(Press-News.org) Children diagnosed with depression as preschoolers are likely to suffer from depression as school-age children and young adolescents, new research shows.
Depressed preschoolers were 2.5 times more likely to suffer from the condition in elementary and middle school than kids who were not depressed at very young ages, according to researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Their study is published in the July issue of the American Journal of Psychiatry.
"It's the same old bad news about depression; it is a chronic and recurrent disorder," said child psychiatrist Joan L. Luby, MD, who directs Washington University's Early Emotional Development Program. "But the good news is that if we can identify depression early, perhaps we have a window of opportunity to treat it more effectively and potentially change the trajectory of the illness so that it is less likely to be chronic and recurring."
The investigators followed 246 children, now ages 9 to 12, who were enrolled in the study as preschoolers when they were 3 to 5 years old. The children and their primary caregivers participated in up to six annual and four semiannual assessments. They were screened using a tool called the Preschool Feelings Checklist, developed by Luby and her colleagues, and evaluated using an age-appropriate diagnostic interview.
As part of the evaluation, caregivers were interviewed about their children's expressions of sadness, irritability, guilt, sleep, appetite and decreased pleasure in activity and play. In addition, researchers used two-way mirrors to evaluate child-caregiver interactions because the team's earlier research had shown that a lack of parental nurturing is an important risk factor for recurrence of depression.
The study was designed to follow children as they grew and to evaluate them for depression and other psychiatric conditions. However, if children were found to be seriously depressed or in danger of self harm, or if their caregivers requested treatment, they were referred to mental health providers. Currently, there are no proven treatments for depression that arises in the preschool years. Even in depressed adults, available treatments and medications are effective only about half the time.
At the start of the study, 74 of the children were diagnosed with depression. When the researchers evaluated the same group six years later, they found that 79 children met the full criteria for clinical depression based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-V). This manual contains the American Psychiatric Association's most up-to-date official guidelines for diagnosing and treating psychiatric illnesses.
More than 51 percent of the 74 children who originally were diagnosed as preschoolers also were depressed as school-age kids. Only 24 percent of the 172 children who were not depressed as preschoolers went on to develop depression during their elementary and middle school years.
Luby's group also found that school-age children had a high risk of depression if their mothers were depressed. And they noted that children diagnosed with a conduct disorder as preschoolers had an elevated risk of depression by school age and early adolescence, but this risk declined if the children were found to have significant maternal support. But neither a mother with depression nor a conduct disorder in preschool increased the risk for later depression as much as a diagnosis of depression during preschool years.
"Preschool depression predicted school-age depression over and above any of the other well-established risk factors," Luby explained. "Those children appear to be on a trajectory for depression that's independent of other psychosocial variables."
Luby said her findings continue to contradict doctors and scientists who have maintained that children as young as 3 or 4 could not be clinically depressed. She advocates including depression screenings in regular medical checkups for preschoolers, but she said such monitoring is unlikely to begin anytime soon.
"The reason it hasn't yet become a huge call to action is because we don't yet have any proven, effective treatments for depressed preschoolers," she explained. "Pediatricians don't usually want to screen for a condition if they can't then refer patients to someone who can help."
Luby now is testing potential parent-child psychotherapies that appear promising for preschoolers with depression, but it's too early to determine whether they work. Her team also will continue following this group of children through puberty to determine whether depression during preschool remains a risk factor for depression during young adulthood.
INFORMATION:
Many depressed preschoolers still suffer in later school years
2014-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Penn researchers: Naltrexone may diminish impulse control disorders in Parkinson's disease patients
2014-07-30
(PHILADELPHIA) – Up to 20 percent of Parkinson's disease (PD) patients and their families may confront a common but largely unrecognized challenge: the occurrence of impulse control disorders (ICDs) such as compulsive gambling, sexual behavior, eating, or spending. Yet the presence of PD in these patients can severely limit or complicate treatment options. A team of investigators from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the Parkinson's Disease Research, Education and Clinical Center (PADRECC) at the Philadelphia Veterans Affairs Medical ...
Study: Telephone support program beneficial for caregivers of those with dementia
2014-07-30
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – Rhode Island Hospital researchers have found that a support program administered entirely by telephone can significantly reduce depression and other symptoms in informal caregivers, such as family or friends, of individuals with dementia. The study is published online in advance of print in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia.
