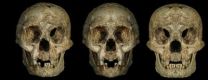
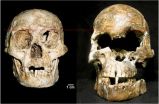
(Press-News.org) In October 2004, excavation of fragmentary skeletal remains from the island of Flores in Indonesia yielded what was called "the most important find in human evolution for 100 years." Its discoverers dubbed the find Homo floresiensis, a name suggesting a previously unknown species of human.
Now detailed reanalysis by an international team of researchers including Robert B. Eckhardt, professor of developmental genetics and evolution at Penn State, Maciej Henneberg, professor of anatomy and pathology at the University of Adelaide, and Kenneth Hsü, a Chinese geologist and paleoclimatologist, suggests that the single specimen on which the new designation depends, known as LB1, does not represent a new species. Instead, it is the skeleton of a developmentally abnormal human and, according to the researchers, contains important features most consistent with a diagnosis of Down syndrome.
"The skeletal sample from Liang Bua cave contains fragmentary remains of several individuals," Eckhardt said. "LB1 has the only skull and thigh bones in the entire sample."
No substantial new bone discoveries have been made in the cave since the finding of LB1.
Initial descriptions of Homo floresiensis focused on LB1's unusual anatomical characteristics: a cranial volume reported as only 380 milliliters (23.2 cubic inches), suggesting a brain less than one third the size of an average modern human's and short thigh bones, which were used to reconstruct a creature standing 1.06 meters (about 3.5 feet tall). Although LB1 lived only 15,000 years ago, comparisons were made to earlier hominins, including Homo erectus and Australopithecus. Other traits were characterized as unique and therefore indicative of a new species.
A thorough reexamination of the available evidence in the context of clinical studies, the researchers said, suggests a different explanation.
The researchers report their findings in two papers published today (Aug. 4) in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In the first place, they write, the original figures for cranial volume and stature are underestimates, "markedly lower than any later attempts to confirm them." Eckhardt, Henneberg, and other researchers have consistently found a cranial volume of about 430 milliliters (26.2 cubic inches).
"The difference is significant, and the revised figure falls in the range predicted for a modern human with Down syndrome from the same geographic region," Eckhardt said.
The original estimate of 3.5 feet for the creature's height was based on extrapolation combining the short thigh bone with a formula derived from an African pygmy population. But humans with Down syndrome also have diagnostically short thigh bones, Eckhardt said.
Though these and other features are unusual, he acknowledged, "unusual does not equal unique. The originally reported traits are not so rare as to have required the invention of a new hominin species."
Instead, the researchers build the case for an alternative diagnosis: that of Down syndrome, one of the most commonly occurring developmental disorders in modern humans.
"When we first saw these bones, several of us immediately spotted a developmental disturbance," said Eckhardt, "but we did not assign a specific diagnosis because the bones were so fragmentary. Over the years, several lines of evidence have converged on Down syndrome."
The first indicator is craniofacial asymmetry, a left-right mismatch of the skull that is characteristic of this and other disorders. Eckhardt and colleagues noted this asymmetry in LB1 as early as 2006, but it had not been reported by the excavating team and was later dismissed as a result of the skull's being long buried, he said.
A previously unpublished measurement of LB1's occipital-frontal circumference -- the circumference of the skull taken roughly above the tops of the ears -- allowed the researchers to compare LB1 to clinical data routinely collected on patients with developmental disorders. Here too, the brain size they estimate is within the range expected for an Australomelanesian human with Down syndrome.
LB1's short thigh bones not only match the height reduction seen in Down syndrome, Eckhardt said, but when corrected statistically for normal growth, they would yield a stature of about 1.26 meters, or just over four feet, a figure matched by some humans now living on Flores and in surrounding regions.
These and other Down-like characteristics, the researchers state, are present only in LB1, and not in the other Liang Bua skeletal remains, further evidence of LB1's abnormality.
"This work is not presented in the form of a fanciful story, but to test a hypothesis: Are the skeletons from Liang Bua cave sufficiently unusual to require invention of a new human species?" Eckhardt said.
"Our reanalysis shows that they are not. The less strained explanation is a developmental disorder. Here the signs point rather clearly to Down syndrome, which occurs in more than one per thousand human births around the world."
INFORMATION: END
Flores bones show features of Down syndrome, not a new 'hobbit' human
2014-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Triple therapy revs up immune system against common brain tumor
2014-08-04
A triple therapy for glioblastoma, including two types of immunotherapy and targeted radiation, has significantly prolonged the survival of mice with these brain cancers, according to a new report by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
Mice with implanted, mouse-derived glioblastoma cells lived an average of 67 days after the triple therapy, compared with mice that lasted 24 days when they received only the two immunotherapies. Half of the mice who received the triple therapy lived 100 days or more and were protected against further tumors when new cancer ...
