(Press-News.org) Laboratory-grown replacement organs have moved a step closer with the completion of a new study.
Scientists have grown a fully functional organ from transplanted laboratory-created cells in a living animal for the first time.
The researchers have created a thymus - an organ next to the heart that produces immune cells known as T cells that are vital for guarding against disease.
They hope that, with further research, the discovery could lead to new treatments for people with a weakened immune system.
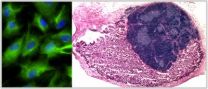
The team from the MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Edinburgh took cells called fibroblasts from a mouse embryo. They turned the fibroblasts into a completely different type of cell called thymus cells, using a technique called reprogramming.
The reprogrammed cells changed shape to look like thymus cells and were also capable of supporting development of T cells in the lab – a specialised function that only thymus cells can perform.
When the researchers mixed reprogrammed cells with other key thymus cell types and transplanted them into a mouse, the cells formed a replacement organ. The new organ had the same structure, complexity and function as a healthy adult thymus.
It is the first time that scientists have made an entire living organ from cells that were created outside of the body by reprogramming.
Doctors have already shown that patients with thymus disorders can be treated with infusions of extra immune cells or transplantation of a thymus organ soon after birth. The problem is that both are limited by a lack of donors and problems matching tissue to the recipient.
With further refinement, the researchers hope that their lab-grown cells could form the basis of a thymus transplant treatment for people with a weakened immune system.
The technique may also offer a way of making patient-matched T cells in the laboratory that could be used in cell therapies.
Such treatments could benefit bone marrow transplant patients, by helping speed up the rate at which they rebuild their immune system after transplant.
The discovery offers hope to babies born with genetic conditions that prevent the thymus from developing properly. Older people could also be helped as the thymus is the first organ to deteriorate with age.
The study is published today in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Professor Clare Blackburn from the MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Edinburgh, who led the research, said: "Our research represents an important step towards the goal of generating a clinically useful artificial thymus in the lab."
Dr Rob Buckle, Head of Regenerative Medicine at the MRC, said: "This is an exciting study but much more work will be needed before this process can be reproduced in a safe and tightly controlled way suitable for use in humans."
INFORMATION:
Scientists first to grow organ in animal from cells created in lab
2014-08-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
American Heart Association issues e-cigarette recommendations
2014-08-25
The American Heart Association issued new policy recommendations (link live at embargo) today on the use of e-cigarettes and their impact on tobacco-control efforts. The guidance was published in the association's journal, Circulation.
Based on the current evidence, the association's position is that e-cigarettes that contain nicotine are tobacco products and should be subject to all laws that apply to these products. The association also calls for strong new regulations to prevent access, sales and marketing of e-cigarettes to youth, and for more research into the product's ...
Medicaid reimbursements may affect cancer screening rates among beneficiaries
2014-08-25
A recent study has found that in states with higher Medicaid payments for office visits, Medicaid beneficiaries were more likely to be screened for breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the findings may help policy makers address barriers to access to care and improve the use of recommended cancer screening services.
Although Medicaid is a joint state-federal government health insurance program, each state sets the policies for its own Medicaid program within requirements set ...
New term will banish stigma, educate providers on postmenopausal problems
2014-08-25
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Tuesday, August 19, 2014)—Talking about genital, sexual, and urinary problems can be uncomfortable for postmenopausal women and their doctors. Having a term that doesn't carry stigma, isn't embarrassing to say, and is medically accurate could go a long way in helping women get the help they need and allowing them to make smarter healthcare decisions. That term is "genitourinary syndrome of menopause" or GSM, developed and endorsed by The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and the International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health (ISSWSH). ...
'Robo Brain' will teach robots everything from the Internet
2014-08-25
ITHACA, N.Y. – Robo Brain – a large-scale computational system that learns from publicly available Internet resources – is currently downloading and processing about 1 billion images, 120,000 YouTube videos, and 100 million how-to documents and appliance manuals. The information is being translated and stored in a robot-friendly format that robots will be able to draw on when they need it.
To serve as helpers in our homes, offices and factories, robots will need to understand how the world works and how the humans around them behave. Robotics researchers have been teaching ...
Train your heart to protect your mind
2014-08-25
Exercising to improve our cardiovascular strength may protect us from cognitive impairment as we age, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Montreal and its affiliated Institut universitaire de gératrie de Montréal Research Centre. "Our body's arteries stiffen with age, and the vessel hardening is believed to begin in the aorta, the main vessel coming out of the heart, before reaching the brain. Indeed, the hardening may contribute to cognitive changes that occur during a similar time frame," explained Claudine Gauthier, first author of the study. ...
Study suggests repurposing anti-depressant medication to target medulloblastoma
2014-08-24
CINCINNATI – An international research team reports in Nature Medicine a novel molecular pathway that causes an aggressive form of medulloblastoma, and suggests repurposing an anti-depressant medication to target the new pathway may help combat one of the most common brain cancers in children.
The multi-institutional group, led by scientists at Cancer and Blood Diseases Institute (CBDI) at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, publish their results in the journal's online edition on Aug. 24. The researchers suggest their laboratory findings in mouse models of ...
Evolutionary history of honeybees revealed by genomics
2014-08-24
In a study published in Nature Genetics, researchers from Uppsala University present the first global analysis of genome variation in honeybees. The findings show a surprisingly high level of genetic diversity in honeybees, and indicate that the species most probably originates from Asia, and not from Africa as previously thought.
The honeybee (Apis mellifera) is of crucial importance for humanity. One third of our food is dependent on the pollination of fruits, nuts and vegetables by bees and other insects. Extensive losses of honeybee colonies in recent years are a ...
Signatures of selection inscribed on poplar genomes
2014-08-24
One aspect of the climate change models researchers have been developing looks at how plant ranges might shift, and how factors such as temperature, water availability, and light levels might come into play. Forests creeping steadily north and becoming established in the thawing Arctic is just one of the predicted effects of rising global temperatures.
A recent study published online August 24, 2014 in Nature Genetics offers a more in-depth, population-based approach to identifying such mechanisms for adaptation, and describes a method that could be harnessed for developing ...
Mimicking natural evolution with 'promiscuous reactions' to improve the diversity of drugs
2014-08-24
A revolutionary new scientific method developed at the University of Leeds will improve the diversity of 'biologically active molecules', such as antibiotics and anti-cancer agents.
The researchers, who report their findings online today in the journal Nature Chemistry, took their inspiration from evolution in nature. The research may uncover new pharmaceutical drugs that traditional methods would never have found.
"Nature produces some amazing structures with really interesting biological activity, but the plant or animal did not design them. Instead the organisms ...
Study: Cutting emissions pays for itself
2014-08-24
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Lower rates of asthma and other health problems are frequently cited as benefits of policies aimed at cutting carbon emissions from sources like power plants and vehicles, because these policies also lead to reductions in other harmful types of air pollution.
But just how large are the health benefits of cleaner air in comparison to the costs of reducing carbon emissions? MIT researchers looked at three policies achieving the same reductions in the U.S., and found that the savings on health care spending and other costs related to illness can be big ...