(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND, Ohio – In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers at University Hospitals Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital (UH Rainbow) found that lap infants may be at greater risk for death on a commercial airline flight. The study analyzed pediatric medical emergencies on flights worldwide between January 2010 and June 2013 and found 90 percent of deaths occurred in children under the age of 2.
The study was conducted in partnership with MedAire to characterize the rare event of an in-flight pediatric fatality onboard commercial airline flights worldwide. Through a detailed analysis of more than 7,000 reported medical emergencies involving children (newborn to age 18) over a three-year period, researchers found death most commonly occurred in previously healthy children under the age of 2, and in children with a preexisting medical condition.
"The pattern we identified in our analysis is intriguing and could indicate lap infants are at greater risk of death related to in-flight environmental factors such as sleeping arrangements," says Alexandre Rotta, MD, FCCM, Chief, Division of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine at UH Rainbow and the studies' principal investigator. Dr. Rotta, who is also Professor of Pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, says the pattern would have gone unnoticed through single case analysis of these relatively rare events.
The fatalities were identified by searching records of all in-flight medical emergencies for child passengers that were reported to MedAire, the world's busiest global emergency response center and the leading provider of ground-based medical support to commercial airlines worldwide. Of the 7,573 reported emergencies, 10 resulted in death, and six had no previous medical history. Four passengers had preflight medical conditions, including two children traveling for the purpose of accessing advanced medical care. Dr. Rotta speculates these infants were at increased risk from exposure to a hypoxic cabin environment, or by sharing a seat with an adult and co-sleeping during a long flight, but there could also be another yet unknown factor.
The majority of pediatric in-flight emergencies are related to infections, neurological conditions, and respiratory issues such as asthma, seldom require alteration of flight route and do not pose significant risk to life. Because an in-flight pediatric death is such a rare event, large datasets were necessary to capture a meaningful number of observations.
"I hope our findings lead to further research on this important subject," says Dr. Rotta. "It is my belief the pattern we discovered should promote the development of preventative strategies and travel policies to protect the health of all pediatric airplane passengers, especially infants."
INFORMATION:
The study published today, ahead of print, in the Pediatric Critical Care Medicine Journal: http://journals.lww.com/pccmjournal/Abstract/publishahead/Fatalities_Above_30
About University Hospitals Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital
Located on the campus of University Hospitals Case Medical Center in Cleveland, Ohio, University Hospitals Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital is a 244-bed, full-service children's hospital and academic medical center dedicated to the health care needs of children. A trusted leader in children's health care for more than 125 years, UH Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital consistently ranks among the top children's hospitals in the nation. As the region's premier resource for pediatric referrals, UH Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital's dedicated team of more than 1,300 pediatric specialists uses the most advanced treatments and latest innovations to deliver the complete range of pediatric specialty services for more than 700,000 patient encounters each year. Learn more at RainbowBabies.org.
Among the nation's leading academic medical centers, UH Case Medical Center is the primary affiliate of Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, a nationally recognized leader in medical research and education.
New research characterizes in-flight pediatric deaths
Researchers find lap infants at increased risk
2014-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Best evidence yet for coronal heating theory detected by NASA sounding rocket
2014-08-01
VIDEO:
NASA's EUNIS sounding rocket mission spotted evidence to explain why the sun's atmosphere is so much hotter than its surface.
Click here for more information.
Scientists have recently gathered some of the strongest evidence to date to explain what makes the sun's outer atmosphere so much hotter than its surface. The new observations of the small-scale extremely hot temperatures are consistent with only one current theory: something called nanoflares – a constant ...
Scientists solve 2,000-year-old mystery of the binding media in China's polychrome Terracotta Army
2014-08-01
Even as he conquered rival kingdoms to create the first united Chinese empire in 221 B.C., China's First Emperor Qin Shihuang ordered the building of a glorious underground palace complex, mirroring his imperial capital near present-day Xi'an, that would last for an eternity.
To protect his underworld palaces, the First Emperor issued instructions that his imperial guard be replicated, down to the finest details, in red-brown terracotta clay, poised to do battle. Thousands of these imperial guards were initially discovered in 1974; some contained patches of pigment that ...
