cold, high thunderstorm cloud top temperatures of powerful storms surrounding the center, with what appears to be an eye developing. Microwave satellite data also shows a small eye, with tightly-curved bands of ...
Good outcomes with multiple limb salvage after severe combat injuries, reports Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
2014-07-29
July 29, 2014 – For survivors of severe combat injuries threatening more than one limb, reconstructive surgical procedures using tissue flaps have a good record of safety and effectiveness in avoiding amputation, reports a paper in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Experience with multiple limb salvage procedures in solders injured in Iraq and Afghanistan shows good success rates, with no increase in complications compared to single-flap techniques, report Dr. Ian Valerio ...
Beware of claims about cosmetic stem cells procedures, says review in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
2014-07-29
July 29, 2014 – Advertising claims for cosmetic procedures using stem cells are running far ahead of the scientific evidence for safety and effectiveness, according to a review in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
"Stem cells offer tremendous potential, but the marketplace is saturated with unsubstantiated and sometimes fraudulent claims that may place patients at risk," write Dr Michael T. Longaker of Stanford University Medical Center and colleagues.
'Worrying advertisements' ...
NASA-funded X-ray instrument settles interstellar debate
2014-07-29
VIDEO:
This animation illustrates solar wind charge exchange in action. An atom of interstellar helium (blue) collides with a solar wind ion (red), losing one of its electrons (yellow) to the...
Click here for more information.
New findings from a NASA-funded instrument have resolved a decades-old puzzle about a fog of low-energy X-rays observed over the entire sky. Thanks to refurbished detectors first flown on a NASA sounding rocket in the 1970s, astronomers have now confirmed ...