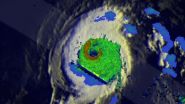
(Press-News.org) NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM flew directly over the eye of powerful Hurricane Iselle and found extremely heavy rainfall rates occurring there.
On August 4, 2014 at 1037 UTC (6:37 a.m. EDT) when TRMM passed over the storm, Iselle had winds of about 120 knots (about 138 mph) at that time making it a dangerous category four hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale. Rainfall from TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) instruments was overlaid on an enhanced infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West satellite that showed cloud extent. The composite image showed the diameter of the storm and the rate in which rain was falling within it. The TRMM PR saw rain falling at a rate of almost 182 mm (about 7.2 inches) per hour in Iselle's eye wall.
TRMM data was also used to create a 3-D image of the storm to help forecasters see cloud heights. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, a 3-D image was produced using radar reflectivity values from TRMM's Precipitation Radar (PR) instrument. The 3-D image showed storms in Iselle's eye wall reaching from 13km (8 miles) to the surface of the ocean below.
On August 4 at 19:40 UTC (3:40 p.m. EDT), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite took a visible image of Hurricane Iselle that showed a clear, cloud-free eye. The visible image also showed a thick band of powerful thunderstorms circling the eye. The image was created by the MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA Goddard.
On August 5, at 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) the center of Hurricane Iselle was located near latitude 15.9 north and longitude 138.6 west. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) reported that Iselle's maximum sustained winds are near 125 mph (205 kph), making Iselle a category three hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane wind scale. Further weakening is forecast during the next couple of days.
VIDEO:
NASA's TRMM Satellite found storms in Iselle's eye wall reaching from 13km (8 miles) high and very heavy rain falling at a rate of almost 182 mm (about 7.2 inches)...
Click here for more information.
NHC noted that Iselle is moving toward the west near 8 mph (13 kph) and this general motion is expected to continue this morning. Iselle should turn toward the west-northwest at a faster forward speed later today and Wednesday, August 3. The estimated minimum central pressure is 955 millibars.
Hurricane Iselle is predicted by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) to weaken as it heads westward into the Central Pacific Ocean. Iselle is expected to move over the Big Island as a tropical storm late Thursday, August 5, 2014.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Hal Pierce
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees heavy rain in Hurricane Iselle as it heads toward Hawaii
2014-08-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new 'whey' to control diabetes
2014-08-05
Blood sugar surges — after-meal glucose "spikes" — can be life threatening for the 29 million Americans with diabetes. Diabetic blood sugar spikes have been linked to cardiovascular disease, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, kidney failure, and retinal damage. Now a new Tel Aviv University study, published in Diabetologia, suggests a novel way to suppress these deadly post-meal glucose surges: the consumption of whey protein concentrate, found in the watery portion of milk separated from cheese curds, before breakfast.
According to TAU's Prof. Daniela Jakubowicz and Dr. Julio ...
Pump up the music -- especially the bass -- to make you feel powerful
2014-08-05
August 5, 2014 - It's the day of the big game – before heading out to the field, you put on your headphones and blast some music to pump you up. The music seemingly empowers you to do great things. This effect is not all in your head – according to new research, music truly does make us feel powerful. But not all songs have the same effect, researchers found, and the levels of bass are a key factor in their effectiveness.
"When watching major sports events, my coauthors and I frequently noticed athletes with their earphones on while entering the stadium and in the locker ...
Cancer fighter can help battle pneumonia
2014-08-05
AUGUSTA, Ga. – The tip of an immune molecule known for its skill at fighting cancer may also help patients survive pneumonia, scientists report.
A synthesized version of the tip of tumor necrosis factor appears to work like a doorstop to keep sodium channels open inside the air sacs of the lungs so excess fluid can be cleared, according to a study published in the American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine.
This TIP peptide is attracted to the sugar coating at the mouth of the sodium channel. Once the two connect, they move inside the small but essential ...
Planet-like object may have spent its youth as hot as a star
2014-08-05
Washington, D.C.—Astronomers have discovered an extremely cool object that could have a particularly diverse history—although it is now as cool as a planet, it may have spent much of its youth as hot as a star.
The current temperature of the object is 200 to 300 degrees Fahrenheit (100 to 150 degrees Celsius), which is intermediate between that of the Earth and of Venus. However, the object shows evidence of a possible ancient origin, implying that a large change in temperature has taken place. In the past this object would have been as hot as a star for many millions ...
What drives cybersex addiction among female internet pornography users?
2014-08-05
New Rochelle, NY, August 5, 2014 -- Women who visit Internet pornography sites are at risk of developing cybersex addiction. A comparison of the tendency toward cybersex addiction among heterosexual women who do or do not use Internet pornography and factors predictive of developing cybersex addiction are described in a study published in Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking website.
In "Cybersex Addiction ...
Marital tension between mom and dad can harm each parent's bond with child, study finds
2014-08-05
Children suffer consequences, too, when mom and dad argue or have tension in their relationship, experts warn.
Dads, in particular, let the negative emotions and tension from their marriage spill over and harm the bond they have with their child, says a new study's lead author, psychologist Chrystyna D. Kouros, Southern Methodist University, Dallas.
The findings drive home the conclusion that the quality of a marriage is closely tied to each parent's bond with their child, Kouros said.
The findings are based on data provided by 203 families, where family members completed ...
NASA's Aqua satellite puts two eyes on Hurricane Bertha
2014-08-05
Two instruments or "eyes" from NASA's Aqua satellite were peering at Hurricane Bertha in the North Atlantic Ocean shortly after it became the season's second hurricane. Bertha's hurricane status didn't last long as it weakened to a tropical storm today, August 5.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua provides infrared data, while the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provides visible data. Together, these instruments give scientists and forecasters a good look inside and outside of the storm to help determine what's ...
Training schemes help jobless men feel better about themselves
2014-08-05
Do the UK government's welfare-to-work training schemes improve the happiness and well-being of its unemployed citizens? Yes, and especially that of jobless men, says Daniel Sage of the University of Stirling in the UK in an article in Springer's Journal of Happiness Studies. His detailed analysis of data from the UK's Annual Population Survey shows that such active labor market programs that mimic the routines of the workplace work best.
Being unemployed can have a long-term scarring effect on a person's subjective sense of well-being and levels of life worth, happiness, ...
Does your training routine really need to be that complicated?
2014-08-05
This news release is available in French. Ottawa, ON -- A new study just published in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism investigated the value of the Pre-Exhaustion (PreEx) training method and found that that the various arrangements of different exercise protocols is of less relevance than simply performing resistance training exercises with a high intensity of effort within any protocol. As resistance training is becoming a major intervention for health and disease prevention, improved understanding in this area is increasingly important.
PreEx ...
Surprise discovery could see graphene used to improve health
2014-08-05
A chance discovery about the 'wonder material' graphene – already exciting scientists because of its potential uses in electronics, energy storage and energy generation – takes it a step closer to being used in medicine and human health.
Researchers from Monash University have discovered that graphene oxide sheets can change structure to become liquid crystal droplets spontaneously and without any specialist equipment.
With graphene droplets now easy to produce, researchers say this opens up possibilities for its use in drug delivery and disease detection.
The findings, ...