(Press-News.org) By combining plasmonics and optical microresonators, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have created a new optical amplifier (or laser) design, paving the way for power-on-a-chip applications.
"We have made optical systems at the microscopic scale that amplify light and produce ultra-narrowband spectral output," explained J. Gary Eden, a professor of electrical and computer engineering (ECE) at Illinois. "These new optical amplifiers are well-suited for routing optical power on a chip containing both electronic and optical components.
"Their potential applications in medicine are exciting because the amplifiers are actuated ('pumped') by light that is able to pass through human skin. For this reason, these microsphere-based amplifiers are able to transmit signals from cells and buried biomedical sensors to electrical and optical networks outside the body."
The speed of currently available semiconductor electronics is limited to about 10 GHz due to heat generation and interconnects delay time issues. Though, not limited by speed, dielectric-based photonics are limited in size by the fundamental laws of diffraction. The researchers, led by Eden and ECE associate professor Logan Liu, found that plasmonics—metal nanostructures—can serve as a bridge between photonics and nanoelectronics, to combine the size of nanoelectronics and the speed of dielectric photonics.
"We have demonstrated a novel optoplasmonic system comprising plasmonic nanoantennas and optical microcavities capable of active nanoscale field modulation, frequency switching, and amplification of signals," states Manas Ranjan Gartia, lead author of the article, "Injection- Seeded Optoplasmonic Amplifier in the Visible," published in the journal Scientific Reports. "This is an important step forward for monolithically building on-chip light sources inside future chips that can use much less energy while providing superior speed performance of the chips."
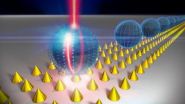
At the heart of the amplifier is a microsphere (made of polystyrene or glass) that is approximately 10 microns in diameter. When activated by an intense beam of light, the sphere generates internally a narrowband optical signal that is produced by a process known as Raman scattering. Molecules tethered to the surface of the sphere by a protein amplify the Raman signal, and in concert with a nano-structured surface in contact to the sphere, the amplifier produces visible (red or green) light having a bandwidth that matches the internally-generated signal.
The proposed design is well-suited for routing narrowband optical power on-a-chip. Over the past five decades, optical oscillators and amplifiers have typically been based on the buildup of the field from the spontaneous emission background. Doing so limits the temporal coherence of the output, lengthens the time required for the optical field to grow from the noise, and often is responsible for complex, multiline spectra.
"In our design, we use Raman assisted injection-seeded locking to overcome the above problems. In addition to the spectral control afforded by injection-locking, the effective Q of the amplifier can be specified by the bandwidth of the injected Raman signal," Gartia said. This characteristic contrasts with previous WGM-based lasers and amplifiers for which the Q is determined solely by the WGM resonator.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Eden, Liu, and Gartia, co-authors of the paper include Sujin Seo, Junhwan Kim, Te-Wei Chang, Assistant Professor Gaurav Bahl from Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois, and Prof. Meng Lu, ECE alumnus and currently assistant professor at Iowa State University. The research was done at Micro and Nano Technology Laboratory at Illinois.
Symphony of nanoplasmonic and optical resonators produces laser-like light emission
New optical amplifier design paves the way for power-on-a-chip applications
2014-08-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Change in tube feeding practice improves nutrition for ICU patients, audit finds
2014-08-26
While the importance of enteral nutrition (EN), or feeding patients through a tube, in an intensive care unit is well understood, underfeeding is still common. A practice of a certain amount of feeding per hour can be interrupted by tests, procedures, or emergencies. Changing to a volume-based system, which calls for a certain nutrition volume per day, could reduce underfeeding.
Such a system was found to be effective in ICU patients according to a quality improvement audit published in the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition's (A.S.P.E.N.) Nutrition ...
Study finds less domestic violence among married couples who smoke pot
2014-08-26
BUFFALO, N.Y. – New research findings from a study of 634 couples found that the more often they smoked marijuana, the less likely they were to engage in domestic violence.
The study, conducted by researchers in the University at Buffalo School of Public Health and Health Professions and Research Institute on Addictions (RIA), appeared in the online edition of Psychology of Addictive Behaviors in August.
