Novel oncogenic RET mutation found in small cell lung cancer
2014-08-22
(Press-News.org) DENVER – For the first time an oncogenic somatic mutation at amino acid 918 in the RET (rearranged during transfection) protein has been identified in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) tumors and enforced expression of this mutation within SCLC cell lines produced increased intracellular signaling and cell growth.
SCLC is a highly malignant form of lung cancer representing 15% of all lung cancers and is strongly associated with tobacco smoking. NSCLC, representing 85% of lung cancer, has been extensively examined for genomic alterations and targeted therapies are approved for patients with certain mutations, however SCLC has not been examined with the same rigor and there are no approved targeted therapies for SCLC.
Investigators at Case Western University examined 6 SCLC tumors, 3 each from primary and metastatic tumors, for 238 somatic mutations across 19 oncogenes. RET wild type and mutant protein was then overexpressed in SCLC cell lines and these cell lines were examined for cell signaling, cell growth and responsiveness to two tyrosine kinase inhibitors of RET.
Results reported in the September issue of the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC), revealed the RET M918T mutation in a metastatic SCLC tumor and that overexpression of this mutant protein in SCLC cell lines resulted in increased ERK signaling, MYC expression and increased cell proliferation. Likewise, these cell lines overexpressing the RET protein became sensitive to ponatinib and vandetanib, tyrosine kinase inhibitors of RET. Decreased cell growth was the result of this inhibition of RET.
The authors say that their work "suggests that RET mutations play a potential role in some cases of SCLC as no other activating mutations were identified among the 19 oncogenes assayed in the tumor harboring the RET M918T mutation, potentially making M918T the driver mutation in this tumor". However, the authors caution that "the role of oncogenic RET mutations cannot be judged fairly until a larger number of tumors are genomically analyzed, including metastatic tumors".
INFORMATION:
Co-author Dr. Shahab Babakoohi is a member of IASLC.
About the IASLC
The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) is the only global organization dedicated to the study of lung cancer. Founded in 1974, the association's membership includes more than 4,000 lung cancer specialists in 80 countries. To learn more about IASLC please visit http://www.iaslc.org
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High concordance between EGFR mutations from circulating-free tumor DNA and tumor tissue in non-small cell lung cancer
2014-08-22
DENVER – Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations found in the circulating free tumor DNA (ctDNA) from the plasma of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients correlates well with the EGFR mutations from patient-matched tumor tissue DNA.
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy is approved for EGFR activating mutation positive patients with advanced NSCLC, but the standard for determining mutation status is with DNA derived directly from tumor tissue, which can be limited or not available. A more abundant and less invasive source of tumor DNA may ...
Study shows cognitive-behavioral coping skills training has positive effects on rheumatoid arthritis
2014-08-22
DETROIT – Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a complex autoimmune disease that affects 1 to 2 percent of adults, requires patients to not only cope with pain, disability and joint disfigurements, but also other stressors such as disrupted work, family life and marital functioning. While many pharmacological advances help some RA patients, residual pain and disability is common. In addition, some patients avoid newer medications due to their high cost or side effects. Because of this, there is interest in psychosocial interventions for RA such as cognitive-behavioral and emotional ...
Study shows Hera Therapeutics compound combats HPV types that cause most cervical cancer
2014-08-22
La Jolla, CA – Research presented at the 29th Annual International Papillomavirus Conference shows that a therapy being developed by Hera Therapeutics Inc. combats three types of human papillomavirus, including the two that cause 70 percent of all cervical cancer.
When tested in several cultured human cell models, HTI-1968 blocked the replication of HPV-16, HPV-18 and HPV-11 cells, according to Louise T. Chow, Ph.D. and Thomas Broker, Ph.D., who presented the findings at the Seattle conference. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in the National ...
Penn study: Electronic alerts significantly reduce catheter-associated urinary tract infections
2014-08-22
(PHILADELPHIA) - A Penn Medicine team has found that targeted automated alerts in electronic health records significantly reduce urinary tract infections in hospital patients with urinary catheters. In addition, when the design of the alert was simplified, the rate of improvement dramatically increased.
The alerts help physicians decide whether their patients need urinary catheters in the first place and then alert them to reassess the need for catheters that have not been removed within a recommended time period. The electronic alert, developed by medical researchers ...
From happiness to pain: Understanding serotonin's function
2014-08-22
In a study published today (August 22nd), in the scientific journal PLoS One, researchers at the Champalimaud Neuroscience Programme establish the effect of serotonin on sensitivity to pain using a combination of advanced genetic and optical techniques.
"Serotonin is a small molecule known to be implicated in a wide range of brain functions, from the control of sleep and appetite, to the regulation of complex emotional behaviours, This neurotransmitter is also popularly thought to contribute to feelings of well being and happiness, as some anti-depression medications work ...
Kessler Foundation study of self-awareness in MS has implications for rehabilitation
2014-08-22
West Orange, NJ. August 22, 2014. A new study of self-awareness by Kessler Foundation researchers shows that persons with multiple sclerosis (MS) may be able to improve their self-awareness through task-oriented cognitive rehabilitation. The study was epublished ahead of print on July 2 in NeuroRehabilitation. (Yael Goverover, Helen Genova, Hali Griswold, Nancy D. Chiaravalloti & John DeLuca: Metacognitive knowledge and online awareness in persons with multiple sclerosis doi: 10.3233/NRE-141113). Self-awareness is one's ability to recognize cognitive problems caused by ...
Good news for diabetics who are sick of the finger prick
2014-08-22
WASHINGTON, August 21, 2014 — Diabetes affects nearly 10 percent of the U.S. population. Among the biggest complaints of diabetics: constant finger pricking to test blood glucose levels. Fortunately, research published in ACS Chemical Biology reports the development of a protein that could lead to less pain and more accurate results for diabetes patients. In the American Chemical Society's (ACS') newest Breakthrough Science video, Sylvia Daunert, Ph.D., shows off her "designer protein" that could eventually allow diabetics to check their blood sugar from their iPhones. ...
Tissue regeneration using anti-inflammatory nanomolecules
2014-08-22
Anyone who has suffered an injury can probably remember the after-effects, including pain, swelling or redness. These are signs that the body is fighting back against the injury. When tissue in the body is damaged, biological programs are activated to aid in tissue regeneration. An inflammatory response acts as a protective mechanism to enable repair and regeneration, helping the body to heal after injuries such as wounds and burns. However, the same mechanism may interfere with healing in situations in which foreign material is introduced, for example when synthetics are ...
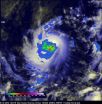
NASA sees Tropical Storm Karina get a boost
2014-08-22
NASA's TRMM satellite saw Tropical Storm Karina get a boost on August 22 in the form of some moderate rainfall and towering thunderstorms in the center of the storm.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed directly above the center of Tropical Storm Karina on August 22, 2014 at 0151 UTC (Aug. 21 at 9:51 p.m. EDT). A rainfall analysis that used data from TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) showed that storms near Karina's center were dropping rain at a rate near 25 mm/1 inch per hour. Where the heaviest rainfall was occurring, TRMM spotted a couple ...
New enzyme targets for selective cancer therapies
2014-08-22
(Edmonton) Thanks to important discoveries in basic and clinical research and technological advances, the fight against cancer has mobilized into a complex offensive spanning multiple fronts.
Work happening in a University of Alberta chemistry lab could help find new and more selective therapies for cancer. Researchers have developed a compound that targets a specific enzyme overexpressed in certain cancers—and they have tested its activity in cells from brain tumours.
Chemistry professor Christopher Cairo and his team synthesized a first-of-its-kind inhibitor that ...