(Press-News.org) While hiking through the Ozarks' characteristic oak and hickory forests as a teenager, ecologist Scott Woolbright discovered something decidedly uncharacteristic for the region: prickly pear cacti growing on an exposed, rocky ledge.
In a recent paper published in Trends in Ecology and Evolution, Woolbright describes how populations and communities like these, known as climate relicts, can help scientists understand how ecological communities are affected by climate change.
Rocky, well-drained slopes in the Ozarks often create habitat "islands" within the surrounding forest known as glade ecosystems, said Woolbright, who is a postdoctoral fellow at the Institute for Genomic Biology (IGB) in the Genomic Ecology of Global Change research theme at the University of Illinois. In the Ozarks, glades often help to preserve isolated communities of cacti and other desert and prairie species that dominated the area during the Hypsithermal, a period of warming that occurred four to eight thousand years ago.
Ecologists have recently begun to discuss climate relicts as potential "natural laboratories" for studying the evolution of single plant species. Woolbright and co-authors suggest expanding such studies to include interactions between plants and other organisms that can drive community and ecosystem patterns.
It can be very difficult to replicate the long-term effects of climate change over very large geographic areas in the laboratory or field. But isolated climate relicts that are distributed across landscapes create "natural experiments" that help to overcome these problems of scale.
Using the genomic technologies he's learned at the IGB, Woolbright hopes to develop a research program that investigates climate-driven changes in species interactions at the gene level. While such a program would contribute to basic community and ecosystem research, it also has significant implications for ecological conservation and restoration.
"We're learning that you often can't just go out and preserve a single species," Woolbright said. "Interactions with other species can play very important roles in species survival. If we don't take those interactions into account, we can miss things that are really important."
Many climate relicts are threatened by small population size, ongoing environmental change in already stressful environments, invasions from species in adjacent non-relict communities, and human encroachment.
Woolbright said it will take the cooperation of many stakeholders to conserve relicts for their historical, ecological and aesthetic value.
INFORMATION:
Thomas Whitham, Catherine Gehring, and Gerard Allan from Northern Arizona University as well as Joseph Bailey from the University of Tennessee were co-authors in this study.
The IGB's fellows program supported Woolbright, who was inspired to pursue a career in climate change ecology by his encounter with Ozark glades.
Climate relicts may help researchers understand climate change
2014-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA sees the end of Tropical Depression Genevieve
2014-08-12
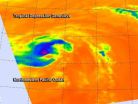
Cloud tops were warming and precipitation was waning in Tropical Depression Genevieve when NASA's Aqua satellite flew overhead. Genevieve moved through all three Pacific Ocean regions (eastern, central and western) in its two week lifetime and met its end today.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression Genevieve on Aug. 11 at 01:29 UTC and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) captured infrared data on the storm. AIRS data showed a small area of the strongest thunderstorms were occurring over the northern quadrant, where temperatures approached -63F/-52C. ...
Roadside research from the pinelands and coast to coast
2014-08-12
PHILADELPHIA (August 12, 2014)— "Roads are essentially the primary feature of human civilization at this point," according to Dane Ward, a doctoral student in environmental science at Drexel University who is presenting research at the Ecological Society of America (ESA) meeting.
Perhaps not surprisingly, Ward, along with fellow doctoral students Ryan Rebozo and Kevin P.W. Smith from the Laboratory of Pinelands Research led by Walter Bien, PhD in Drexel's College of Arts and Sciences, took advantage of a cross-country roadtrip from Philadelphia to the meeting in Sacramento ...
UMN and NYBC research finds potential MERS transmission mechanism between bats and humans
2014-08-12
Researchers have identified the mechanism used by the deadly MERS virus to transmit from bats to humans. Bats are a native reservoir for MERS and the finding could be critical for understanding the animal origins of the virus, as well as preventing and controlling the spread of MERS and related viruses in humans.
The findings were published in the most recent edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Leading the research was Fang Li, Ph.D., associate professor of Pharmacology at the University of Minnesota Medical School. Graduate students Yang ...
Notre Dame paper offers insights into a new class of semiconducting materials
2014-08-12
A new paper by University of Notre Dame researchers describes their investigations of the fundamental optical properties of a new class of semiconducting materials known as organic-inorganic "hybrid" perovskites.
The research was conducted at the Notre Dame Radiation Laboratory by Joseph Manser, a doctoral student in chemical and biomolecular engineering, under the direction of Prashant Kamat, Rev. John A. Zahm Professor of Science. The findings appear in a paper in the August 10 edition of the journal Nature Photonics.
The term "perovskites" refers to the structural ...
New analysis reveals tumor weaknesses
2014-08-12
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Scientists have known for decades that cancer can be caused by genetic mutations, but more recently they have discovered that chemical modifications of a gene can also contribute to cancer. These alterations, known as epigenetic modifications, control whether a gene is turned on or off.
Analyzing these modifications can provide important clues to the type of tumor a patient has, and how it will respond to different drugs. For example, patients with glioblastoma, a type of brain tumor, respond well to a certain class of drugs known as alkylating agents ...
Federal Drug Discount Program faces challenges, report finds
2014-08-12
A federal program that provides billions in drug discounts to safety net hospitals and other health care providers is expanding under health care reform, but divergent views on the purpose and future scope of the program creates uncertainty for safety net providers and drug manufacturers, according to new report from the RAND Corporation.
The so-called 340B program faces a number of critical issues, such as whether to change and better define eligibility, strengthen compliance efforts and provide greater transparency about the discounts provided through the program, according ...
Digital literacy reduces cognitive decline in older adults, experts find
2014-08-12
Researchers have found a link between digital literacy and a reduction in cognitive decline, according to a study published in The Journals of Gerontology, Series A: Medical Sciences on July 8th.
Led by Andre Junqueira Xavier at the Universidade do Sul de Santa Catarina, this is the first major study to show that digital literacy, or the ability to engage, plan and execute digital actions such as web browsing and exchanging emails, can improve memory.
Drawn from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing, the study followed 6442 participants in the UK between the ages ...
Regional anesthesia for pediatric knee surgery reduces pain, speeds recovery
2014-08-12
VIDEO:
As many as 98 percent of all pediatric knee surgeries performed at Nationwide Children's Hospital were done in an outpatient setting, as a result of this method that reduces...
Click here for more information.
A recent study of an ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia technique, called femoral nerve block, shows that it leads to less opioid use and allows the majority of patients to go home within hours of surgery. As many as 98 percent of all pediatric knee surgeries ...
Oxidative stress is significant predictor for hip fracture, research shows
2014-08-12
CINCINNATI—Oxidative stress is a significant predictor for hip fracture in postmenopausal women, according to new research led by University of Cincinnati (UC) epidemiologists.
The research, appearing online ahead of print in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, was led by Tianying Wu, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in the UC College of Medicine Department of Environmental Health, and Shuman Yang, a postdoctoral fellow in the department. They collaborated with researchers from the Harvard School of Public Health and Harvard Medical School.
"To our knowledge, this ...
Fires in Northern Washington State
2014-08-12
The Pacific Northwest has been inundated with wildfires most stemming from lightning strikes during summer storms. Four of these wildfires can be seen in this natural-color Aqua satellite image collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, MODIS, instrument aboard. This image was taken on August 11, 2014. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red.
The Upper Falls wildfire was started by a lightning strike on August 03. It is located 17 Miles North of Winthrop WA, 37 miles Northwest of Omak, WA and has grown to ...