(Press-News.org) Transport accounts for 30% of CO2 emissions in the EU, with emissions rising 36% between 1990 and 2007. The research, carried out by Lund University and the University of Surrey a found a need to dissect the widely-held view that new technologies, such as biofuel and improved aircraft design, will result in carbon reduction targets being met.
In the paper, researchers highlight the fact that policy makers are turning to the perceived benefits of such technologies to drive decarbonisation policy, despite contrary evidence. They argue that in order to cut damaging carbon emissions, politicians need to address 'transport taboos' rather than focus just on technological innovation.
These transport taboos are defined as transport 'norms', such as societies' growing appetite for frequent, long-distance travel, the unjust relationship between mobility and income, and the powerful position of lobbyists and industry in influencing policy. The team of researchers found that policies which challenged these taboos are regarded as serious threats to political position and are therefore ignored by politicians.
"This study shows what a pervasive force the transport industry is in influencing carbon-reduction policy. Politicians continue to ignore evidence of what works in favour of optimistic headlines about technological innovation, driven by industry and lobbyists," said co-author, Dr Scott Cohen from the University of Surrey
"There is a lot of exaggeration surrounding 'wonder' technologies that promise to reduce carbon levels while allowing privileged sections of society to continue to travel without limits. These optimistic claims are largely undebated in political circles, as this would force politicians to face some harsh truths."
Researchers found that it is the most highly mobile and environmentally aware travellers who refuse to reduce travel, with men in higher income groups the most frequent and long-distance flyers. "The richest and politically powerful contribute the most to global carbon emissions. Ironically they are offered rewards for this behaviour with air miles, as well as earning prestige among peers who view international travel as a status symbol. Our research explores how these transport taboos are driving policies that are contradictory to carbon emission targets. For example, energy intensive air transport is the least taxed and most subsidised. In one year, Ryanair received subsidies of 800m Euro while encouraging frequent, low-cost flight. Rather than maintain the status quo, we need to start challenging these damaging norms."
INFORMATION: END
Politicians need to address transport taboos, not just new technology, to meet carbon targets
2014-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
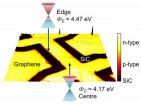
On the edge of graphene
2014-08-15
Researchers at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) have discovered that the conductivity at the edges of graphene devices is different to that of the central material.
Local scanning electrical techniques were used to examine the local nanoscale electronic properties of epitaxial graphene, in particular the differences between the edges and central parts of graphene Hall bar devices. The research was published in Scientific Reports, an open access publication from Nature Publishing Group.
The researchers found that the central part of the graphene channel demonstrated ...
TUM researchers develop defense against cyberattacks
2014-08-15
Port scanners are programs that search the Internet for systems that exhibit potential vulnerabilities. According to the report published today by journalists at Heise Online, Hacienda is one such port scanning program. The report says that this program is being put into service by the "Five Eyes," a federation of the secret services of the USA, Canada, the UK, Australia and New Zealand. "The goal is to identify as many servers as possible in other countries that can be remotely controlled," explains Dr. Christian Grothoff, Emmy Noether research group leader at the TUM ...
Experts close to perfect in determining truth in interrogations using active question methods
2014-08-15
Washington, DC (August 12, 2014) – Determining deception is a tool of the trade for law enforcement. The Good Cop/Bad Cop routine is etched in our minds as an effective method of finding out the truth. But prior research has shown that lie detecting is a 50/50 shot for experts and non-experts alike. So what exactly can we do to find out the truth? A recent study published in Human Communication Research by researchers at Korea University, Michigan State University, and Texas State University - San Marcos found that using active questioning of individuals yielded near-perfect ...
The beetle's white album
2014-08-15
The physical properties of the ultra-white scales on certain species of beetle could be used to make whiter paper, plastics and paints, while using far less material than is used in current manufacturing methods.
The Cyphochilus beetle, which is native to South-East Asia, is whiter than paper, thanks to ultra-thin scales which cover its body. A new investigation of the optical properties of these scales has shown that they are able to scatter light more efficiently than any other biological tissue known, which is how they are able to achieve such a bright whiteness. ...
Personal, public costs of scientific misconduct calculated
2014-08-15
Much has been assumed about the private and public damage of scientific misconduct. Yet few have tried to measure the costs to perpetrators and to society.
A recent study calculated some of the career impacts, as well as federal funding wasted, when biomedical research papers are retracted. The results appear in the Aug. 15 issue of the journal eLife.
In questioning common assumptions, the study authors determined that scientific misconduct typically, but not always, exacts a personal toll in derailing careers. On the public side, the cost to federal funding sources ...
Previous pulmonary disease linked to increased lung cancer risk in large study
2014-08-15
Links between a number of common respiratory diseases and an increased risk of developing lung cancer have been found in a large pooled analysis of seven studies involving more than 25,000 individuals.
"Associations between various respiratory diseases and lung cancer have been shown in earlier studies, but few of these studies considered multiple respiratory diseases simultaneously," said researcher Ann Olsson, PhD, of the International Agency for Research in Cancer in Lyon, France. "In our pooled analysis of seven case-control studies involving more than 12,500 cases ...
Human milk fat improves growth in premature infants
2014-08-15
HOUSTON – (August 15, 2014) – For premature infants, adequate growth while in the neonatal intensive care unit is an indicator of better long-term health and developmental outcomes. Researchers at the USDA/ARS Children's Nutrition Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children's Hospital have now successfully incorporated a cream supplement into premature infants' diets that improved their growth outcomes in the NICU. The report appears today in the Journal of Pediatrics.
"For premature babies who weigh less than 1,000 grams (about 2 pounds, 2 ounces), ...
Woodrats' genes help them to win the arms race against their food
2014-08-15
A handful of genes arm the woodrat against the toxic chemicals in its foodstuff, the creosote plant, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Ecology.
It's long been a mystery exactly how the woodrat developed the ability to handle the chemicals in the creosote plant, which are toxic to other rodents. Previous research has suggested that they are protected by factors such as gut bacteria. But the new study identifies the genes switched on in two species of woodrat with resistance to the plant poisons, showing that the genes that they are born with ...
Experimental chikungunya vaccine induces robust antibody response
2014-08-15
An experimental vaccine to prevent the mosquito-borne viral illness chikungunya elicited neutralizing antibodies in all 25 adult volunteers who participated in a recent early-stage clinical trial conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. The results are reported in the current issue of The Lancet.
The most distinctive symptom of chikungunya infection is severe joint pain accompanied by headache and fever. There are currently no vaccines or specific drug treatments for chikungunya. ...
The Lancet: European Society of Cardiology Congress media alert
2014-08-15
The Lancet is pleased to announce that the following papers will be published ahead of the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2014, taking place in Barcelona, Spain, from 30 August to 3 September 2014. This includes a special Series of three papers on lipids and cardiovascular disease.
Blood pressure-lowering treatment based on cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of individual patient data by Dr Johan Sundström et al
This study investigated whether the success of blood pressure-lowering drugs is dependent on baseline cardiovascular risk, and whether this could ...