(Press-News.org) Researchers have strived for years to determine how neurons are produced and integrated into the brain throughout adult life. In an intriguing twist, scientists reporting in the August 11 issue of the Cell Press journal Developmental Cell provide evidence that adult-born neurons are derived from a special type of circulating blood cell produced by the immune system. The findings—which were made in crayfish—suggest that the immune system may contribute to the development of the unknown role of certain brain diseases in the development of brain and other tissues.
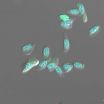
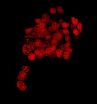
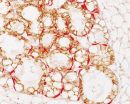
In many adult organisms, including humans, neurons in some parts of the brain are continually replenished. While this process is critical for ongoing health, dysfunctions in the production of new neurons may also contribute to several neurological diseases, including clinical depression and some neurodegenerative disorders. Dr. Barbara Beltz of Wellesley College and her colleagues studied crayfish to understand how new neurons are made in adult organisms. When they marked the cells of one crayfish and used this animal as a blood donor for transfusions into another crayfish, the researchers found that the donor blood cells could generate neurons in the recipient.
"These blood cells—called hemocytes—have functions similar to certain white blood cells in mammals and are produced by the immune system in a blood-forming organ that is functionally analogous to bone marrow," explains Dr. Beltz. "When these cells are released into the circulation, they are attracted to a specialized region in the brain where stem cells divide, and their descendants develop into functional neurons."
The current work demonstrates that the immune system can produce cells with stem cell properties that can give rise to different types of cells, including both hemocytes and nerve cells. "Our findings in crayfish indicate that the immune system is intimately tied to mechanisms of adult neurogenesis, suggesting a much closer relationship between the immune system and nervous system than has been previously appreciated," says co-author Dr. Irene Söderhäll, of Uppsala University in Sweden. The flexibility of these immune cells in producing neurons in adult animals raises the intriguing possibility of the presence of similar types of flexibility in other animals. If further studies demonstrated a similar relationship between the immune system and brain in mammals, the findings would stimulate a new area of research into immune therapies to target neurological diseases.
INFORMATION:
Developmental Cell, Benton et al.: "Cells from the immune system generate adult-born neurons in crayfish."
Blood cells are a new and unexpected source of neurons in crayfish
Study demonstrates that the immune system can produce cells with stem cell properties that can create different types of cells such as neurons in the adult animal
2014-08-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How breast cancer usurps the powers of mammary stem cells
2014-08-11
During pregnancy, certain hormones trigger specialized mammary stem cells to create milk-producing cells essential to lactation. Scientists at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Moores Cancer Center have found that mammary stem cells associated with the pregnant mammary gland are related to stem cells found in breast cancer.
Writing in the August 11, 2014 issue of Developmental Cell, David A. Cheresh, PhD, Distinguished Professor of Pathology and vice-chair for research and development, Jay Desgrosellier, PhD, assistant professor of pathology ...
Malaria medicine chloroquine inhibits tumor growth and metastases
2014-08-11
A recent study by investigators at VIB and KU Leuven has demonstrated that chloroquine also normalizes the abnormal blood vessels in tumors. This blood vessel normalization results in an increased barrier function on the one hand -- thereby blocking cancer cell dissemination and metastasis -- and in enhanced tumor perfusion on the other hand, which increases the response of the tumor to chemotherapy.
The anti-cancer effect of the antimalarial agent chloroquine when combined with conventional chemotherapy has been well documented in experimental animal models. To date, ...
Climate change negatively impacting Great Lakes, GVSU researcher says
2014-08-11
MUSKEGON, Mich. -- Climate change is having a direct negative effect on the Great Lakes, including impacts to recreational value, drinking water potential, and becoming more suited to invasive species and infectious pathogens, according to a Grand Valley State University researcher.
The impact of climate change on the Great Lakes, as well as other natural resources in the United States, was explored in the report "Science, Education, and Outreach Roadmap for Natural Resources," recently released by the Association of Public and Land-grant Universities. Kevin Strychar, ...
