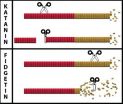
(Press-News.org) The immediate aftermath of an oil spill
The fate of oil during the first day after an accidental oil spill is still poorly understood, with researchers often arriving on the scene only after several days. New findings from a field experiment carried out in the North Sea provide valuable insight that could help shape the emergency response in the immediate wake of disasters.
It is well known that oil and water don't mix. Less well known is the fact that when petroleum is spilt onto a water surface, a fraction of the oil immediately begins to evaporate into the air or dissolve into the seawater. These dissolved toxic hydrocarbons can threaten aquatic species, while evaporated compounds may pose a risk to rescue workers or populations downwind of an accident site. Publishing in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, a team of European and American researchers report on a unique study focused on the fate of hydrocarbons during the 24 hours that follow an oil spill.
Following a spill, oil suddenly finds itself in a radically new environment – exposed to light, air, and the water surface after millions of years underground. "In its new environment, the oil immediately begins to change its composition, and much of that change happens on the first day," explains Samuel Arey, a researcher at EPFL and Eawag in Switzerland and corresponding author of the study. Oil is a complex mixture of many hydrocarbon compounds. Certain volatile compounds evaporate within hours, contaminating the overlying atmosphere. Others, such as toxic naphthalene, simultaneously dissolve into the seawater, posing a threat to aquatic life.
Especially since the Exxon Valdez catastrophe in 1990, which released over 40,000 cubic meters of oil into the ocean, researchers have sought to evaluate to what extent marine species in the vicinity of an oil spill are exposed to toxic hydrocarbons. But this question has largely remained debated, because many of the hydrocarbons are dispersed into the water or the overlying air well before scientists arrive at the site.
In order to collect data on the immediate aftermath of an oil spill, the researchers collaborated with emergency response specialists of the Dutch Rijkswaterstaat to recreate a four cubic meter oil spill in the North Sea, in a shipping zone already burdened by pollutants, 200 kilometers off the coast of the Netherlands. By studying this relatively small oil release, they were able to gain a better understanding of what goes on in much larger spills, with findings that could be useful to assess the risks to underwater life, as well as to emergency response team workers at the sea surface.
No two oil spills are alike. Aside from the sheer volume of oil released onto the sea surface, the environmental impact of an oil spill depends on external factors, such as the wind, waves, and the temperature of the air and the water. The North Sea experiment, for instance, was carried out on a summer day with two-meter high waves. Within just over a day, the surface oil slick had almost dissipated. On a cooler day with less wind and smaller waves, the slick would have likely persisted longer.
Thanks to a computer model that was tested against the data collected in the North Sea, the researchers are now able to extrapolate their findings to larger spills and other environmental conditions. Results from the study will provide the researchers with tools to better assess the immediate impact of future disasters on humans and on the environment, as well as to plan the emergency response, even in settings that differ strongly from those encountered in the North Sea.
INFORMATION:
The research was carried out in partnership with the Royal Netherlands Institute of Sea Research, the Dutch Rijkswaterstaat, the University of Lausanne in Switzerland, the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research in Leipzig, Germany, and the Woods Hole Oceanographic institution in Massachusetts, USA.
The immediate aftermath of an oil spill
The fate of oil during the first day after an accidental oil spill is still poorly understood, with researchers often arriving on the scene only after several days. New findings from a field experiment carried out in the North Sea provide valuable insight
2014-08-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wiggly microRNA binding implies a more complex genome regulation
2014-08-08
(PHILDELPHIA) – MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate protein-coding gene abundance levels by interacting with the 3´ end of various messenger RNAs. Each target site matches the first few nucleotides of the targeting miRNA, the so called "seed" region, and this interaction leads to the degradation of the target or prevents its translation into amino acids. This dogma has led researchers to largely look for perfect base-pair matching of the "seed" region among candidate targets.
New research published today (August 8th) in Nature's open access journal Scientific Reports suggests ...
Scientists unravel mystery of brain cell growth
2014-08-08
In the developing brain, special proteins that act like molecular tugboats push or pull on growing nerve cells, or neurons, helping them navigate to their assigned places amidst the brain's wiring.
How a single protein can exert both a push and a pull force to nudge a neuron in the desired direction is a longstanding mystery that has now been solved by scientists from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and collaborators in Europe and China.
Jia-huai Wang, PhD, who led the work at Dana-Farber and Peking University in Beijing, is a corresponding author of a report published ...
