(Press-News.org) DENVER (July 31, 2014) – A recently released study by a researcher at the University of Colorado Denver and published in the Journal of Humanistic Counseling explores why people of Latin American descent self-identify using terms like Latina/o, Hispanic, and Chicana/o. Carlos Hipolito-Delgado, an associate professor in the School of Education & Human Development at the University of Colorado Denver, found a difference between preferred ethnic labels and how a person identifies with their cultural heritage and United States values.
An expert in ethnic identity development, Hipolito-Delgado surveyed college students of Latin-American descent across the country to determine if the perception of ethnic heritage and U.S. culture is linked to ethnic identifiers, or the way people identify with their ethnicity. Through his research, Hipolito-Delgado found that there is a distinction between participants who identified as Chicana/o, Latina/o, Hispanic, hyphenated American, or those who identify by nationality—the labels chosen created a spectrum of self-identifying names.
In his survey, Hipolito-Delgado asked students about their ethnic identity, how they associate with U.S. culture and values, and how closely they identify with their ethnic heritage. Participants also selected the ethnic label to which they most closely associated. Though the definitions of these labels have been long contested, generally Latino/a reflects a direct link to Latin American heritage (ethnic origins in Latin American countries); Hispanic is linked to Spanish heritage (ethnic origin in Spain) and may also include the ability to speak or understand the Spanish language; and Chicano/a can be linked to Mexican heritage but often conveys more of a political or indigenous identity.
The study found that students identifying with the label Hispanic felt a stronger allegiance to traditional values of the United States and were much less likely to identify with their own cultural heritage. These students responded positively to statements such as, "Being U.S. American plays an important part in my life" and "I am proud of being U.S. American."
On the other end of the spectrum, students who identified as Chicana/o were significantly more likely to be more likely to identify with their cultural heritage and much less likely to endorse U.S. values. Students who identified as Chicano/a responded positively to questions like, "I have a strong sense of belonging and attachment to my own ethnic group."
In the middle were students who identified either by Latina/o, by heritage (Mexican, Brazilian, etc.), or by a hyphenated derivative (Mexican-American, Guatemalan-American, etc.). These respondents were influenced both by their heritage and U.S. cultural values.
"When you identify yourself using an ethnic label, you are making a value judgment," Hipolito-Delgado said. "For example, Chicano is a label that traditionally has been associated with social and political activism whereas Hispanic may not be as politically charged."
Hipolito-Delgado's study indicates that no matter what identifier is used, people feel that it is an important part of their identity, which has huge implications for counselors and care-providers.
As a professor in the University of Colorado Denver's Counseling program and chair of the Association for Multicultural Counseling Development, Hipolito-Delgado understands the relevance of self-identification to a successful relationship between counselor and client. He suggests that counselors and care providers working with people of Latin American descent simply ask their clients how they identify themselves, instead of making a blanket assumption.
"Labels make a difference," Hipolito-Delgado said. "A counselor who uses the wrong term with a client can send the wrong message and derail a session. If a counselor uses the wrong identifier, there may be a perception that you don't get who I am as a client. That person may never come back."
INFORMATION:
A copy of the study will be provided upon request.
CU Denver study links self-identified ethnic labels to cultural values
Study explores why people of Latin American descent self-identify using terms like Latina/o, Hispanic, and Chicana/o
2014-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Carnegie Mellon chemists create nanofibers using unprecedented new method
2014-07-31
PITTSBURGH—Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University have developed a novel method for creating self-assembled protein/polymer nanostructures that are reminiscent of fibers found in living cells. The work offers a promising new way to fabricate materials for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications. The findings were published in the July 28 issue of Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
"We have demonstrated that, by adding flexible linkers to protein molecules, we can form completely new types of aggregates. These aggregates can act as a structural material ...
Groundbreaking research maps cultural history
2014-07-31
New research from Northeastern University has mapped the intellectual migration network in North America and Europe over a 2,000-year span. The team of network scientists used the birth and death locations of more than 150,000 intellectuals to map their mobility patterns in order to identify the major cultural centers on the two continents over two millennia.
In the new paper, to be published Friday in the journal Science, the researchers found how locations such as Rome, London, and Paris have emerged as cultural hubs as more intellectuals died in these cities than ...
NIST corrosion lab tests suggest need for underground gas tank retrofits
2014-07-31
A hidden hazard lurks beneath many of the roughly 156,000 gas stations across the United States.