CRI scientists pinpoint gene likely to promote childhood cancers
2014-08-11
DALLAS – Aug. 11, 2014 – Researchers at the Children’s Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) have identified a gene that contributes to the development of several childhood cancers, in a study conducted with mice designed to model the cancers. If the findings prove to be applicable to humans, the research could lead to new strategies for targeting certain childhood cancers at a molecular level. The study was published today in the journal Cancer Cell.
“We and others have found that Lin28b – a gene that is normally turned on in fetal but not adult ...
US immigration is associated with rise in smoking among Latinos and Asians
2014-08-11
Immigration to the U.S. may result in increased smoking in Latino and Asian women, according to new research from sociologists at Rice University, Duke University and the University of Southern California.
The study, "Gender, Acculturation and Smoking Behavior Among U.S. Asian and Latino Immigrants," examines smoking prevalence and frequency among Asian and Latino U.S. immigrants. The research focuses on how gender differences in smoking behavior are shaped by aspects of acculturation and the original decision to migrate. The study was published recently in the journal ...
Kessler Foundation researchers publish study on task constraint and task switching
2014-08-11
West Orange, NJ. August 11, 2014 -- Kessler Foundation scientists have published results of cognitive research that show the negative effects that unexpected task constraint, following self-generated task choice, has on task-switching performance. The article, "You can't always get what you want: The influence of unexpected task constraint on voluntary task switching", was published online on June 11 by The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology (DOI:10.1080/17470218.2014.917115). The authors are Starla Weaver, PhD, and Glenn Wylie, DPhil, of Kessler Foundation, John ...
Study: 1 out of 5 adult orthopaedic trauma patients sought additional providers for narcotic prescriptions
2014-08-11
ROSEMONT, Ill.─"Doctor shopping," the growing practice of obtaining narcotic prescriptions from multiple providers, has led to measurable increases in drug use among postoperative trauma patients. The study, "Narcotic Use and Postoperative Doctor Shopping in the Orthopaedic Trauma Population," appearing in the August issue of the Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS), links doctor shopping to higher narcotic use among orthopaedic patients. The data was presented earlier this year at the 2014 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS).
"There ...
Keeping viruses at bay
2014-08-11
>
Our immunosensory system detects virus such as influenza via specific characteristics of viral ribonucleic acid. Previously, it was unclear how the immune system prevents viruses from simply donning molecular camouflage in order to escape detection. An international team of researchers from the University of Bonn Hospital and the London Research Institute have now discovered that our immunosensory system attacks viruses on a molecular level. In this way, a healthy organism can keep rotaviruses, a common cause of diarrheal epidemics, at bay. The results have been published ...
Fertile discovery
2014-08-11
Queen's University researcher Richard Oko and his co-investigators have come up with a promising method of treating male infertility using a synthetic version of the sperm-originated protein known as PAWP.
They found this protein is sufficient and required to initiate the fertilization process.
Dr. Oko's research promises to diagnose and treat cases of male factor infertility where a patient's sperm is unable to initiate or induce activation of the egg to form an early embryo.
"PAWP is able to induce embryo development in human eggs in a fashion similar to the natural ...
Penn-led expert panel calls for public health research on natural gas drilling
2014-08-11
PHILADELPHIA – Groundwater and air quality testing before, during, and after natural gas drilling – which includes hydraulic fracturing -- should be key components of efforts to ensure the safety of communities near these sites, according to an expert panel convened to weigh in on public health research needs associated with unconventional natural gas drilling operations (UNGDO). The panel also urges that any research conducted should use "community-based participatory research principles" so that the concerns of the many stakeholders involved in these activities can be ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Blood cells are a new and unexpected source of neurons in crayfishStudy demonstrates that the immune system can produce cells with stem cell properties that can create different types of cells such as neurons in the adult animal