(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
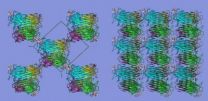
Thanks to certain helper substances, in PCFs proteins are fixated in a way so as to align themselves symmetrically, forming highly stable crystals. Next, the HZB and Fudan University researchers are planning on looking into how PCFs may be used as functional materials. Their findings are being published today in the scientific journal Nature Communications (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5634).
Proteins are sensitive molecules. Everyone knows that – at least from having boiled eggs. Under certain circumstances – like immersion in boiling water – they denature, losing their natural shape, and becoming hard. True, researchers have been able to handle these substances for some time now, even to the point of crystallizing them in their native state. Admittedly, though, this does require considerable effort, but it is the only way how researchers can find out the structure of these substances at high resolution. Moreover, protein crystals are extremely fragile, highly sensitive and hard to handle.
Now, for the first time ever, scientists at China's Fudan University have managed to work around these downsides by linking the protein concanavalin A to helper molecules belonging to the sugar family, and to the dye rhodamin. The concanavalin molecules that have been thus fixated tended to arrange themselves symmetrically within the helper molecule framework, forming crystals, in which the proteins achieve high stability and are intricately interconnected – into a protein crystalline framework.
Developing molecular structures like these is pointless unless you know exactly how they form and what their structure looks like at the level of the atoms. During the quest for suitable experimental methods, the Shanghai researchers turned to a Chinese scientist working at the HZB for help. She called her colleagues' attention to the MX beamlines at the HZB's electron storage ring BESSY II.
"Here at the HZB, we were able to offer them our highly specialized crystallography stations – the perfect venue for characterizing PCFs at high resolutions," says Dr. Manfred Weiss, one of the leading scientists working at the HZB-MX laboratory. It quickly became clear that the helper molecules even allowed the researchers to decide how powerfully they wanted them to penetrate the protein frameworks. "This gives the PCFs a great deal of flexibility and variability, which we'll always keep in mind when doing research on potential applications," says Manfred Weiss.
INFORMATION:
Original publication:
Sakai, F. et al. Protein crystalline frameworks with controllable interpenetration directed by dual supramolecular interactions. Nat. Commun. 5:4634 doi: 10.1038/ncomms5634 (2014).
Proteins: New class of materials discovered
German-Chinese research team gleans seminal insights into protein crystalline frameworks at HZB's BESSY II
2014-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research underway to create pomegranate drug to stem Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
2014-08-22
THE onset of Alzheimer's disease can be slowed and some of its symptoms curbed by a natural compound that is found in pomegranate. Also, the painful inflammation that accompanies illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis and Parkinson's disease could be reduced, according to the findings of a two-year project headed by University of Huddersfield scientist Dr Olumayokun Olajide, who specialises in the anti-inflammatory properties of natural products.
Now, a new phase of research can explore the development of drugs that will stem the development of dementias such as Alzheimer's, ...
Scientists uncover why major cow milk allergen is actually allergenic
2014-08-22
Milk allergy is frequently confused with lactose intolerance. However, these are two entirely different mechanisms that occur in the body. People with lactose intolerance do not digest lactose properly because they lack an enzyme known as lactase. In the case of the potentially much more dangerous cow milk allergy, however, the body's immune system attacks milk proteins with its own IgE antibodies.
According to statistics, about two to three percent of children in Europe suffer from a genuine milk allergy. Less adults are diagnosed with the disease. The formation of so-called ...
Study identifies challenges faced by NYU nurses after Hurricane Sandy
2014-08-22
Many recall the dramatic images of nurses at New York University's Langone Medical Center (NYULMC) heroically evacuating over three hundred patients, carrying many including the youngest and most vulnerable down flights of stairs during the power outage resulting from the storm surge generated by Hurricane Sandy.
Now, a recent study by researchers at the New York University Colleges of Nursing (NYUCN) and of Dentistry (NYUCD), published in The Journal of Urban Health examines the impact on NYULMC nurses' post-Sandy deployment to help address patient surge in eight local ...