Microtubule-based strategies for promoting nerve regeneration after injury
2014-08-08
After injury, damaged axons have the capacity to regenerate, but the regenerative capacity of the axon, particularly axons of the central nervous system, is quite limited. This is because the damaged axons tend to retract, because they encounter obstacles such as scar tissue and inhibitory molecules, and because their growth rates simply do not match those of a juvenile axon. Prof. Peter W. Baas from Drexel University, USA focus on microtubules as among the most important factors in encouraging injured adult axons to regenerate. Microtubules are hollow polymeric filaments ...
Role of Notch-1 signaling pathway in PC12 cell apoptosis induced by amyloid beta-peptide (25-35)
2014-08-08
Recent studies have demonstrated that Notch-1 expression is increased in the hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease patients. Huimin Liang and co-workers from Second Affliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, China speculate that Notch-1 signaling may be involved in PC12 cell apoptosis induced by amyloid beta-peptide (25-35) (Aβ25-35). In a study reported on the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 13, 2014), PC12 cells were cultured with different doses (0, 0.1, 1.0, 10 and 100 nmol/L) of N-[N-(3,5-Difuorophen-acetyl)-L-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester, a Notch-1 ...
Violent solar system history uncovered by WA meteorite
2014-08-08
Curtin University planetary scientists have shed some light on the bombardment history of our solar system by studying a unique volcanic meteorite recovered in Western Australia.
Captured on camera seven years ago falling on the WA side of the Nullarbor Plain, the Bunburra Rockhole Meterorite has unique characteristics that suggest it came from a large asteroid that has never before been identified.
Associate Professor Fred Jourdan, along with colleagues Professor Phil Bland and Dr Gretchen Benedix from Curtin's Department of Applied Geology, believe the meteorite is ...
A*Star scientists make breakthroughs in ovarian cancer research
2014-08-08
Scientists at A*STAR's Institute of Medical Biology (IMB) and the Bioinformatics Institute (BII) have found new clues to early detection and personalised treatment of ovarian cancer, currently one of the most difficult cancers to diagnose early due to the lack of symptoms that are unique to the illness.
There are three predominant cancers that affect women – breast, ovarian and womb cancer. Of the three, ovarian cancer is of the greatest concern as it is usually diagnosed only at an advanced stage due to the absence of clear early warning symptoms. Successful treatment ...
Study: Few juvenile suspects exercise constitutional rights during interrogations
2014-08-08
WASHINGTON –- Even when not under arrest, juvenile suspects being interrogated for a crime may be strikingly unaware of their constitutional rights and confess without legal counsel or even a parent present, according to research presented at the American Psychological Association's 122nd Annual Convention.
An analysis of 57 videotaped juvenile interrogations at 17 police departments around the country revealed none of the suspects, who ranged in age from 13 to 17, had an attorney present while they were questioned, according to Hayley Cleary, PhD, of Virginia Commonwealth ...
Parents part of problem in distracted teen driving, study finds
2014-08-08
WASHINGTON –- Parents play a direct role in distracted teen driving, with more than half of teens talking on cellphones with their mother or father while driving, according to new research presented at the American Psychological Association's 122nd Annual Convention.
Researchers interviewed or surveyed more than 400 teen drivers, ages 15 to 18, from 31 states to find out why they continue to talk and text behind the wheel, despite warnings about the serious hazards of distracted driving.
"Teens said parents expect to be able to reach them, that parents get mad if they ...
Stem cells show promise for stroke in pilot study
2014-08-08
A stroke therapy using stem cells extracted from patients' bone marrow has shown promising results in the first trial of its kind in humans.
Five patients received the treatment in a pilot study conducted by doctors at Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust and scientists at Imperial College London.
The therapy was found to be safe, and all the patients showed improvements in clinical measures of disability.
The findings are published in the journal Stem Cells Translational Medicine. It is the first UK human trial of a stem cell treatment for acute stroke to be published.
The ...
Scientists enhance synthesis of chromium dioxide (100) epitaxial thin film growth
2014-08-08
Half-metallic ferromagnet CrO2 has attracted much attention not only because of its fundamental physics related with high spin polarization but also because of its possible applications in the emerging area of spintronics.
In these applications, synthesis of CrO2 films is of fundamental importance, primarily because of the difficulty in its synthesis, as it is not known to form under ambient pressures in a pure form. Extensive efforts have been made to grow high quality CrO2 films, but the growth technology still deserves research.
The high quality CrO2 film on the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
[Press-News.org] The immediate aftermath of an oil spillThe fate of oil during the first day after an accidental oil spill is still poorly understood, with researchers often arriving on the scene only after several days. New findings from a field experiment carried out in the North Sea provide valuable insight