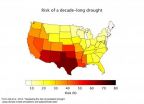
(Press-News.org) Due to global warming, scientists say, the chances of the southwestern United States experiencing a decade long drought is at least 50 percent, and the chances of a "megadrought" – one that lasts over 30 years – ranges from 20 to 50 percent over the next century.
The study by Cornell University, University of Arizona and U.S. Geological Survey researchers will be published in a forthcoming issue of the American Meteorological Society's Journal of Climate.
"For the southwestern U.S., I'm not optimistic about avoiding real megadroughts," said Toby Ault, Cornell assistant professor of earth and atmospheric sciences and lead author of the paper. "As we add greenhouse gases into the atmosphere – and we haven't put the brakes on stopping this – we are weighting the dice for megadrought conditions."
As of mid-August, most of California sits in a D4 "exceptional drought," which is in the most severe category. Oregon, Arizona, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas also loiter between moderate and exceptional drought. Ault says climatologists don't know whether the severe western and southwestern drought will continue, but he said, "With ongoing climate change, this is a glimpse of things to come. It's a preview of our future."
Ault said that the West and Southwest must look for mitigation strategies to cope with looming long-drought scenarios. "This will be worse than anything seen during the last 2,000 years and would pose unprecedented challenges to water resources in the region," he said.
In computer models, while California, Arizona and New Mexico will likely face drought, the researchers show the chances for drought in parts of Washington, Montana and Idaho may decrease.
Beyond the United States, southern Africa, Australia and the Amazon basin are also vulnerable to the possibility of a megadrought. With increases in temperatures, drought severity will likely worsen, "implying that our results should be viewed as conservative," the study reports.
"These results help us take the long view of future drought risk in the Southwest - and the picture is not pretty. We hope this opens up new discussions about how to best use and conserve the precious water that we have," said Julia Cole, UA professor of geosciences and of atmospheric sciences.
INFORMATION:
The study, "Assessing the Risk of Persistent Drought Using Climate Model Simulations and Paleoclimate Data," was also co-authored by Julia E. Cole, David M. Meko and Jonathan T. Overpeck of University of Arizona; and Gregory T. Pederson of the U.S. Geological Survey.
The National Science Foundation, National Center for Atmospheric Research, the U.S. Geological Survey and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration funded the research.
Southwest may face 'megadrought' this century
2014-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientist uncovers red planet's climate history in unique meteorite
2014-08-27
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Was Mars — now a cold, dry place — once a warm, wet planet that sustained life? And if so, how long has it been cold and dry?
Research underway at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory may one day answer those questions — and perhaps even help pave the way for future colonization of the Red Planet. By analyzing the chemical clues locked inside an ancient Martian meteorite known as Black Beauty, Florida State University Professor Munir Humayun and an international research team are revealing the story of Mars' ancient, and sometimes startling, ...
MU researchers develop more accurate Twitter analysis tools
2014-08-27
COLUMBIA, Mo. – "Trending" topics on the social media platform Twitter show the quantity of tweets associated with a specific event. However, trends only show the highest volume keywords and hashtags, and may not give qualitative information about the tweets themselves. Now, using data associated with the Super Bowl and World Series, researchers at the University of Missouri have developed and validated a software program that analyzes event-based tweets and measures the context of tweets rather than just the quantity. The program will help Twitter analysts gain better ...
Marijuana compound may offer treatment for Alzheimer's disease
2014-08-27
Tampa, FL (Aug. 26, 2014) -- Extremely low levels of the compound in marijuana known as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, may slow or halt the progression of Alzheimer's disease, a recent study from neuroscientists at the University of South Florida shows.
Findings from the experiments, using a cellular model of Alzheimer's disease, were reported online in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
Researchers from the USF Health Byrd Alzheimer's Institute showed that extremely low doses of THC reduce the production of amyloid beta, found in a soluble form in most aging ...
More wolf spiders feasting on American toads due to invasive grass, UGA study shows
2014-08-27
Athens, Ga. – An invasive grass species frequently found in forests has created a thriving habitat for wolf spiders, who then feed on American toads, a new University of Georgia study has found.
Japanese stiltgrass, which was accidentally introduced to the U.S. in the early 1900s, is one of the most pervasive invasive species and has spread to more than a dozen states in the past century, particularly in the Southeast. Typically found along roads and in forests, it can survive in widely diverse ecosystems and has been found to impact native plant species, invertebrate ...
Orion rocks! Pebble-size particles may jump-start planet formation
2014-08-27
Rocky planets like Earth start out as microscopic bits of dust tinier than a grain of sand, or so theories predict.
Astronomers using the National Science Foundation's (NSF) Green Bank Telescope (GBT) have discovered that filaments of star-forming gas near the Orion Nebula may be brimming with pebble-size particles -- planetary building blocks 100 to 1,000 times larger than the dust grains typically found around protostars. If confirmed, these dense ribbons of rocky material may well represent a new, mid-size class of interstellar particles that could help jump-start ...
AGU: Yellowstone supereruption would send ash across North America
2014-08-27
WASHINGTON, D.C. – In the unlikely event of a volcanic supereruption at Yellowstone National Park, the northern Rocky Mountains would be blanketed in meters of ash, and millimeters would be deposited as far away as New York City, Los Angeles and Miami, according to a new study.
An improved computer model developed by the study's authors finds that the hypothetical, large eruption would create a distinctive kind of ash cloud known as an umbrella, which expands evenly in all directions, sending ash across North America.
A supereruption is the largest class of volcanic ...
'Junk' blood tests may offer life-saving information
2014-08-27
Tel Aviv — Some 30 percent of all positive hospital blood culture samples are discarded every day because they're "contaminated" — they reflect the presence of skin germs instead of specific disease-causing bacteria.
Rather than toss these compromised samples into the trash, clinicians may be able to use the resistance profiles of skin bacteria identified by these tests to treat patients with antibiotics appropriate to their ailment, Tel Aviv University researchers say. Dr. Gidi Stein and Dr. Danny Alon of TAU's Sackler Faculty of Medicine and the Department of Internal ...
Big data approach identifies Europe's most dangerous human and domestic animal pathogens
2014-08-27
The pathogens posing the greatest risk to Europe based upon a proxy for impact have been identified by University of Liverpool researchers using a 'big data' approach to scientific research.
The researchers from the University's Institute of Infection and Global Health ranked the top 100 pathogens affecting humans and the top 100 affecting domestic animals using a system which, they believe, will help governments across the continent plan for risks associated with the spread of infectious diseases, including as a result of climate change, and for biosecurity.
The top ...
Drug represents first potential treatment for common anemia
2014-08-27
(WASHINGTON, August, 27, 2014) – An experimental drug designed to help regulate the blood's iron supply shows promise as a viable first treatment for anemia of inflammation, according to results from the first human study of the treatment published online today in Blood, the Journal of the American Society of Hematology
Anemia is a condition that occurs when red blood cells are in short supply or do not function properly. When an individual has anemia, the body does not get enough oxygen, since there are fewer red blood cells to carry the iron-rich protein hemoglobin ...
Pacific plate shrinking as it cools
2014-08-27
HOUSTON – (Aug. 27, 2014) – The tectonic plate that dominates the Pacific "Ring of Fire" is not as rigid as many scientists assume, according to researchers at Rice University and the University of Nevada.
Rice geophysicist Richard Gordon and his colleague, Corné Kreemer, an associate professor at the University of Nevada, Reno, have determined that cooling of the lithosphere -- the outermost layer of Earth -- makes some sections of the Pacific plate contract horizontally at faster rates than others and cause the plate to deform.
Gordon said the effect detailed this ...