African American professional women positive on medical research
2014-08-04
ROCHESTER, Minn. — If a research survey of African American professional women is any indication, attitudes may be changing towards participation in medical research. Mayo Clinic and The Links, Incorporated researchers teamed up to survey members of the international women's organization, and found that a majority of African American women surveyed are willing to or have taken part in medical research. The results appear in the Journal of Women's Health.
"Our findings are highly encouraging," says Sharonne Hayes, M.D., Mayo Clinic cardiologist, co-author of the study, ...
Fires in California and Oregon
2014-08-04
The Little Deer fire in California began as a lightning strike on July 31, 2014. Currently it has burned 4,700 acres and is 43% contained however there has been increased humidity over the fire the last 24 hours with shifting wind conditions. The threat of thunder storms today (08/04) and tomorrow (08/05) may cause an increase in fire activity.
The Beaver Complex is comprised of the Salt Creek Fire (20 miles northwest of Medford) and the Oregon Gulch Fire (15 miles east of Ashland), which are lightning-started fires that started on July 30-31, 2014. After it was first ...
Eiler and Bald Fires in California
2014-08-04
The Eiler wildfire which began on July 31, 2014, has almost consumed 26,000 acres. It is currently unknown as to the cause of this fire. The weather patterns currently around this fire do not bode well for a quick containment. Maximum temperatures are in the mid- to high 80's with 10-20% relative humidity. There is an unstable atmosphere at work along with thunderstorm chances which are increasingly today (08/04) through Wednesday (08/06). A Red Flag Warning in effect for dry lightning on Monday (08/04).
The Bald Fire began with a lightning strike on July 30, 2014. ...
Smoke from Canadian wildfires over Baffin Bay
2014-08-04
Canadian wildfires have been raging this summer and some of the smoke from those fires already drifted downward into the U.S. over the Great Lakes (see the image feature from July 25 below). In this image collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on August 02, 2014 the large swath of smoke from these fires has taken a northward track and settled over the Bay of Baffin which borders Greenland.
To view the other Canadian fire images from July 2014:
Smoke from Canadian Fires Hovers Over Great Lakes - July 25, 2014
Smoke ...
Wildfires consume parts of eastern Russia
2014-08-04
Wildfires in far eastern Russia dot the landscape and what isn't covered by the fires is covered by the smoke that rises from these wildfires. This image taken by the Terra satellite shows the entire area covered with a blanket of heavy smoke coming off of dozens of wildfires that have broken out in the remote areas of Russia. Usually these fires are caused by lightning strikes that then consume the dry vegetation. With nothing to stop the spread, these fires take off and cover the landscape, especially during this time of year.INFORMATION:
NASA's Terra satellite collected ...
A hellacious two weeks on Jupiter's moon Io
2014-08-04
Three massive volcanic eruptions occurred on Jupiter's moon Io within a two-week period last August, leading astronomers to speculate that these presumed rare "outbursts," which can send material hundreds of miles above the surface, might be much more common than astronomers thought.
"We typically expect one huge outburst every one or two years, and they're usually not this bright," said Imke de Pater, professor and chair of astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley, and lead author of one of two papers describing the eruptions. "Here we had three extremely ...
Single-fraction RT as effective as multiple-fraction RT for palliation of bone metastases
2014-08-04
Fairfax, Va., August 4, 2014—Standardizing prescribing practices for single-fraction radiation therapy (SFRT) for palliation of bone metastases could lead to cost savings and improvement in patients' quality of life, according to a study published in the August 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Bone metastases are a common manifestation of distant spread of disease, occurring most frequently with prostate, breast ...
How long does it take to make a natural fracture?
2014-08-04
Boulder, Colo., USA – How long does it take for natural Earth processes to form hydraulic fractures? Is the formation driven by sediment compaction, oil and gas generation, or something else? What role do these natural fractures play in modern hydraulic fracturing production? A new GSA BULLETIN study by András Fall and colleagues from The University of Texas at Austin, Virginia Tech, and ExxonMobil addresses these questions, and the article is open-access online.
The process of fracture formation by a natural increase in pore-fluid pressure has previously been referred ...
Bottling up sound waves
2014-08-04
There's a new wave of sound on the horizon carrying with it a broad scope of tantalizing potential applications, including advanced ultrasonic imaging and therapy, acoustic cloaking, and levitation and particle manipulation. Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have developed a technique for generating acoustic bottles in open air that can bend the paths of sound waves along prescribed convex trajectories.
Sound waves move much like light waves. They travel on a straight path but this path - through ...