(Press-News.org) July 29, 2014 – For survivors of severe combat injuries threatening more than one limb, reconstructive surgical procedures using tissue flaps have a good record of safety and effectiveness in avoiding amputation, reports a paper in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Experience with multiple limb salvage procedures in solders injured in Iraq and Afghanistan shows good success rates, with no increase in complications compared to single-flap techniques, report Dr. Ian Valerio of Walter Reed National Military Medical Center and colleagues.
Encouraging Results with Multiple Limb Salvage Procedures
The researchers analyzed limb salvage procedures in military personnel sustaining combat-related injuries to multiple limbs while serving in Iraq and Afghanistan. "Limb salvage" refers to surgical reconstruction carried out to avoid amputation and maximize functioning of the surviving extremity.
From 2003 through 2012, a total of 359 limb salvage procedures were performed at the National Capital Consortium. Of these, 48 procedures involved attempts to salvage two or more injured limbs. "Critical to each of the cases presented in our series was maintenance of residual limb length and a functioning joint (wrist joint and knee joint)," Dr. Valerio and colleagues write.
The limb salvage procedures were performed an average of about one month after initial injury. About 90 percent of patients were injured by blasts from improvised explosive devices; about 60 percent of the threatened limbs were lower extremities (leg to foot). Injuries were more severe in the multiple-extremity salvage group, based on a standard scoring system.
Yet the overall complication rate was similar between groups: 26 percent for patients undergoing single-extremity salvage versus 33 percent in the multiple-limb group. This was so despite the use of additional tissue flaps for reconstruction in patients undergoing multiple-limb salvage.
With Improvements in Survival, Need for Advanced Reconstruction
The overall flap success rate was about 90 percent in both groups. Long-term amputation rates were similar as well. Complications related to one type of tissue flap (free flaps) were higher in the multiple limb-salvage group.
Advances in forward surgical care have increased the survivability of severe blast-related combat injuries. "The conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan have highlighted a unique group of patients surviving multiple extremity war injuries complicated by open fractures requiring complex reconstruction," according to Dr. Valerio and coauthors.
The new study is one of the first to focus on the outcomes of limb-salvage procedures in these severely injured patients. For patients who may have already lost one or more limbs, preservation of the remaining limbs is "even more critical" to facilitate early ambulation (walking) as well as potentially optimizing rehabilitation and related activities of daily living goals after reconstruction, the authors note.
"Our experience supports limb salvage in the multiple extremity injured patients with avoidance of higher limb amputation levels, despite a higher injury severity score." Dr. Valerio and coauthors conclude. They hope their experience will contribute to further improving the outcomes of surgical reconstruction—and thus long-term rehabilitation and functioning—for survivors of severe and limb-threatening combat injuries.
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Multiple Limbs Salvaged Using Tissue Transfers in the Same Casualty: A Cohort Comparison Study Chronicling a Decade of War-Injured Patients."
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
About Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
For more than 60 years, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® has been the one consistently excellent reference for every specialist who uses plastic surgery techniques or works in conjunction with a plastic surgeon. The official journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®brings subscribers up-to-the-minute reports on the latest techniques and follow-up for all areas of plastic and reconstructive surgery, including breast reconstruction, experimental studies, maxillofacial reconstruction, hand and microsurgery, burn repair, and cosmetic surgery, as well as news on medico-legal issues.
About ASPS
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) is the world's largest organization of board-certified plastic surgeons. Representing more than 7,000 Member Surgeons, the Society is recognized as a leading authority and information source on aesthetic and reconstructive plastic surgery. ASPS comprises more than 94 percent of all board-certified plastic surgeons in the United States. Founded in 1931, the Society represents physicians certified by The American Board of Plastic Surgery or The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada. ASPS advances quality care to plastic surgery patients by encouraging high standards of training, ethics, physician practice and research in plastic surgery. You can learn more and visit the American Society of Plastic Surgeons at http://www.plasticsurgery.org or http://www.facebook.com/PlasticSurgeryASPS and http://www.twitter.com/ASPS_news.
About Wolters Kluwer Health
Wolters Kluwer Health is a leading global provider of information, business intelligence and point-of-care solutions for the healthcare industry. Serving more than 150 countries worldwide, clinicians rely on Wolters Kluwer Health's market leading information-enabled tools and software solutions throughout their professional careers from training to research to practice. Major brands include Health Language®, Lexicomp®, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Medicom®, Medknow, Ovid®, Pharmacy OneSource®, ProVation® Medical and UpToDate®.
Wolters Kluwer Health is part of Wolters Kluwer, a market-leading global information services company. Wolters Kluwer had 2013 annual revenues of €3.6 billion ($4.7 billion), employs approximately 19,000 people worldwide, and maintains operations in over 40 countries across Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, and Latin America. Follow our official Twitter handle: @WKHealth.
