(Press-News.org) Members of the brown argus butterfly species that moved north in response to recent climate change have evolved a narrower diet dependent on wild Geranium plants, UK researchers report. However, butterflies that did not move north have more diverse diets, including plants such as Rockrose that are abundant in southern parts of the UK.
So although rapid evolutionary changes have allowed the brown argus to move north and track the warming climate, they have led to a more restricted diet. This increased specialization may limit this butterfly's continued spread north, into areas where Rockrose is common.
"Our data confirm that rapid evolutionary change in a species' diet is important for responding to recent climate change, but as a consequence, variation in this ecologically-important trait may be lost," said Dr. Jon Bridle, co-author of the Ecology Letters study. "In addition, unlike the brown argus, many butterflies already have restricted diets, so they may be unable to rapidly evolve changes in their diets to survive ongoing climate change," said co-author Dr. James Buckley.
INFORMATION: END
Butterflies' evolutionary responses to warmer temperatures may compromise their ability to adapt to future climate change
2014-08-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Invasion of the Americas by mosquito-borne virus likely
2014-08-18
While media attention has been focused recently on coronavirus cases in the Arabian peninsula and the Ebola outbreak in West Africa, experts note that another threat lies in the spread of Chikungunya fever, an illness that is transmitted by mosquitoes and can cause fever, joint and muscle pain, headaches, and rashes. While it does not often cause death, the symptoms can be severe and disabling, with no treatment available.
The potential for worldwide spread of Chikungunya virus is much higher than the risk of dissemination of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus ...
Study suggests hatha yoga boosts brain function in older adults
2014-08-18
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Practicing hatha yoga three times a week for eight weeks improved sedentary older adults' performance on cognitive tasks that are relevant to everyday life, researchers report.
The findings involved 108 adults between the ages of 55 and 79 years of age, 61 of whom attended hatha yoga classes. The others met for the same number and length of sessions and engaged in stretching and toning exercises instead of yoga.
At the end of the eight weeks, the yoga group was speedier and more accurate on tests of information recall, mental flexibility and task-switching ...
The double threat of climate and land use change enhances risks to biodiversity
2014-08-18
Researchers from Aarhus University, Denmark, and the University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, have developed a new approach to measure the combined exposure of species to both climate and land use change. This new metric was used to assess the risk to species in the face of combined rates of climate and land use for the US from 2001 to 2051.
Their results, which have just been published in Nature Climate Change, highlight areas expected to be most vulnerable to losses in biodiversity and ecosystem function due to the individual or combined effects of climate and land use ...
BGRF announces OncoFinder algorithm for reducing errors in transcriptome analysis
2014-08-18
Scientists from the Biogerontology Research Foundation (BGRF), a UK-based charity founded to support ageing research and address the challenges of a rapidly ageing population, propose a new concept for signalome-wide analysis of changes in intracellular pathways, called OncoFinder, which allows for accurate and robust cross-platform analysis of gene expression data. This new technique will allow scientists to derive useful information from and compare the hundreds of thousands of data sets obtained using legacy equipment as well as data sets obtained from biological samples ...
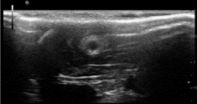
Ultrasound imaging of chitosan nerve conduits that bridge sciatic nerve defects in rats
2014-08-18
New simple and effective methods are needed to better evaluate the outcomes of repair using nerve conduits in vivo. Ultrasound is a common noninvasive clinical detection modality that has been used in many fields. However, ultrasound has only rarely been used to observe implanted nerve conduits in vivo. Hongkui Wang and co-workers from Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University report the first use of ultrasound to noninvasively observe the changes in chitosan nerve conduits implanted in rats over time. The ultrasound imaging clearly showed whether there are unsatisfactory ...
An inside-out vein graft filled with PRP for repair of a short sciatic nerve defect
2014-08-18
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) containing various growth factors can promote nerve regeneration. An inside-out vein graft can substitute nerve autograft to repair short nerve defects. It is hypothesized that an inside-out vein graft filled with platelet-rich plasma shows better effects in the repair of short sciatic nerve defects. In a study reported on the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 14, 2014), an inside-out vein autograft filled with platelet-rich plasma was used to bridge a 10 mm-long sciatic nerve defect in rats. At 6 and 8 weeks, the sciatic nerve function ...
Club cells are 'bad guys' during flu infection
2014-08-18
A specialized subset of lung cells can shake flu infection, yet they remain stamped with an inflammatory gene signature that wreaks havoc in the lung, according to a study published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Seasonal flu is caused by influenza virus, which can infect a variety of cell types in the lung. Infected cells are typically destroyed by the virus itself or by immune cells that attack infected cells. The resulting inflammation can linger on long after the virus has been eliminated leading to persistent symptoms and, in some cases, severe tissue damage.
Club ...
Myc inhibition is an effective therapeutic strategy against most aggressive brain tumors
2014-08-18
Barcelona, 18 August 2014. Research led by the Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO) evidence the most conclusive preclinical results to-date validating Myc inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in glioma – a highly agressive tumor type that notoriously outsmarts current anti-cancer therapies. The study led by Laura Soucek, Principal Investigator of VHIO´s Mouse Models of Cancer Therapies Group, published today in Nature Communications, not only represents an important step forward in ultimately providing brain glioma patients with new therapeutic avenues, but also ...
Sun's activity influences natural climate change
2014-08-18
For the first time, a research team has been able to reconstruct the solar activity at the end of the last ice age, around 20,000-10,000 years ago, by analysing trace elements in ice cores in Greenland and cave formations from China. During the last glacial maximum, Sweden was covered in a thick ice sheet that stretched all the way down to northern Germany and sea levels were more than 100 metres lower than they are today, because the water was frozen in the extensive ice caps. The new study shows that the sun's variation influences the climate in a similar way regardless ...
Antibiotics in early life may alter immunity long-term
2014-08-18
New University of British Columbia research found that receiving antibiotic treatments early in life can increase susceptibility to specific diseases later on.
Most bacteria living in the gut play a positive role in promoting a healthy immune system, but antibiotic treatments often do not discriminate between good and bad bacteria. The study published today in Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology helps scientists understand how different antibiotics affect good bacteria.
"This is the first step to understanding which bacteria are absolutely necessary to develop ...