Scientists map risk of premature menopause after cancer treatment
2014-08-22
Women treated for the cancer Hodgkin lymphoma will be able to better understand their risks of future infertility after researchers estimated their risk of premature menopause with different treatments.
The findings, set out in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, are based on the experience of more than 2,000 young women in England and Wales treated for the cancer over a period of more than 40 years.
Previous research has suggested that women with Hodgkin lymphoma who receive certain types of chemotherapy or radiotherapy are at increased risk of going through ...
More common procedures for painful facial tics carry high costs, reports study in Neurosurgery
2014-08-22
August 22, 2014 – For patients who need surgery for facial pain caused by trigeminal neuralgia, the most cost-effective procedure is the least often used, reports a study in the September issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Percutaneous stereotaxic rhizotomy (PSR) provides good pain relief at much lower cost than other types of surgical treatments for trigeminal neuralgia, according to the report by Dr. Siviero Agazzi and colleagues ...
Hormone analysis helps identify horny rhinos
2014-08-22
The first comprehensive study of captive black rhino reproduction in Europe highlights how hormone analysis could improve the success of breeding programmes.
Researchers from Chester Zoo, The University of Manchester and the University of Liverpool carried out a six-year study which encompassed 90% of European population of black rhino.
Dr Katie Edwards led the research as part of her PhD at the University of Liverpool. She says: "Although some black rhinoceros breed well in captivity, not all do therefore reducing the vital genetic reserve that these populations represent. ...
Poll finds many in US lack knowledge about Ebola and its transmission
2014-08-22
Boston, MA – Although the Centers for Disease and Prevention (CDC) reports no known cases of Ebola transmission in the United States, a Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH)/SSRS poll released today (August 21, 2014) shows that four in ten (39%) adults in the U.S. are concerned that there will be a large outbreak in the U.S., and a quarter (26%) are concerned that they or someone in their immediate family may get sick with Ebola over the next year.
The nationally representative poll of 1,025 adults was conducted August 13-17, 2014 by researchers at HSPH and SSRS, an ...
In our digital world, are young people losing the ability to read emotions?
2014-08-22
Children's social skills may be declining as they have less time for face-to-face interaction due to their increased use of digital media, according to a UCLA psychology study.
UCLA scientists found that sixth-graders who went five days without even glancing at a smartphone, television or other digital screen did substantially better at reading human emotions than sixth-graders from the same school who continued to spend hours each day looking at their electronic devices.
"Many people are looking at the benefits of digital media in education, and not many are looking ...
Green tea polyphenols protect spinal cord neurons against oxidative stress
2014-08-22
Green tea polyphenols are strong antioxidants and can reduce free radical damage. Can they protect spinal cord neurons against oxidative stress? Jianbo Zhao and co-workers from the First Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, China discovered that green tea polyphenol effectively alleviated oxidative stress and inhibit neuronal apoptosis, indicating green tea polyphenols play a protective role in spinal cord neurons under oxidative stress. The relevant study has been published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 14, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: ...
Recombinant adenovirus-mediated DHCR24 inhibits neural apoptosis
2014-08-22
3β-Hydroxysteroid-Δ24 reductase (DHCR24) is a multifunctional enzyme that localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and has neuroprotective and cholesterol-synthesizing activities. DHCR24 overexpression confers neuroprotection against apoptosis caused by amyloid β deposition. Dr. Xiuli Lu and colleagues from Liaoning University in China constructed two recombinant adenoviruses (Ad-rSYN1-DHCR24-myc and Ad-hSYN1-DHCR24-myc) that drive DHCR24 expression specifically in neuronal cells. They also found that adenovirus transfection inhibits apoptosis through scavenging ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
[Press-News.org] Proteins: New class of materials discoveredGerman-Chinese research team gleans seminal insights into protein crystalline frameworks at HZB's BESSY II