Good outcomes with multiple limb salvage after severe combat injuries, reports Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Experience shows no increase in complications, compared to single-limb salvage techniques
2014-07-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Beware of claims about cosmetic stem cells procedures, says review in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
2014-07-29
July 29, 2014 – Advertising claims for cosmetic procedures using stem cells are running far ahead of the scientific evidence for safety and effectiveness, according to a review in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
"Stem cells offer tremendous potential, but the marketplace is saturated with unsubstantiated and sometimes fraudulent claims that may place patients at risk," write Dr Michael T. Longaker of Stanford University Medical Center and colleagues.
'Worrying advertisements' ...
NASA-funded X-ray instrument settles interstellar debate
2014-07-29
VIDEO:
This animation illustrates solar wind charge exchange in action. An atom of interstellar helium (blue) collides with a solar wind ion (red), losing one of its electrons (yellow) to the...
Click here for more information.
New findings from a NASA-funded instrument have resolved a decades-old puzzle about a fog of low-energy X-rays observed over the entire sky. Thanks to refurbished detectors first flown on a NASA sounding rocket in the 1970s, astronomers have now confirmed ...
Revolutionary microshutter technology hurdles significant challenges
2014-07-29
NASA technologists have hurdled a number of significant technological challenges in their quest to improve an already revolutionary observing technology originally created for the James Webb Space Telescope.
The team, led by Principal Investigator Harvey Moseley, a scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, has demonstrated that electrostatically actuated microshutter arrays — that is, those activated by applying an specific voltage — are as functional as the current technology's magnetically activated arrays. This advance makes them a highly ...
Study: Contrary to image, city politicians do adapt to voters
2014-07-29
Political scientists have long wondered whether city governments in the U.S. are really responsive to their voters. Aren't local governments simply mired in machine politics, or under the sway of local big-money interests? Does ideology matter?
Now a uniquely comprehensive study co-authored by an MIT political scientist has produced a pair of distinctive findings: first, that the policies of city governments do closely match the politics of their citizens, and second, that this occurs regardless of the exact form of government than a city has.
That means that urban ...
Short sellers not to blame for 2008 financial crisis, study finds
2014-07-29
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Contrary to widespread media reports, the collapse of several financial firms during the 2008 economic crisis was not triggered by unsettled stock trades, according to new research from the University at Buffalo School of Management.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Financial Economics, analyzed the open interest of fails-to-deliver — stock trades in which shares are not delivered within the three-day trading cycle — in the days before and after the stock crashes of American Insurance Group, Bear Stearns, Lehman Brothers and Merrill Lynch.
The ...
Informal child care significantly impacts rural economies, MU study finds
2014-07-29
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The child care industry has grown significantly in recent years, contributing considerably to the national economy through job creation and increased opportunities for parents to work. However, little knowledge exists of the size and economic impact of child care, especially informal child care, on rural economies. Now, University of Missouri researchers have studied the child care sector in Kansas, particularly in rural areas, and have found that informal child care services create a large economic impact in the state.
Tom Johnson, a professor in the ...
Malaria vaccine shows continued protection during 18 months of follow-up
2014-07-29
A vaccine previously shown to reduce malaria in young infants and children reduces larger numbers of malaria cases in areas of higher malaria transmission, according to results from an ongoing clinical trial published in PLOS Medicine. The effect of vaccination diminished over time, but protection against clinical malaria remained evident 18 months after vaccination.
In the new report, the RTS,S Clinical Trials Partnership* update estimates of vaccine efficacy (the reduction in the risk of malaria in participants who received the vaccine compared to those who received ...
Small increases in Ugandan urbanicity tied to CVD risk factors
2014-07-29
Urban dwellers tend to have higher risk for cardiovascular diseases than people living in more rural locations. In a new study published in PLOS Medicine, Johanna Riha and colleagues, researchers from the University of Cambridge and the MRC/UVRI Research Unit in Uganda, have found that even within rural communities in Uganda that all lacked paved roads and running water, people living in villages with relatively more urban features—such as schools and health facilities –were more likely to have risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as physical inactivity, lower ...
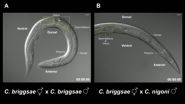
'Killer sperm' prevents mating between worm species
2014-07-29
VIDEO:
These are time-lapse videos of Caenorhabditis hermaphrodites that were (A) mated with the same species and (B) mated with a different species. Male sperm were fluorescently labeled and appear as...
Click here for more information.
The classic definition of a biological species is the ability to breed within its group, and the inability to breed outside it. For instance, breeding a horse and a donkey may result in a live mule offspring, but mules are nearly always sterile ...
Urbanization of rural Africa associated with increased risk of heart disease and diabetes
2014-07-29
The increasing urbanisation of rural areas in sub-Saharan Africa could lead to an explosion in incidences of heart disease and diabetes, according to a new study carried out in Uganda which found that even small changes towards more urban lifestyles was associated with increased risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Over 530 million people live in rural areas of sub-Saharan Africa, where rates of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases tend to be much lower than in urban areas. However, many of these areas are becoming increasingly urbanised, with people living ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
[Press-News.org] Good outcomes with multiple limb salvage after severe combat injuries, reports Plastic and Reconstructive SurgeryExperience shows no increase in complications, compared to single-limb salvage techniques