(Press-News.org) A group of researchers from the University of Helsinki and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona have been able experimentally to reproduce in mice morphological changes which have taken millions of years to occur. Through small and gradual modifications in the embryonic development of mice teeth, induced in the laboratory, scientists have obtained teeth which morphologically are very similar to those observed in the fossil registry of rodent species which separated from mice millions of years ago.
To modify the development of their teeth, the team from the Institute of Biotechnology of the University of Helsinki worked with embryonic teeth cultures from mice not coded by the ectodysplasin A (EDA) protein, which regulates the formation of structures and differentiation of organs in the embryo throughout its development. The teeth obtained with these cultures which present this mutation develop into very basic forms, with very uniform crowns. Scientists gradually added different amounts of the EDA protein to the embryonic cells and let them develop.
The researchers observed that the teeth formed with different degrees of complexity in their crown. The more primitive changes observed coincide with those which took place in animals of the Triassic period, some two hundred million years ago. The development of more posterior patterns coincides with the different stages of evolution found in rodents which became extinct already in the Palaeocene Epoch, some 60 million years ago. Researchers have thus achieved experimentally to reproduce the transitions observed in the fossil registry of mammal teeth.
The team of scientists were able to contrast the shape of these teeth with a computer-generated prediction model created by Isaac Salazar-Ciudad, researcher at the UAB and at the University of Helsinki, which reproduces how the tooth changes from a group of equal cells to a complex three-dimensional structure, with the full shape of a molar tooth, calculating the position of space of each cell. The model is capable of predicting the changes in the morphology of the tooth when a gene is modified, and therefore offers an explanation of the mechanisms that cause these specific changes to occur in the shape of teeth throughout evolution.
"Evolution has been explained as the ability of individuals to adapt to their environment in different ways" Isaac Salazar-Ciudad states, "but we do not know why or how individuals differ morphologically. The research helps to understand evolution, in each generation, as a game between the possible variations in form and natural selection".
INFORMATION:
In addition to the University of Helsinki, Finland, and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, participating in the research were scientists from the University of California, San Francisco; the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing; the Monash University, Victoria, and the Museum Victoria in Melbourne. The research appears today in Nature.
Scientists reproduce evolutionary changes by manipulating embryonic development of mice
Evolution inside the Lab
2014-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Conservation scientists asking wrong questions on climate change impacts on wildlife
2014-07-30
Scientists studying the potential effects of climate change on the world's animal and plant species are focusing on the wrong factors, according to a new paper by a research team from the Wildlife Conservation Society, University of Queensland, and other organizations. The authors claim that most of the conservation science is missing the point when it comes to climate change.
While the majority of climate change scientists focus on the "direct" threats of changing temperatures and precipitation after 2031, far fewer researchers are studying how short-term human adaptation ...
Antarctic ice sheet is result of CO2 decrease, not continental breakup
2014-07-30
DURHAM, N.H. – Climate modelers from the University of New Hampshire have shown that the most likely explanation for the initiation of Antarctic glaciation during a major climate shift 34 million years ago was decreased carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. The finding counters a 40-year-old theory suggesting massive rearrangements of Earth's continents caused global cooling and the abrupt formation of the Antarctic ice sheet. It will provide scientists insight into the climate change implications of current rising global CO2 levels.
In a paper published today in Nature, Matthew ...
NASA catches two tropical troublemakers in Northwestern Pacific: Halong and 96W
2014-07-30
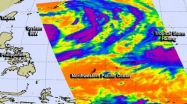
There are two tropical low pressure areas in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean today and they're close enough to each other to be captured in one image generated from data gathered by NASA's Aqua satellite.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over both Tropical Storm Halong and developing System 96W early on July 30 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured infrared data on them in one image. Both systems show powerful thunderstorms stretching high into the troposphere with cloud top temperatures as cold as -63F/-52C. Those thunderstorms have the potential for ...
Watching Schrödinger's cat die (or come to life)
2014-07-30
One of the famous examples of the weirdness of quantum mechanics is the paradox of Schrödinger's cat.
If you put a cat inside an opaque box and make his life dependent on a random event, when does the cat die? When the random event occurs, or when you open the box?
Though common sense suggests the former, quantum mechanics – or at least the most common "Copenhagen" interpretation enunciated by Danish physicist Neils Bohr in the 1920s – says it's the latter. Someone has to observe the result before it becomes final. Until then, paradoxically, the cat is both dead and ...
Fear of losing money, not spending habits, affects investor risk tolerance, MU study finds
2014-07-30
As the U.S. economy slowly recovers, many investors remain wary about investing in the stock market. Investors' "risk tolerance," or their willingness to take risks, is an important factor for investors deciding whether, and how much, to invest in the stock market. Now, Michael Guillemette, an assistant professor of personal financial planning in the University of Missouri College of Human Environmental Sciences, along with David Nanigian, an associate professor at the American College, analyzed the causes of risk tolerance and found that loss aversion, or the fear of losing ...
When cooperation counts
2014-07-30
Everybody knows the shortest distance between two points is a straight line, and now Harvard researchers have evidence that sperm have been taking the familiar axiom to heart.
Though competition among individual sperm is usually thought to be intense, with each racing for the chance to fertilize the egg, Harvard scientists say in some species, sperm form cooperative groups that allow them to take a straighter path to potential fertilization.
A new study, conducted by Heidi Fisher, a post-doctoral student working in the lab of Hopi Hoekstra, Howard Hughes Investigator ...
Scientists call for new strategy in pursuit of HIV-free generation
2014-07-30
In light of the recent news that HIV has been detected in the Mississippi baby previously thought to have been cured of the disease, researchers are assessing how to help those born to HIV-infected mothers. These infants around the world are in need of new immune-based protective strategies, including vaccines delivered to mothers and babies and the means to boost potentially protective maternal antibodies, say researchers who write in the Cell Press journal Trends in Microbiology on July 30th.
"There is a real need for additional HIV-1 prevention methods for infants," ...
Study: Marine pest provides advances in maritime anti-fouling and biomedicine
2014-07-30
A team of biologists, led by Clemson University associate professor Andrew S. Mount, performed cutting-edge research on a marine pest that will pave the way for novel anti-fouling paint for ships and boats and also improve bio-adhesives for medical and industrial applications.
The team's findings, published in Nature Communications, examined the last larval stage of barnacles that attaches to a wide variety of surfaces using highly versatile, natural, possibly polymeric material that acts as an underwater heavy-duty adhesive.
"In previous research, we were trying to ...
Dissolvable fabric loaded with medicine might offer faster protection against HIV
2014-07-30
Soon, protection from HIV infection could be as simple as inserting a medicated, disappearing fabric minutes before having sex.
University of Washington bioengineers have discovered a potentially faster way to deliver a topical drug that protects women from contracting HIV. Their method spins the drug into silk-like fibers that quickly dissolve when in contact with moisture, releasing higher doses of the drug than possible with other topical materials such as gels or creams.
"This could offer women a potentially more effective, discreet way to protect themselves from ...
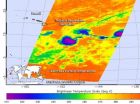
NASA sees zombie Tropical Depression Genevieve reborn
2014-07-30
Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite helped confirm that the remnant low pressure area of former Tropical Storm Genevieve has become a Zombie storm, and has been reborn as a tropical depression on July 30.
Tropical Storm Genevieve weakened to a tropical depression on Sunday, July 27 and the National Hurricane Center issued their final advisory on the system as it was entering the Central Pacific. Now, after three days of living as a remnant low pressure area, Genevieve reorganized and was classified as a tropical depression again.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Scientists reproduce evolutionary changes by manipulating embryonic development of miceEvolution inside the Lab