The study attempted to clarify inconsistent findings about domestic violence among pot-smoking couples that primarily has been based on cross-sectional data (i.e., ...
Study finds young driver's gender linked to crash type, injury severity
2014-08-26
MANHATTAN, Kansas — Gender is often related to what type of severe or fatal crash a young male or young female driver will be involved in, according to a Kansas State University study.
The university's Sunanda Dissanayake, professor of civil engineering, and Niranga Amarasingha, doctoral student in civil engineering, looked at the gender differences and similarities of young drivers involved in all motor vehicle crashes in Kansas across five years. Their findings may help reduce the number and severity of these crashes by improving educational material used in young driver ...
New statin guidelines an improvement, Yale study shows
2014-08-26
New Haven, Conn. – New national guidelines can improve the way statin drugs are prescribed to patients at risk for cardiovascular disease, a Yale University study has found.
The research, published Aug. 25 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, also showed the new guidelines produce only a modest increase in the number of patients being given the drugs.
Statins are a class of drugs that help lower cholesterol by blocking the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which the body needs in order to produce cholesterol. Common statin medications include Lipitor, Levacor, ...
Some health care workers lack gear to protect from HIV, other bloodborne infections
2014-08-26
Health care workers in some of the world's poorest countries lack basic equipment to shield them from HIV and other bloodborne infections during surgical and other procedures, new research from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health suggests. The findings underscore the lack of adequate protective supplies in nations at the center of the current Ebola outbreak.
In Liberia, one of the countries most affected by Ebola, 56 percent of hospitals had protective eyewear for its doctors and nurses, while 63 percent had sterile gloves, the study found. In Sierra Leone, ...
Outsourcing parenthood? It takes a village AND the marketplace to raise a child
2014-08-26
Ask any parent raising kids in today's fast-paced society and chances are they would agree that there are only so many hours in the day. Recognizing a need for help, many businesses now offer traditional caregiving services ranging from planning birthday parties to teaching children how to ride a bike. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, by outsourcing traditional parental duties, modern-day parents feel they are ultimately protecting parenthood.
"Parents are increasingly outsourcing caregiving activities. The expanding array of caregiving services ...
Do we live in a 2-D hologram?
2014-08-26
A unique experiment at the U.S. Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory called the Holometer has started collecting data that will answer some mind-bending questions about our universe – including whether we live in a hologram.
Much like characters on a television show would not know that their seemingly 3 - D world exists only on a 2 - D screen, we could be clueless that our 3 - D space is just an illusion. The information about everything in our universe could actually be encoded in tiny packets in two dimensions.
Get close enough to your TV screen ...
An inconvenient truth: Does responsible consumption benefit corporations more than society?
2014-08-26
Are environmental and social problems such as global warming and poverty the result of inadequate governmental regulations or does the burden fall on our failure as consumers to make better consumption choices? According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, responsible consumption shifts the burden for solving global problems from governments to consumers and ultimately benefits corporations more than society.
"When businesses convince politicians to encourage responsible consumption instead of implementing policy changes to solve environmental and social ...
Getting things done: How does changing the way you think about deadlines help you reach your goals?
2014-08-26
From doing yard work to finishing up the last few classes required for a college degree, consumers struggle to get things done. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, the way consumers think about deadlines can determine whether or not they start tasks and accomplish their goals.
"Our research shows that the way consumers think about the future influences whether they get started on tasks. In particular, if the deadline for a task is categorized as being similar to the present, they are more likely to initiate the task," write authors Yanping Tu ...
Trash burning worldwide significantly worsens air pollution
2014-08-26
BOULDER -- Unregulated trash burning around the globe is pumping far more pollution into the atmosphere than shown by official records. A new study led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research estimates that more than 40 percent of the world's garbage is burned in such fires, emitting gases and particles that can substantially affect human health and climate change.
The new study provides the first rough estimates, on a country-by-country basis, of pollutants such as particulates, carbon monoxide, and mercury that are emitted by the fires. Such pollutants have ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Symphony of nanoplasmonic and optical resonators produces laser-like light emissionNew optical amplifier design paves the way for power-on-a-chip applications