(Press-News.org) Growing consensus on climate and land use change means that it is reasonable to assume, at the very least, that flood levels in a region may change. Then why, ask Rosner et al. in a new study, do the dominant risk assessment techniques used to decide whether to build new flood protection infrastructure nearly always start with an assumption of "no trend" in flood behavior?
In an argument grounded in an analysis of the inherent limitations of statistical analyses, the authors suggest that researchers' typical starting assumption that flood behavior is not changing—even in the face of suspected trends in extreme events and knowledge of how difficult such trends are to detect—causes water managers to undervalue flood protection benefits, opening the door to unnecessary losses down the line.
When researchers assume no trend, statistical errors could cause them to overlook of the risks of underpreparing for changing flood conditions. Often, potential flood damage due to underpreparedness far exceeds the potential cost of overinvesting in flood protection infrastructure. Flipping the process around, starting with an assumption that a change in flood conditions is occurring, would give critical attention to the risk of underestimating future floods, rather than only considering the risk of wasting money on unneeded infrastructure.
The authors propose a method of risk assessment that starts with the null hypothesis of "no trend" but that explicitly assesses the effect of statistical uncertainties that may cause them to misidentify real trends and the damages those trends might produce.
INFORMATION: END
How should flood risk assessments be done in a changing climate?
2014-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Insights on whale shark populations and evidence for their historic rise and recent decline
2014-08-04
In the largest study on the genetics of whale sharks conducted to date, researchers found that the world's biggest fish likely exist in 2 distinct populations with minimal connectivity between the Indo-Pacific and the Atlantic Ocean. The findings suggest that mixing of whale sharks between the Indian and Atlantic was and is rare.
The Molecular Ecology investigators also found a significant and likely recent population expansion, but a very recent bottleneck might have gone undetected as genetic diversity at Ningaloo Reef in Australia has declined during 5 consecutive ...
Study assesses shark attacks on Atlantic spotted dolphins near the Bahamas
2014-08-04
A Marine Mammal Science analysis on failed shark attacks on the approximately 120 Atlantic spotted dolphins that are residents of the waters near Bimini, The Bahamas, has found that a total of 14 dolphins (15% of 92 cataloged animals) showed some sign of shark attack, and a further 15 (16%) exhibited scars that could not conclusively be classified as shark induced or not.
Of 14 the shark attacks, there was no difference in scars or wounds between the sexes, and there was no significant difference between the location of bodily scars and wounds. No shark-related injuries ...
Humane strategy reduces shark attacks
2014-08-04
A simple and humane technique may be an effective strategy to reduce human encounters with sharks without harming populations of threatened shark species.
Instead of using advanced (and relatively untested) technology to attempt to repel sharks or nondiscriminatory nets that kill other threatened sea life as bycatch, researchers have simply caught sharks and moved them to where they would not pose a threat to swimmers. The Shark Monitoring Program of Recife, Brazil, reported approximately 100% survival of protected species and a 97% decrease in shark attacks when the ...
Researchers develop food safety social media guide
2014-08-04
To help protect public health, researchers from North Carolina State University have developed guidelines on how to use social media to communicate effectively about food safety.
"In a crisis context, the framework can be used by health officials, businesses or trade organizations affected by foodborne illness to help them reach key audiences with information that could be used to reduce the risk of foodborne illness," says Dr. Ben Chapman, an associate professor at NC State whose research focuses on food safety and lead author of the paper outlining the guidance. Key ...
CU Denver study shows excess parking at some Denver sports stadiums
2014-08-04
DENVER (Aug. 4, 2014) – Sports stadiums in Denver suffer from excess parking, creating unattractive concrete spaces, heat islands, and missed economic opportunities, according to a new study from the University of Colorado Denver.
"We tend to think the more parking, the better," said Wesley Marshall, PhD, PE, assistant professor of civil engineering at the CU Denver College of Engineering and Applied Science. "But too much parking can be as bad as too little."
The study began as a research project for CU Denver engineering student Alejandro Henao and was recently published ...
Weakness of leukaemic stem cells discovered
2014-08-04
FRANKFURT. Despite improved therapy, only one out of every two adult patients survive acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). The mean survival time for this disease, which predominantly occurs in the elderly, is less than a year for patients over 65 years. It is assumed that leukaemic stem cells, which cannot be completely eliminated during treatment, are the origin of relapse. However, as has been discovered by a team of Frankfurt-based researchers, these cells do have a weakness: In the current edition of the high impact journal "Cancer Research", they report that the enzyme ...
Very early treatment may be key to combatting inherited metabolic disorder
2014-08-04
A European Journal of Neuroscience study suggests that it is critical to treat lysosomal storage disorders early, before symptoms arise. These genetic disorders, which are caused by the malfunction of enzymes that normally degrade various substances within cells, lead to numerous ailments including neurological problems.
Although few therapeutic options are available, clinical trials of treatments including lysosomal enzyme replacement are underway. Researchers who used enzyme replacement to treat mice with early, mid- and later-stages of a lysosomal storage disease found ...
Maternal singing during skin-to-skin contact benefits both preterm infants and their mothers
2014-08-04
A mother who sings to her preterm infant while providing 'kangaroo care,' or holding with direct skin-to-skin contact, may see improvements in both her child's and her own health. The finding comes from an Acta Paediatrica study of 86 mother-infant pairs in a neonatal intensive care unit in Meir Hospital in Israel.
Compared with preterm infants whose mothers just held them with direct skin-to-skin contact but did not sing, infants whose mothers both held them and sang to them had improved heart rate variability patterns. This combined effect of holding and singing also ...
Inadequately managed allergies cause significant economic burden in Europe
2014-08-04
New research indicates that avoidable indirect costs per patient insufficiently treated for allergy equal 2,405.00 Euros per year due to absence from work and reduced working capacity. On the other hand, appropriate therapy is available at an average cost of 125 Euros per patient annually, which represents only 5% of the cost of untreated disease.
"Between 55 and 151 billion Euros EU wide could be saved every year by better management of allergies," said Dr. Torsten Zuberbier, lead author of the Allergy study.
INFORMATION: END ...
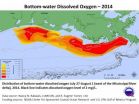
NOAA, EPA-supported scientists find average but large Gulf dead zone
2014-08-04
NOAA- and EPA-supported scientists have mapped the Gulf of Mexico dead zone, an area with low oxygen water, measuring 5,052 square miles this summer--approximately the size of the state of Connecticut. The measurements were taken during the 30th annual hypoxia survey cruise from July 27 to August 2.
This area falls within the predicted range of 4,633 to 5,708 square miles forecast by a suite of NOAA-sponsored models, and confirms the accuracy of the models and their utility for guiding management of nutrients in the Mississippi River watershed.
The size is smaller than ...