Plug n' play protein crystals
2014-08-29
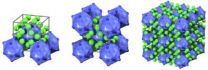
(Press-News.org) Almost a hundred years ago in 1929 Linus Pauling presented the famous Pauling's Rules to describe the principles governing the structure of complex ionic crystals. These rules essentially describe how the arrangement of atoms in a crystal is critically dependent on the size of the atoms, their charge and type of bonding. According to scientists from the Biohybrid Materials Group of Aalto University Finland led by Mauri Kostiainen similar rules can be applied to prepare ionic colloidal crystals consisting of oppositely charged proteins and virus particles. The results can be applied for example in packing and protecting virus particles into crystals that mimic Nature's own occlusion bodies (protein lattices that pack and protect virus particles to maintain their long-term infectivity), preparation of biocompatible metamaterials, biomolecule crystallization and the subsequent structural analysis.
Viruses, which are commonly perceived only as unwanted infectious agents delivering diseases, can be used also to our benefit. Evolution has rendered virus particles with a precisely defined monodisperse structure, which can be utilized for example as template for nanoparticle synthesis and assembly or as a vehicle to deliver drugs or other active ingredients to living organisms. For example in a previous work from the same research group published in Nano Letters they were able to transfect human cells efficiently with DNA origami nanostructures encapsulated inside virus particles.
In the present work (Ville Liljeström et al. Self-Assembly and Modular Functionalization of Three Dimensional Crystals from Oppositely Charged Proteins, Nature Communications, 2014, 5, 4445) Kostiainen and his research team show that cowpea chlorotic mottle virus (CCMV) particles and avidin proteins can form crystals simply by mixing the two components at an optimized electrolyte concentration. The two components are able to self-assemble into ordered structures due to the charge complementarity presented on their surface. Using avidin as a structural component offers several advantages. Most importantly, avidin is able to bind biotin with very high affinity and selectivity. "This enables us to functionalize the crystals in a modular way with almost any biotin tagged ligand. We have demonstrated that it is possible to load the crystals with for example fluorescent dyes, active enzymes and plasmonic gold nanoparticles. Ultimately, using the avidin-biotin interaction allows us to avoid tedious covalent modification of the structures and mimic the process of topotactic intercalation (the insertion of a new component to lattice points of an existing crystal)," Kostiainen says.
The current work deals with only one type of virus particle. "In the future, we will be looking into other virus particles and proteins to 'glue' them together", he adds. " Studying the assembly of for example human viruses or viruses with other structural topology, such as rod-like particles, may open further possibilities for biomedical and materials science related research.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Managing coasts under threat from climate change and sea-level rise
2014-08-29
Coastal regions under threat from climate change and sea-level rise need to tackle the more immediate threats of human-led and other non-climatic changes, according to a team of international scientists.
The team of 27 scientists from five continents, led by Dr Sally Brown at the University of Southampton, reviewed 24 years of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessments (the fifth and latest set being published in 2013 and 2014). They focused on climate change and sea-level rise impacts in the coastal zone, and examined ways of how to better manage and ...
Mobile app on emergency cardiac care aids best decisions in seconds
2014-08-29
Barcelona, Spain –Saturday 30 August 2014: The ACCA Clinical Decision-Making Toolkit mobile app is now available on the App Store and Google Play.
When dealing with acute cardiovascular diseases, a few seconds can make the difference and instant access to the best recommendations can save lives. This led the Acute Cardiovascular Care Association (ACCA) of the ESC to develop a user friendly interactive application, allowing professionals to have immediate access to diagnostics pathways on their mobile devices.
The Toolkit on emergency cardiac care, first published as ...
Breakthrough in light sources for new quantum technology
2014-08-29
Electronic circuits are based on electrons, but one of the most promising technologies for future quantum circuits are photonic circuits, i.e. circuits based on light (photons) instead of electrons. First, it is necessary to be able to create a stream of single photons and control their direction. Researchers around the world have made all sorts of attempts to achieve this control, but now scientists at the Niels Bohr Institute have succeeded in creating a steady stream of photons emitted one at a time and in a particular direction. The breakthrough has been published in ...
Real tremors, or drug-seeking patient? New app can tell
2014-08-29
A 42-year-old investment banker arrives at the emergency department with complaints of nausea, vomiting, anxiety and tremor. He drinks alcohol every day—often at business lunches, and at home every evening. Worried about his health, he decided to quit drinking and had his last Scotch 24 hours before coming to emergency.
It's a common scenario in emergency rooms across Canada—a patient suddenly stops regular, excessive alcohol consumption and develops withdrawal.
Withdrawal is a potentially fatal condition that is easily treated with benzodiazepine drugs, a class of ...
Socioeconomic status and gender are associated with differences in cholesterol levels
2014-08-29
A long-term lifestyle study reports differences between the sexes when it comes to fat profiles associated with socioeconomic status. Research in the open access journal BMC Public Health breaks down factors associated with social class and finds surprising inequalities between men and women.
The researchers found that men in social classes (based on occupation) with manual jobs had lower cholesterol levels than their counterparts in non-manual social classes. In contrast, women's LDL-cholesterol levels were more closely tied to their educational level than men.
The ...
Some women still don't underststand 'overdiagnosis' risk in breast screening
2014-08-29
A third of women who are given information about the chance of 'overdiagnosis' through the NHS breast screening programme may not fully understand the risks involved, according to research published in the British Journal of Cancer (BJC), today (Friday).
In a survey of around 2,200 women, Cancer Research UK scientists at University College London (UCL) found that 64 per cent felt they fully understood the information given about overdiagnosis – the chance that screening will pick up cancers that would never have gone on to cause any harm – by the National breast screening ...
High dietary salt may worsen multiple sclerosis symptoms
2014-08-29
Previous research has indicated that salt may alter the autoimmune response, which is implicated in the development of multiple sclerosis (MS), but it is not clear if it has any direct effect on the course of the disease itself.
The researchers assessed the blood and urine samples of 70 people with the relapsing-remitting form of MS to check for levels of salt; a marker of inflammatory activity called creatinine; and vitamin D, low levels of which have been linked to the disease.
This group were asked to provide urine samples on three separate occasions over a period ...
Plain cigarette packs don't hurt small retailers or boost trade in illicit tobacco
2014-08-29
The findings suggest there is no evidence for these particular arguments against the policy, put forward by the tobacco industry, say the researchers.
Australia was the first country in the world to introduce standardised packaging for tobacco products in December 2012. New Zealand, Ireland, and the UK are currently considering similar legislation.
The researchers wanted to find out if the policy would deter people from buying their tobacco from small independent retailers, prompt a rise in the availability of cheap products sourced from Asia, and increase the use of ...
New model predicts patients with type 1 diabetes who will go on to develop major complications
2014-08-29
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) presents a new model for predicting which patients with type 1 diabetes will go on to develop major complications, through easily and routinely measured risk factors. The research is by Assistant Professor Sabita Soedamah-Muthu, Wageningen University, Netherlands, and colleagues.
To create the model, data were analysed from 1,973 participants with type 1 diabetes followed for seven years in the EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study, and strong prognostic factors ...
The Lancet: China-themed issue
2014-08-29
China's rapid emergence as a global power has coincided with a series of unprecedented challenges to Chinese people's health. The fifth China themed issue of The Lancet provides a picture of the complex health issues facing China, and looks at how better health outcomes for Chinese people can be achieved into the future.
In this issue, the journal highlights the dire consequences that urbanisation and increasing affluence are having on China's chronic disease burden. The journal also reports systematic and comprehensive assessments of China's health-care system and revamping ...