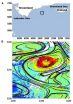
(Press-News.org) An international research team including DESY scientists has observed tiny quantum vortices in cold droplets of liquid helium. The team reports in the journal Science that the exotic vortices arrange themselves as densely packed lattices inside the nanodroplets. It is the first time that the quantum vortices, which have already been observed in larger samples of what is known as superfluid helium, have been detected in nanodroplets. "The experiment has exceeded our best expectations," says Andrey Vilesov of the University of Southern California, one of the experiment's three leads.
The noble gas helium becomes liquid at minus 269 degrees Celsius. Below minus 271 degrees a quantum effect occurs, through which the liquid helium loses all internal friction and becomes superfluid. In this exotic state it can even crawl up walls. To explore the dynamics of superfluid helium, the scientists X-rayed tiny helium nanodroplets with what is currently the world's strongest X-ray laser, the Linac Coherent Light Source LCLS at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in California.
The production of the cold droplets with an average of only 0.2 to 2 thousandths of a millimetre was no easy task. The scientists sprayed the liquid helium through a fine nozzle into a vacuum chamber. A portion of the helium evaporated on the way, and the remaining portion of the drop continued cooling due to evaporative cooling. "After a distance of few millimeters, the drops reached the superfluid state and were struck by the intense X-ray laser flash further downstream," explains DESY scientist Daniel Rolles of the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science CFEL, a joint facility run by DESY, the University of Hamburg and the Max-Planck Society.
An especially detailed recording of the X-ray scattering patterns of the nanodroplets was made possible using the CAMP experimental vacuum chamber, developed by a Max Planck Group in Hamburg at CFEL. "CAMP has two large detectors that can even register individual photons and can determine their energy very precisely," stresses Benjamin Erk of CFEL. "The detectors create a series of 120 images per second while doing so."
"The analyses of the images shows that a surprising number of drops were not spherical as expected, but were pulled length-wise by rapid rotation," says Rolles. "In fact, some drops possessed more of a shape resembling a thick wheel with two almost parallel sides." The rotation stems from the expansion of the liquid helium inside the nozzle, through which they enter the experimental chamber. The droplets rotated up to fourteen million times per second – far faster than a normal round drop could withstand according to the laws of classical physics.
Due to the rapid rotation, tiny "quantum vortices" formed within the nanodroplets, reminiscent of a miniature whirlpool swirling around a bathtub drain. This phenomenon had already been observed in larger units of superfluid helium, but has just now been detected in nanodroplets for the first time. As observed earlier, the vortices form a regular lattice. "In nanodroplets, the quantum vortices are surprisingly 100,000 times more densely packed than in the larger samples of superfluid helium that were previously studied," says Vilesov.
"What we have observed in this experiment is really surprising," stresses co-lead Christopher Bostedt of SLAC. The experiment's third co-lead, Oliver Gessner from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, adds: "Now that we have shown that we can detect and characterize quantum rotation in helium nanodroplets, it will be important to understand its origin and, ultimately, to try and control it."
INFORMATION:
Scientists observe quantum vortices in cold helium droplets
Nanodroplets rotate faster than expected
2014-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hot-spring bacteria reveal ability to use far-red light for photosynthesis
2014-08-21
Bacteria growing in near darkness use a previously unknown process for harvesting energy and producing oxygen from sunlight, a research team led by a Penn State University scientist has discovered. The discovery lays the foundation for further research aimed at improving plant growth, harvesting energy from the Sun, and understanding dense blooms like those now occurring on Lake Erie and other lakes worldwide. A paper describing the discovery will be published in the Science Express edition of the journal Science on 21 August 2014.
"We have shown that some cyanobacteria, ...
New DNA test for diagnosing diseases linked to childhood blindness
2014-08-21
SAN FRANCISCO – Aug. 21, 2014 – Researchers in the United Kingdom have demonstrated that advanced DNA testing for congenital cataracts can quickly and accurately diagnose a number of rare diseases marked by childhood blindness, according to a study published online today in Ophthalmology, the journal of the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Using a single test, doctors were able to tailor care specifically to a child's condition based on their mutations reducing the time and money spent on diagnosis and enabling earlier treatment and genetic counseling.
