(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles and the Chinese Academy of Sciences have pioneered a new study that could greatly improve current methods of localising birdsong data. Their findings, which ascertain the validity of using statistical algorithms to detect multiple-source signals in real time and in three-dimensional space, are of especial significance to modern warfare.
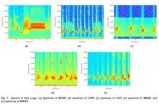
Recently published in the journal Unmanned Systems, the study demonstrates the validity of using approximate maximum likelihood (AML) algorithms to determine the direction of arrival (DOA) of birdsong sources. By first recording birdsong data using omnidirectional microphones and then applying an AML algorithm to that data, researchers were able to obtain a three-dimensional DOA estimation array, which was found to yield more accurate results than conventional two-dimensional DOA estimation arrays.
Whereas two-dimensional arrays are unable to estimate the location of birds with respect to canopy height and are less effective at separating simultaneous birdsong signals, three-dimensional arrays may enable ornithologists, as well as zoologists, to identify the various sources of animal vocalisations in complicated aural environments.
With angular measurements and elevations taking less than ten seconds to be generated, this method of source separation promises to radically alter the ways that researchers of animal behaviour gather experimental data, and even the ways that nations defend themselves.
INFORMATION:
The study can be found here.
About World Scientific Publishing Co.
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research and professional communities. The company publishes about 500 books annually and more than 120 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organisations like the Nobel Foundation, US National Academies Press, as well as its subsidiary, the Imperial College Press, amongst others, to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit http://www.worldscientific.com.
Singing the same tune: Scientists develop novel ways of separating birdsong sources
2014-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gulf oil spill researcher: Bacteria ate some toxins, but worst remain
2014-07-31
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — A Florida State University researcher found that bacteria in the Gulf of Mexico consumed many of the toxic components of the oil released during the Deepwater Horizon spill in the months after the spill, but not the most toxic contaminants.
In two new studies conducted in a deep sea plume, Assistant Professor Olivia Mason found a species of bacteria called Colwellia likely consumed gaseous hydrocarbons and perhaps benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene compounds that were released as part of the oil spill.
But, her research also showed that bacteria ...
Hope for the overweight
2014-07-31
White, brown and beige adipocytes, or fat cells, are inherently different. Each of these cell types has different functions and each plays its own role in metabolism. In the human body, white adipose tissue is by far the most prevalent. Its primary function is energy storage. On the other hand, brown adipocytes utilize available energy to generate heat but are only found in a few places in the adult human body. Beige adipocytes, which represent a special type of brown adipocytes, appear mixed with brown adipocytes in human brown adipose tissue or develop within the white ...
Privileged strategies for direct transformations of inert aliphatic carbon-hydrogen bonds
2014-07-31
Functional group transformations are central to organic synthesis. Traditionally, the functionalities used in such transformations are highly active organic groups such as halogens, ester groups and hydroxyl groups. Carbon–hydrogen bonds are ubiquitous structural motifs in organic compounds, but they are not considered to be functional groups because (1) in general, the bond dissociation energy of a C–H bond is high, and therefore, such bonds are thermodynamically hard to break; and (2) the selective activation of one C–H bond among many similar and different C–H bonds ...
Neutron tomography technique reveals phase fractions of crystalline materials in 3-dimensions
2014-07-31
The method overcomes limitations of existing techniques which are limited to the surface or small-sized specimens, and allows a 3-D representation of the phase fractions within the sample volume. The work has just been published in the journal "Advanced Materials".
"For many engineering applications it is of major importance to characterize the bulk of materials spatially, instead of only probing selected locations. The new method provides exactly that capability, and the HZB-UTK team has demonstrated it by using samples made from stainless steel that undergo a phase ...
Vision-correcting electronic displays could let users dispense with glasses
2014-07-31
Researchers at the MIT Media Laboratory and the University of California at Berkeley have developed a new display technology that automatically corrects for vision defects — no glasses (or contact lenses) required.
The technique could lead to dashboard-mounted GPS displays that farsighted drivers can consult without putting their glasses on, or electronic readers that eliminate the need for reading glasses, among other applications.
"The first spectacles were invented in the 13th century," says Gordon Wetzstein, a research scientist at the Media Lab and one of the display's ...
Vacuum treatment may limit damage after traumatic brain injury
2014-07-31
July 31, 2014 – Controlled application of vacuum pressure is a promising approach to limiting tissue damage after traumatic brain injury (TBI), suggests an experimental study in the August issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"Mechanical tissue resuscitation"—consisting of vacuum pressure applied over the injured area of the brain—shows promise as a safe and effective treatment for TBI, according to the research report by Dr. Louis ...
UT Dallas study reveals effect of loud noises on brain
2014-07-31
Prolonged exposure to loud noise alters how the brain processes speech, potentially increasing the difficulty in distinguishing speech sounds, according to neuroscientists at The University of Texas at Dallas.
In a paper published this week in Ear and Hearing, researchers demonstrated for the first time how noise-induced hearing loss affects the brain's recognition of speech sounds.
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) reaches all corners of the population, affecting an estimated 15 percent of Americans between the ages of 20 and 69, according to the National Institute ...
Monoamine oxidase A: Biomarker for postpartum depression
2014-07-31
This news release is available in German.
Many women suffer from baby blues after giving birth. Some even develop full-blown postpartum depression in the weeks that follow. Monoamine oxidase A, an enzyme responsible for the breakdown of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, plays an important role in this condition. In comparison to healthy women, women who experience postpartum depression present strongly elevated levels of the enzyme in their brains. This was discovered by a Canadian-German research team including Julia Sacher from the Max Planck Institute ...
Research reveals pervasive implicit hierarchies for race, religion, and age
2014-07-31
As much as social equality is advocated in the United States, a new study suggests that besides evaluating their own race and religion most favorably, people share implicit hierarchies for racial, religious, and age groups that may be different from their conscious, explicit attitudes and values.
The study findings appear in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"People from relatively low-status groups can readily report that their group does not have the most power. At the same time, most groups, even if they have less social ...
Key to aging immune system is discovered
2014-07-31
There's a good reason people over 60 are not donor candidates for bone marrow transplantation. The immune system ages and weakens with time, making the elderly prone to life-threatening infection and other maladies, and a UC San Francisco research team now has discovered a reason why.
"We have found the cellular mechanism responsible for the inability of blood-forming cells to maintain blood production over time in an old organism, and have identified molecular defects that could be restored for rejuvenation therapies," said Emmanuelle Passegué, PhD, a professor of medicine ...