Advances in assisted reproduction create more options and new legal issues for LGBT couples
2014-08-01
New Rochelle, NY, August 1, 2014—Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender individuals who want to conceive a child may face the same problems as some of their heterosexual and cisgendered peers, such as reduced fertility, but in addition they often face additional physiological and legal challenges to become parents. A comprehensive review of the most recent advances in assisted reproduction options is presented in the article "LGBT Assisted Reproduction: Current Practice and Future Possibilities," published in LGBT Health, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, ...
On-chip topological light
2014-08-01
Topological transport of light is the photonic analog of topological electron flow in certain semiconductors. In the electron case, the current flows around the edge of the material but not through the bulk. It is "topological" in that even if electrons encounter impurities in the material the electrons will continue to flow without losing energy.
In the photonic equivalent, light flows not through and around a regular material but in a meta-material consisting of an array of tiny glass loops fabricated on a silicon substrate. If the loops are engineered just right, ...
Expressive writing may help breast cancer survivors
2014-08-01
Writing down fears, emotions and the benefits of a cancer diagnosis may improve health outcomes for Asian-American breast cancer survivors, according to a study conducted by a researcher at the University of Houston (UH).
"The key to developing an expressive writing intervention is the writing instruction. Otherwise, writing is just like a journal recording facts and events. Writing a journal can be therapeutic, but oftentimes we don't get the empirical evidence to determine whether it's effective or not," said Qian Lu, assistant professor and director of the Culture ...
Mapping the optimal route between two quantum states
2014-08-01
As a quantum state collapses from a quantum superposition to a classical state or a different superposition, it will follow a path known as a quantum trajectory. For each start and end state there is an optimal or "most likely" path, but it is not as easy to predict the path or track it experimentally as a straight-line between two points would be in our everyday, classical world.
In a new paper featured on the July 30 cover of Nature, scientists from the Institute for Quantum Studies at Chapman University, the University of Rochester, University of California at Berkeley, ...
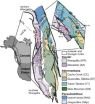
Cordilleran terrane collage
2014-08-01
Boulder, Colo., USA - In the August 2014 issue of LITHOSPHERE, Steve Israel of the Yukon Geological Survey and colleagues provide conclusions regarding the North American Cordillera that they say "are provocative in that they blur the definition of tectonic terranes, showing that many observations of early geologists can be attributed to evolving geologic processes rather than disparate geologic histories."
Western North America is characterized by the Cordilleran accretionary mountain belt, which has seen episodic plate convergence since the early Paleozoic, about 253 ...
On-chipt topological light
2014-08-01
Topological transport of light is the photonic analog of topological electron flow in certain semiconductors. In the electron case, the current flows around the edge of the material but not through the bulk. It is "topological" in that even if electrons encounter impurities in the material the electrons will continue to flow without losing energy.
In the photonic equivalent, light flows not through and around a regular material but in a meta-material consisting of an array of tiny glass loops fabricated on a silicon substrate. If the loops are engineered just right, ...
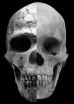
Society bloomed with gentler personalities and more feminine faces
2014-08-01
DURHAM, N.C. -- Modern humans appear in the fossil record about 200,000 years ago, but it was only about 50,000 years ago that making art and advanced tools became widespread.
A new study appearing Aug. 1 in the journal Current Anthropology finds that human skulls changed in ways that indicate a lowering of testosterone levels at around the same time that culture was blossoming.
"The modern human behaviors of technological innovation, making art and rapid cultural exchange probably came at the same time that we developed a more cooperative temperament," said lead author ...
History of culture visualized through art history, physics, complexity
2014-08-01
Coral Gables, Fla. (July 31, 2014) -- Quantifying and transforming the history of culture into visual representation isn't easy. There are thousands of individual stories, across thousands of years, to consider, and some historical conditions are nearly impossible to measure.
Addressing this challenge, Dr. Maximilian Schich, associate professor of arts and technology at The University of Texas at Dallas, brought together a team of network and complexity scientists, including University of Miami physicist Chaoming Song, to create and quantify a big picture of European ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
[Press-News.org] New research characterizes in-flight pediatric deathsResearchers find lap infants at increased risk