Changes in motor function in the unaffected hand of stroke patients should not be ignored
2014-08-12
(Press-News.org) With effective rehabilitation, stroke patients can partially regain their motor control and continue their activities of daily living. Motor function changes in the unaffected hand of stroke patients with hemiplegia. However, these changes are often ignored by clinicians owing to the extent of motor disability of the affected hand. Research group at Shanghai University of Sport, China led by Prof. Zhusheng Yu based on finger tapping frequency and Lind-mark hand function score have found that the motor function of unaffected hands in stroke patients was poorer than that of a healthy control hand. After 2 weeks of rehabilitation treatment, motor function of the unaffected hand of stroke patients was obviously improved. Therefore, attention should also be paid to motor function in the unaffected hand of stroke patients with hemiplegia during rehabilitation.
INFORMATION:
The relevant study has been reported in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 13, 2014)
article: "Changes in motor function in the unaffected hand of stroke patients should not be ignored" by Lingli Zhang, Peihong Li, Zhibang Mao, Xiang Qi, Jun Zou, Zhusheng Yu (Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China)
Zhang LL, Li PH, Mao ZB, Qi X, Zou J, Yu ZS. Changes in motor function in the unaffected hand of stroke patients should not be ignored. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(13):1323-1328. END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neuroprotective effect of tongxinluo: a PET imaging study in small animals
2014-08-12
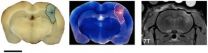
Tongxinluo has been widely used in China for the treatment of acute stroke and for neuroprotection. Research group at Encephalopathy Center, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China intragastrically administered Tongxinluo superfine powder suspension or its vehicle to rats for 5 successive days before middle cerebral artery occlusion. There are many advantages of using small animal PET for drug research. First, the results of the study in vitro cannot be directly applied to human studies, while small animal PET imaging methods and results can ...
ASU-Mayo researchers use calcium isotope analysis to predict myeloma progression
2014-08-12
TEMPE, Ariz. – A team of researchers from Arizona State University and Mayo Clinic is showing how a staple of Earth science research can be used in biomedical settings to predict the course of disease.
The researchers tested a new approach to detecting bone loss in cancer patients by using calcium isotope analysis to predict whether myeloma patients are at risk for developing bone lesions, a hallmark of the disease.
They believe they have a promising technique that could be used to chart the progression of multiple myeloma, a lethal disease that eventually impacts ...
Neutrino detectors could help curb nuclear weapons activity
2014-08-12
Physicists at the Large Hadron Collider in Switzerland and even in the fictional world of CBS' "The Big Bang Theory" look to subatomic particles called neutrinos to answer the big questions about the universe.
Now, a group of scientists led by a physics professor with the College of Science at Virginia Tech are asking whether the neutrino could provide the world with clues about nuclear proliferation in Iran and other political hotspots.
Neutrinos are produced by the decay of radioactive elements, and nuclear reactors produce large amounts of neutrinos that cannot ...
Focal blood-brain-barrier disruption with high-frequency pulsed electric fields
2014-08-12
A team of researchers from the Virginia Tech-Wake Forest University School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences have developed a new way of using electricity to open the blood-brain-barrier (BBB). The Vascular Enabled Integrated Nanosecond pulse (VEIN pulse) procedure consists of inserting minimally invasive needle electrodes into the diseased tissue and applying multiple bursts of nanosecond pulses with alternating polarity. It is thought that the bursts disrupt tight junction proteins responsible for maintaining the integrity of the BBB without causing damage to the ...
A highly sensitive microsphere-based assay for early detection of Type I diabetes
2014-08-12
A team of researchers from the Center for Engineering in Medicine at the Massachusetts General Hospital have developed a novel fluorescence-based assay for sensitive detection of antibodies within microliter volume serum samples. This new assay is at least 50 times more sensitive than the traditional radioimmunoassay (RIA), which is the gold standard currently used in the clinic. This new technology is particularly attractive for immunological assays as it allows: 1) use of very small volumes of sample reagents (5 ¦ÌL), and 2) use of traditional analytical systems such ...
Biomarker could reveal why some develop post-traumatic stress disorder
2014-08-12
(NEW YORK – August 11) Blood expression levels of genes targeted by the stress hormones called glucocorticoids could be a physical measure, or biomarker, of risk for developing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), according to a study conducted in rats by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and published August 11 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). That also makes the steroid hormones' receptor, the glucocorticoid receptor, a potential target for new drugs.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is triggered by a terrifying ...
Robotic-assisted imaging: from trans-Atlantic evaluation to help in daily practice
2014-08-12
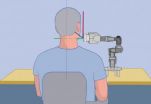
While in Germany, Partho P. Sengupta, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai used a computer to perform a robot-assisted trans-Atlantic ultrasound examination on a person in Boston. In another study Kurt Boman, MD, of Umeå University in Sweden in collaboration with Mount Sinai, showed how a cardiologist's video e-consultation, coupled with a remote robot-assisted echocardiogram test, dramatically reduces the waiting time for a diagnosis faced by heart failure patients who live in a rural communities far from the hospital from nearly four months to less than one ...
The Maldives and the whale shark: The world's biggest fish adds value to paradise
2014-08-12
They are the largest fish in the world but the impact of this majestic and charismatic animal on the economy of the island nation of the Maldives was largely unknown. A new study by scientists of the Maldives Whale Shark Research Programme (MWSRP) reveals that a small group of whale sharks in a single Maldivian Atoll accounts for nearly 3% of the global shark ecotourism and nearly half that of the Maldives'.
"The Republic of Maldives hosts one of few known year round aggregation sites for whale sharks", said James Hancock co-author and a director of MWSRP. "We have seen ...
Is empathy in humans and apes actually different?
2014-08-12
Whether or not humans are the only empathic beings is still under debate. In a new study, researchers directly compared the 'yawn contagion' effect between humans and bonobos (our closest evolutionary cousins). By doing so they were able to directly compare the empathic abilities of ourselves with another species, and found that a close relationship between individuals is more important to their empathic response than the fact that individuals might be from the same species.
The ability to experience others' emotions is hard to quantify in any species, and, as a result, ...
Sniffing out billions in US currency smuggled across the border to Mexico
2014-08-12
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 12, 2014 — Criminals are smuggling an estimated $30 billion in U.S. currency into Mexico each year from the United States, but help could be on the way for border guards, researchers will report here today. The answer to the problem: a portable device that identifies specific vapors given off by U.S. paper money.
They will present the new research at the 248th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society. The meeting features nearly 12,000 reports on new advances in science and other ...