"Those caring for people with Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia are often under a great deal of pressure," said principal investigator Geoffrey Tremont, Ph.D, of the division of neuropsychology in the department of ...
Supportive moms and sisters boost female baboon's rank
2014-07-30
DURHAM, N.C. -- A study of dominance in female baboons suggests that the route to a higher rank is to maintain close ties with mom, and to have lots of supportive sisters.
A female baboon's social status is dictated not by size or strength, but by the rank of her mother -– the higher the mother is ranked, the higher-ranked her daughter will be. For this reason, dominance rank in female baboons is thought to be determined at birth. Females born to high-ranking mothers are guaranteed a good spot in the pecking order, whereas females born to low-ranking mothers are usually ...
Scientists pinpoint bladder cancer patients who could benefit from 'tumor-softening' treatment
2014-07-30
Scientists in Manchester have identified a protein that could help doctors decide which bladder cancer patients would benefit from a treatment that makes radiotherapy more effective, according to a study* published in the British Journal of Cancer (BJC).
The team from The University of Manchester, funded by the Medical Research Council, found that patients whose bladder tumour had high levels of a protein, called 'HIF-1α', were more likely to benefit from having carbogen – oxygen mixed with carbon dioxide gas – and nicotinamide tablets at the same time as their radiotherapy. ...
The promise and profits driving our pill-popping culture
2014-07-30
New Rochelle, NY, July 30, 2014—We have pills to ease pain, to cure infection, to help us lose weight, to treat chronic conditions, and to enhance our sexual and athletic prowess. Why do pills play such a central role in today's society and could we benefit from taking fewer pills? This provocative topic is explored in the article "'Take Your Pill': The Role and Fantasy of Pills in Modern Medicine," published in The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on The ...
Decades-old amber collection offers new views of a lost world
2014-07-30
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists are searching through a massive collection of 20-million-year-old amber found in the Dominican Republic more than 50 years ago, and the effort is yielding fresh insights into ancient tropical insects and the world they inhabited.
When the collection is fully curated, a task that will take many years, it will be the largest unbiased Dominican amber collection in the world, the researchers report.
Perhaps the most striking discovery thus far is that of a pygmy locust, a tiny grasshopper the size of a rose thorn that lived 18- to 20-million ...
F1000Research brings static research figures to life
2014-07-30
F1000Research today published new research from Bjorn Brembs, professor of neurogenetics at the Institute of Zoology, Universitaet Regensburg, in Germany, with a proof-of-concept figure allowing readers and reviewers to run the underlying code within the online article. This represents an important leap forward for scientific publishing, by demonstrating a completely novel framework for assessing the quality of a scholarly output.
Figure 3 in fact doesn't really exist. The authors submitted their data and their code to F1000Research, and the figure is generated 'on the ...
Income is a major driver of avoidable hospitalizations across New Jersey
2014-07-30
NEW BRUNSWICK, N.J. – The household income of its residents is the most important factor in whether a community has high or low rates of avoidable hospital visits – conditions that could be better managed in a doctor's office or other health care settings if treated at an early stage, according to a report released today by the Rutgers Center for State Health Policy (CSHP).
An analysis of hospital billing records and demographic data by Rutgers researchers across 13 low-income communities in New Jersey found that as an area's per capita income rises, the number of patients ...
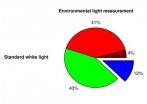
Dimly lit working environments: Correcting your body clock is possible!
2014-07-30
This news release is available in French.
Researchers at Inserm, led by Claude Gronfier (Inserm Unit 846: Stem Cell and Brain Institute), have, for the first time, conducted a study under real conditions on the body clocks of members of the international polar research station Concordia. The researchers have shown that a particular kind of artificial light is capable of ensuring that their biological rhythms are correctly synchronised despite the absence of sunlight. The full significance of this result can be appreciated with the knowledge that disturbance to this ...
Saving seeds the right way can save the world's plants
2014-07-30
KNOXVILLE—Exotic pests, shrinking ranges and a changing climate threaten some of the world's most rare and ecologically important plants, and so conservationists establish seed collections to save the seeds in banks or botanical gardens in hopes of preserving some genetic diversity.
For decades, these seed collections have been guided by simple models that offer a one-size-fits-all approach for how many seeds to gather, such as recommending saving 50 seed samples regardless of species' pollination mode, growth habitat and population size.
A new study, however, has found ...