(Press-News.org) ATLANTA – August 6, 2014–Nearly one in ten cancer survivors reports smoking many years after a diagnosis, according to a new study by American Cancer Society researchers. Further, among ten cancer sites included in the analysis, the highest rates of smoking were in bladder and lung cancers, two sites strongly associated with smoking. The study appears early online in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
Cigarette smoking decreases the effectiveness of cancer treatments, increases the probability of recurrence, and reduces survival time. Nonetheless, some studies show a significant proportion of cancer survivors continue to smoke after being diagnosed. Most of those studies cover a relatively short time period. There remains a lack of information on smoking prevalence for survivors many years after diagnosis.
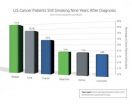
To help close that gap, researchers led by Lee Westmaas, PhD, looked at survey responses from nearly three thousand cancer survivors in the American Cancer Society's Study of Cancer Survivors–I (SCS-I), a longitudinal nationwide study of adult cancer survivors. The study was limited to those with one of the 10 most highly incident cancers at the time of enrollment (breast, prostate, bladder, uterine, melanoma, colorectal, kidney, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, ovarian, and lung).
Interviewed about nine years after diagnosis, 9.3% of the survivors reported being current smokers, 41.2% were former smokers, and 49.6% were never smokers. Among current smokers, 83.1% smoked every day. Nearly half (46.6%) indicated they planned to quit, while 10.1% did not and 43.3% were not sure. Of the 1,209 former smokers, 88.6% had quit before their diagnosis.
Several sociodemographic variables were associated with current smoking status. Survivors who were younger, female, had lower education, and lower income were most likely to remain smokers. The study also found that married smokers had lower intentions of quitting, an unexpected finding that the researchers say has not been previously reported.
"Effective cessation treatment for cancer survivors exists," write the authors, "but future population-based studies examining the importance of psychosocial variables, and their relationships to other health-related variables in predicting current smoking or motivation to quit, will further contribute to enhancing cessation strategies for all survivors who smoke."
The authors conclude that "Those who smoke heavily long after their diagnosis may require more intense treatment addressing specific psychosocial characteristics such as perceptions of risk, beliefs of fatalism, etc. that may influence motivation to quit."
INFORMATION:
Article: Prevalence and Correlates of Smoking and Cessation-Related Behavior among Survivors of Ten Cancers: Findings from a Nation-Wide Survey Nine Years after Diagnosis, Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, Published online Aug 6, 2014 doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0046
Study: Many cancer survivors smoke years after diagnosis
2014-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nearly 10 percent of patients with cancer still smoke
2014-08-06
PHILADELPHIA — Nine years after diagnosis, 9.3 percent of U.S. cancer survivors were current smokers and 83 percent of these individuals were daily smokers who averaged 14.7 cigarettes per day, according to a report in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
"We need to follow up with cancer survivors long after their diagnoses to see whether they are still smoking and offer appropriate counseling, interventions, and possible medications to help them quit," said Lee Westmaas, PhD, director of tobacco ...
Healthy diet set early in life
2014-08-06
Promoting a healthy diet from infancy is important to prevent childhood obesity and the onset of chronic disease.
This is the finding from a study published in the latest issue of Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health.
Led by Rebecca Byrne from QUT, the study described quantity and diversity of food and drinks consumed by children aged 12-16 months.
"The toddler years are a critical age in the development of long-term food preferences, but this is also the age that autonomy, independence and food fussiness begins," Ms Byrne said.
"Childhood obesity in ...
Nutrition an issue for Indigenous Australians
2014-08-06
Nutrition has not been given enough priority in national Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health policy in recent years.
This is the finding from a study published in the latest issue of Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health.
Led by Jennifer Browne from La Trobe University, the study examined Aboriginal-specific health policies and strategies developed between 2000 and 2012.
"Increased inclusion of nutrition in Aboriginal health policy was identified during the first half of this period, but less during the second where a much greater emphasis was ...
Crime Victims' Institute tracks the state of stalking in Texas
2014-08-06
HUNTVILLE (8/6/14) -- According to a 2010 survey by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), an estimated 1.4 million women in Texas experience stalking during their lifetimes. Despite recent laws adopted in the state to protect stalking victims, little information is available about the crime or policies and procedures to aid the criminal justice system, according to a report from the Crime Victims' Institute (CVI).
According to CDC estimates, 15.6 percent of the female population in Texas will experience stalking, slightly less than the 16.2 percent national ...
Vanderbilt finding may aid recovery from spinal cord injury
2014-08-05
Researchers in the Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS) have achieved the first conclusive non-invasive measurement of neural signaling in the spinal cords of healthy human volunteers.
Their technique, described today in the journal eLife, may aid efforts to help patients recover from spinal cord injuries and other disorders affecting spinal cord function, including multiple sclerosis.
"We definitely hope that this work can be translated to address many neurological disorders," said the paper's first author, Robert Barry, Ph.D., a postdoctoral ...
Researchers boost insect aggression by altering brain metabolism
2014-08-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists report they can crank up insect aggression simply by interfering with a basic metabolic pathway in the insect brain. Their study, of fruit flies and honey bees, shows a direct, causal link between brain metabolism (how the brain generates the energy it needs to function) and aggression.
The team reports its findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The new research follows up on previous work from the laboratory of University of Illinois entomology professor and Institute for Genomic Biology director Gene Robinson, ...
This week from AGU: Sea-level spikes, volcanic risk, volcanos cause drought
2014-08-05
From AGU's blogs: Sea-level spikes can harm beaches worse than hurricane
Unforeseen, short-term increases in sea level caused by strong winds, pressure changes and fluctuating ocean currents can cause more damage to beaches on the East Coast over the course of a year than a powerful hurricane making landfall, according to a new study. The new research suggests that these sea-level anomalies could be more of a threat to coastal homes and businesses than previously thought, and could become higher and more frequent as a result of climate change, according to a new study ...
Biology made simpler with clear tissues
2014-08-05
In general, our knowledge of biology—and much of science in general—is limited by our ability to actually see things. Researchers who study developmental problems and disease, in particular, are often limited by their inability to look inside an organism to figure out exactly what went wrong and when.
Now, thanks to techniques developed at Caltech, scientists can see through tissues, organs, and even an entire body. The techniques offer new insight into the cell-by-cell makeup of organisms—and the promise of novel diagnostic medical applications.
"Large volumes of tissue ...
Researchers uncover novel process for creation of fuel and chemical compounds
2014-08-05
MADISON, Wis. — A team of researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison has identified the genes and enzymes that create a promising compound — the 19 carbon furan-containing fatty acid (19Fu-FA). The compound has a variety of potential uses as a biological alternative for compounds currently derived from fossil fuels.
Researchers from the Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center (GLBRC), which is headquartered at UW-Madison and funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, discovered the cellular genomes that direct 19Fu-FA's synthesis and published the new findings Aug. ...
Baby aspirin? Many doctors don't recommend, despite guidelines
2014-08-05
A majority of middle-aged men and women eligible to take aspirin to prevent heart attack and stroke do not recall their doctors ever telling them to do so, according to a University of Rochester study of a national sample of more than 3,000 patients.
Published online by the Journal of General Internal Medicine, the finding illustrates a common disconnect between public health guidelines and what occurs in clinical practice. The UR study is consistent with other research showing that physicians often do not recommend aspirin as prevention therapy to the general population, ...