The hazard is corrosion in parts of underground gas storage tanks—corrosion that could result in failures, leaks and contamination of groundwater, a source of drinking water. In recent years, field inspectors in nine states have reported many rapidly corroding gas storage tank components such as sump pumps. These incidents are generally associated with use of gasoline-ethanol blends and the presence of bacteria, Acetobacter aceti, which convert ethanol to acetic acid, a component ...
New bipartisan House bill draws on U-M health research
2014-07-31
ANN ARBOR—A new bill introduced in Congress with bipartisan support would allow Medicare to test a concept born from University of Michigan research, which could improve the health of patients with chronic illness while reducing what they spend on the medicines and tests they need most.
The bill, introduced last week by U.S. Reps. Diane Black and Earl Blumenauer, grew out of a decade of work by health policy researchers affiliated with the U-M's Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation. It would allow Medicare Advantage plans to use innovative "value-based" insurance ...
Parenting skills improve in ADHD parents with medication
2014-07-31
Parenting skills of adults with ADHD improve when their ADHD is treated with medication, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers.
At least 25 percent of clinic-referred children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder have a parent with ADHD.
"Parents with ADHD are at increased risk to engage in problematic parenting techniques, including inconsistent disciplinary practices, making ineffectual commands and diminished use of praise," said James Waxmonsky, associate professor of psychiatry. "Having a parent with ADHD also decreases the chances that ...
The 'memory' of starvation is in your genes
2014-07-31
During the winter of 1944, the Nazis blocked food supplies to the western Netherlands, creating a period of widespread famine and devastation. The impact of starvation on expectant mothers produced one of the first known epigenetic "experiments" — changes resulting from external rather than genetic influences — which suggested that the body's physiological responses to hardship could be inherited. The underlying mechanism, however, remained a mystery.
In a paper published recently in the journal Cell, Dr. Oded Rechavi, Dr. Leah Houri-Ze'ev and Dr. Sarit Anava of Tel ...
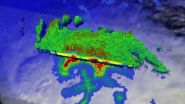
NASA sees Tropical Storm Halong move northwest of Guam
2014-07-31
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM Satellite passed over Guam as heavy rain fell over the island while Tropical Storm Halong's center passed just to the north of the island.
The TRMM satellite flew above tropical storm Halong on July 31, 2014 at 0904 UTC (August 1, 2014 at 7:04 p.m. local time, Guam).
At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland TRMM data was used to create a rainfall analysis. The analysis derived TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data was overlaid on a visible/infrared image from Japan's MTSAT-2 ...
Asteroid attacks significantly altered ancient Earth
2014-07-31
TEMPE, Ariz. – New research shows that more than four billion years ago, the surface of Earth was heavily reprocessed – or mixed, buried and melted – as a result of giant asteroid impacts. A new terrestrial bombardment model based on existing lunar and terrestrial data sheds light on the role asteroid bombardments played in the geological evolution of the uppermost layers of the Hadean Earth (approximately 4 to 4.5 billion years ago).
An international team of researchers published their findings in the July 31, 2014 issue of Nature.
"When we look at the present day, ...
Mosaicism: Study clarifies parents as source of new disease mutations
2014-07-31
HOUSTON – (July 31, 2014) – Scientists have long speculated that mosaicism – a biological phenomenon, in which cells within the same person have a different genetic makeup – plays a bigger role in the transmission of rare disease mutations than is currently known. A study conducted by an international team of scientists led by Baylor College of Medicine sheds new light on the frequency of mosaicism in genomic disorders and its influence on recurrence risk.
The study, which was published today in the American Journal of Human Genetics, also included scientists from the ...
In high-stakes soccer, goalkeepers exhibit 'gambler's fallacy'
2014-07-31
When goalkeepers are pitted against multiple kickers in tense penalty shootouts, their attempts to dive for the ball show a predictable pattern that kickers would do well to exploit. After kickers repeatedly kick in one direction, goalkeepers become increasingly likely to dive in the opposite direction, according to an analysis of all 361 kicks from the 37 penalty shootouts that occurred in World Cup and UEFA Euro Cup matches over a 36-year period.
The findings reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on July 31 highlight the importance of monitoring and predicting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
[Press-News.org] CU Denver study links self-identified ethnic labels to cultural valuesStudy explores why people of Latin American descent self-identify using terms like Latina/o, Hispanic, and Chicana/o