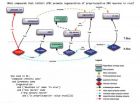
(Press-News.org) Progress in developing robust therapies for spinal cord injury (SCI), traumatic brain injury (TBI) and peripheral nerve injury has been slow. A great deal has been learned over the past 30 years regarding both the intrinsic factors and the environmental factors that regulate axon growth, but this large body of information has not yet resulted in clinically available therapeutics. Prof. Lemmon and his team from University of Miami in USA proposed this therapeutic bottleneck has many root causes, but a consensus is emerging that one contributing factor is a lack of standards for experimental design and reporting. The absence of reporting standards, and even of commonly accepted definitions of key words, also make data mining and bioinformatics analysis of neural plasticity and regeneration difficult, if not impossible. These findings, published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 1, 2014), this short review will consider relevant background and potential solutions to this problem in the axon regeneration domain.
INFORMATION:
Article: " Facilitating transparency in spinal cord injury studies using data standards and ontologies " by Vance P. Lemmon1, 2, 3, Saminda Abeyruwan3, 4, Ubbo Visser3, 4 , John L. Bixby1, 2, 3, 5 (1 Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Miami, Miami, FL 33136, USA; 2 Miami Project to Cure Paralysis, University of Miami, Miami, FL 33136, USA; 3 Center for Computational Science, University of Miami, Miami, FL 33146, USA; 4 Department of Computer Science, University of Miami, Miami, FL 33146, USA; 5 Department of Molecular & Cellular Pharmacology, University of Miami, Miami, FL 33136, USA)
Lemmon VP, Abeyruwan S, Visser U, Bixby JL. Facilitating transparency in spinal cord injury studies using data standards and ontologies. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(1):6-7.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Facilitating transparency in spinal cord injury studies using recognized information standards
2014-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dyscalculia: Burdened by blunders with numbers
2014-07-30
Between 3 and 6% of schoolchildren suffer from an arithmetic-related learning disability. Researchers at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich now show that these children are also more likely to exhibit deficits in reading and spelling than had been previously suspected.
Addition and subtraction, multiplication and division are the four basic operations in arithmetic. But for some children, learning these fundamental skills is particularly challenging. Studies show that they have problems grasping the concepts of number, magnitude, and quantity, and that they ...
Older adults are at risk of financial abuse
2014-07-30
Nearly one in every twenty elderly American adults is being financially exploited – often by their own family members. This burgeoning public health crisis especially affects poor and black people. It merits the scrutiny of clinicians, policy makers, researchers, and any citizen who cares about the dignity and well-being of older Americans, says Dr. Janey Peterson of Weill Cornell Medical College in the US. She led one of the largest American studies¹ ever on elder abuse, the findings of which appear in the Journal of General Internal Medicine², published by Springer.
With ...
Sugar mimics guide stem cells toward neural fate
2014-07-30
Embryonic stem cells can develop into a multitude of cells types. Researchers would like to understand how to channel that development into the specific types of mature cells that make up the organs and other structures of living organisms.
One key seems to be long chains of sugars that dangle from proteins on surfaces of cells.
Kamil Godula's group at the University of California, San Diego, has created synthetic molecules that can stand in for the natural sugars, but can be more easily manipulated to direct the process, they report in the Journal of the American ...
Peru's carbon quantified: Economic and conservation boon
2014-07-30
Washington, DC—Today scientists unveiled the first high-resolution map of the carbon stocks stored on land throughout the entire country of Perú. The new and improved methodology used to make the map marks a sea change for future market-based carbon economies. The new carbon map also reveals Perú's extremely high ecological diversity and it provides the critical input to studies of deforestation and forest degradation for conservation, land use, and enforcement purposes. The technique includes the determination of uncertainty of carbon stores throughout the country, which ...
New catalyst converts carbon dioxide to fuel
2014-07-30
Scientists from the University of Illinois at Chicago have synthesized a catalyst that improves their system for converting waste carbon dioxide into syngas, a precursor of gasoline and other energy-rich products, bringing the process closer to commercial viability.
Amin Salehi-Khojin, UIC professor of mechanical and industrial engineering, and his coworkers developed a unique two-step catalytic process that uses molybdenum disulfide and an ionic liquid to "reduce," or transfer electrons, to carbon dioxide in a chemical reaction. The new catalyst improves efficiency and ...
Spin-based electronics: New material successfully tested
2014-07-30
Spintronics is an emerging field of electronics, where devices work by manipulating the spin of electrons rather than the current generated by their motion. This field can offer significant advantages to computer technology. Controlling electron spin can be achieved with materials called 'topological insulators', which conduct electrons only across their surface but not through their interior. One such material, samarium hexaboride (SmB6), has long been theorized to be an ideal and robust topological insulator, but this has never been shown practically. Publishing in Nature ...
Big data confirms climate extremes are here to stay
2014-07-30
In a paper published online today in the journal Scientific Reports, published by Nature, Northeastern researchers Evan Kodra and Auroop Ganguly found that while global temperature is indeed increasing, so too is the variability in temperature extremes. For instance, while each year's average hottest and coldest temperatures will likely rise, those averages will also tend to fall within a wider range of potential high and low temperate extremes than are currently being observed. This means that even as overall temperatures rise, we may still continue to experience extreme ...
A blood test for suicide?
2014-07-30
Johns Hopkins researchers say they have discovered a chemical alteration in a single human gene linked to stress reactions that, if confirmed in larger studies, could give doctors a simple blood test to reliably predict a person's risk of attempting suicide.
The discovery, described online in The American Journal of Psychiatry, suggests that changes in a gene involved in the function of the brain's response to stress hormones plays a significant role in turning what might otherwise be an unremarkable reaction to the strain of everyday life into suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
"Suicide ...
Acupuncture improves quality of life for breast cancer patients using aromatase inhibitors
2014-07-30
PHILADELPHIA – Use of electroacupuncture (EA) – a form of acupuncture where a small electric current is passed between pairs of acupuncture needles – produces significant improvements in fatigue, anxiety and depression in as little as eight weeks for early stage breast cancer patients experiencing joint pain related to the use of aromatase inhibitors (AIs) to treat breast cancer. The results of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial examining the intervention led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania are published online this ...
Soy may help women's hearts if they start early
2014-07-30
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Wednesday, July 30, 2014)—A diet rich in soy may help feminine hearts, but timing matters, finds a new study published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society.
Lifelong soy consumption, similar to the diet of women in Asia, produces the least atherosclerosis. Switching to a Western diet after menopause, similar to Asian migrants to North America, leads to just as much atherosclerosis as a lifelong Western diet, and switching to soy from a Western diet after menopause helps only if there isn't much atherosclerosis ...