Each year, ...
USC Eye Institute study shows Native American ancestry a risk factor for eye disease
2014-08-21
LOS ANGELES — New research led by the University of Southern California (USC) Eye Institute, part of Keck Medicine of USC, shows for the first time that Native American ancestry is a significant risk factor for vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy among Latinos with Type 2 diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in working-age adults in the United States, affecting more than 4 million Americans age 40 and older.
The research was published online today in Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, the peer-reviewed academic journal of The ...
Novel recycling methods: The fluorescent fingerprint of plastics
2014-08-21
Researchers at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have developed a new process which will greatly simplify the process of sorting plastics in recycling plants. The method enables automated identification of polymers, facilitating rapid separation of plastics for re-use.
A team of researchers led by Professor Heinz Langhals of LMU's Department of Chemistry has taken a significant step which promises to markedly expedite the recycling of plastic waste. They have developed a technique which provides for automated recognition of their polymer constituents, thus ...
CHEST releases new expert guidance in care of the critically ill and injured
2014-08-21
The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) announces the immediate release of Care of the Critically Ill and Injured During Pandemics and Disasters: CHEST Consensus Statement today in the Online First section of the journal CHEST while the global health-care community cares for patients with the Ebola virus. The consensus statement aims to guide ethical decision-making, coordination of care, resource conservation, and research in crises. The statement was developed by over 100 clinicians and experts representing a broad variety and scope of clinical fields from more ...
Laser device may end pin pricks, improve quality of life for diabetics
2014-08-21
Princeton University researchers have developed a way to use a laser to measure people's blood sugar, and, with more work to shrink the laser system to a portable size, the technique could allow diabetics to check their condition without pricking themselves to draw blood.
"We are working hard to turn engineering solutions into useful tools for people to use in their daily lives," said Claire Gmachl, the Eugene Higgins Professor of Electrical Engineering and the project's senior researcher. "With this work we hope to improve the lives of many diabetes sufferers who depend ...
Objectification in romantic relationships related to sexual pressure and coercion
2014-08-21
To sexually objectify a woman is to focus on her body in terms of how it can provide sexual pleasure rather than viewing her as a complete human being with thoughts and feelings. While objectification has long been considered a problem in the media, how does it affect individual romantic relationships? New research published in Psychology of Women Quarterly, a SAGE journal, finds that more objectification of a female partner's body is related to higher incidents of sexual pressure and coercion.
Researchers Laura R. Ramsey and Tiffany Hoyt surveyed 119 males and 162 females ...
Primary care physicians can be critical resource for abused women in rural areas
2014-08-21
Many primary care physicians in rural communities do not routinely screen women for intimate partner violence (IPV), according to Penn State medical and public health researchers. Rural women who are exposed to such violence have limited resources if they seek help.
"Rural health care providers are uniquely positioned to help women," said Jennifer S. McCall-Hosenfeld, a primary care physician and assistant professor of medicine and public health sciences, Penn State College of Medicine. "However, in rural settings, it might be even more important for physicians to step ...
Viruses take down massive algal blooms, with big implications for climate
2014-08-21
Algae might seem easy to ignore, but they are the ultimate source of all organic matter that marine animals depend upon. Humans are increasingly dependent on algae, too, to suck up climate-warming carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and sink it to the bottom of the ocean. Now, by using a combination of satellite imagery and laboratory experiments, researchers have evidence showing that viruses infecting those algae are driving the life-and-death dynamics of the algae's blooms, even when all else stays essentially the same, and this has important implications for our climate.
According ...
Biologists reprogram skin cells to mimic rare disease
2014-08-21
Johns Hopkins stem cell biologists have found a way to reprogram a patient's skin cells into cells that mimic and display many biological features of a rare genetic disorder called familial dysautonomia. The process requires growing the skin cells in a bath of proteins and chemical additives while turning on a gene to produce neural crest cells, which give rise to several adult cell types. The researchers say their work substantially expedites the creation of neural crest cells from any patient with a neural crest-related disorder, a tool that lets physicians and scientists ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Scientists observe quantum vortices in cold helium dropletsNanodroplets rotate faster than expected