(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
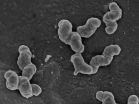
Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria are key players in the natural nitrogen cycle on Earth and in biological wastewater treatment plants. For decades, these specialist bacteria were thought to depend on nitrite as their source of energy. An international team of scientists led by Holger Daims, a microbiologist at the University of Vienna, has now shown that nitrite-oxidizing bacteria can use hydrogen as an alternative source of energy. The oxidation of hydrogen with oxygen enables their growth independent of nitrite and a lifestyle outside the nitrogen cycle. The study is published in the current issue of the journal Science.
Nitrogen, an essential chemical element for life, is transformed into its different chemical forms in numerous steps of the global nitrogen cycle. Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria are important players in nitrogen cycling since they convert the toxic nitrite to the less harmful nitrate. "Humans exploit this process in biological wastewater treatment. Moreover, the formed nitrate is a substrate for other important microbial processes and a source of nitrogen for many plants" explains Hanna Koch, first author of the study and Ph.D. student at the Department of Microbiology and Ecosystem Science of the University of Vienna. Since the description of the first nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in the 19th century, scientists have assumed that the survival of these microorganisms would depend on nitrite as their source of energy. Therefore, the presence of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in the environment and in wastewater treatment plants has commonly been associated with the nitrogen cycle.
Nitrospira: Nitrite oxidizers with surprising features
The environmentally most widespread nitrite oxidizers belong to the genus Nitrospira. These bacteria occur in the most different habitats such as soil, rivers, lakes and oceans, and even in hot springs. In addition, Nitrospira are the key nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in wastewater treatment plants. A team of scientists from Austria, Denmark, Germany, and France has now revealed surprising facts about these microorganisms. "The genome analysis of a Nitrospira species indicated that this bacterium might use hydrogen as an alternative source of energy" says Holger Daims from the Department of Microbiology and Ecosystem Science of the University of Vienna. The potential of Nitrospira to use hydrogen was then studied in detail.
NanoSIMS at the University of Vienna for high-resolution single-cell analyses
The hydrogen-dependent growth of Nitrospira could be visualized in individual bacterial cells by using the high-resolution secondary ion mass spectrometer, also called "NanoSIMS", at the University of Vienna. Under high vacuum conditions like in space, this method shoots small particles out of single bacterial cells for subsequent identification by mass spectrometry. "This exciting approach is feasible at very few research institutions worldwide", says Daims about this high-tech equipment. The scientists could show that Nitrospira cells, which use hydrogen as the source of energy, incorporate carbon dioxide into their biomass. This metabolic activity is linked to cell proliferation and was important evidence that the Nitrospira bacteria indeed use hydrogen for growth. These newly discovered features raise numerous questions about the lifestyle of the "free-living" close relatives of this Nitrospira species in the environment and wastewater treatment plants.
New insights into the ecology of nitrite oxidizers
"The oxidation of hydrogen not only enables Nitrospira to colonize unexpected habitats, but also sustains their activity when nitrite is not available" explains Hanna Koch. Holger Daims adds: "This discovery was a great surprise to us. In the next step, we will explore how extensively environmental nitrite oxidizers use hydrogen as an energy source. Our goal is to better understand the ecology of these important bacteria and their significance for the global cycles of nitrogen and carbon".
INFORMATION:
This study on nitrite-oxidizing bacteria was funded by the Vienna Science and Technology Fund (WWTF) and the Austrian Science Fund (FWF).
Publication in Science:
Growth of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria by aerobic hydrogen oxidation: Hanna Koch, Alexander Galushko, Mads Albertsen, Arno Schintlmeister, Christiane Gruber-Dorninger, Sebastian Lücker, Eric Pelletier, Denis Le Paslier, Eva Spieck, Andreas Richter, Per H. Nielsen, Michael Wagner, und Holger Daims. In: Science. DOI: 10.1126/science.1256985
The University of Vienna, founded in 1365, is one of the oldest and largest universities in Europe. About 9,500 employees, 6,700 of who are academic employees, work at 15 faculties and four centres. This makes the University of Vienna Austria's largest research and education institution. About 92,000 national and international students are currently enrolled at the University of Vienna. With more than 180 degree programmes, the University offers the most diverse range of studies in Austria. The University of Vienna is also a major provider of continuing education. In 2015, the Alma Mater Rudolphina Vindobonensis celebrates its 650th Anniversary. http://www.univie.ac.at
Hydrogen powers important nitrogen-transforming bacteria
2014-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA animation shows Hurricane Marie winding down
2014-08-29
VIDEO:
This video of NOAA's GOES-West satellite imagery from Aug. 26-29 shows Hurricane Marie winding down into a post-tropical storm.
Click here for more information.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite keeps a continuous eye on the Eastern Pacific and has been covering Hurricane Marie since birth. NASA's GOES Project uses NOAA data and creates animations and did so to show the end of Hurricane Marie.
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) on Friday, August 29, Marie became a post-tropical storm ...
'Face time' for the heart diagnoses cardiac disease
2014-08-29
To the careful observer, a person's face has long provided insight into what is going on beneath the surface. Now, with the assistance of a web camera and software algorithms, the face can also reveal whether or not an individual is experiencing atrial fibrillation, a treatable but potentially dangerous heart condition.
A pilot project, the results of which were published online today in the journal Heart Rhythm, demonstrates that subtle changes in skin color can be used to detect the uneven blood flow caused by atrial fibrillation. The technology was developed in a ...
Not all phytoplankton in the ocean need to take their vitamins
2014-08-29
Some species of marine phytoplankton, such as the prolific bloomer Emiliania huxleyi, can grow without consuming vitamin B1 (thiamine), researchers have discovered. The finding contradicts the common view that E. huxleyi and many other eukaryotic microbes depend on scarce supplies of thiamine in the ocean to survive.
"It's a really different way to think about the ocean," says CIFAR Senior Fellow Alexandra Worden, co-author on The ISME Journal paper with CIFAR fellows John Archibald (Dalhousie University), Adrián Reyes-Prieto (University of New Brunswick) and three lead ...
Ready for mating at the right time
2014-08-29
This news release is available in German. The exchange of chemical signals between organisms is considered the oldest form of communication. Acting as messenger molecules, pheromones regulate social interactions between conspecifics, for example, the sexual attraction between males and females. Fish rely on pheromones to trigger social responses and to coordinate reproductive behavior in males and females. Scientists at the Marine Science Center at the University of the Algarve in Faro, Portugal, and at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, ...
China's reform of R&D budget management doesn't go far enough
2014-08-29
In almost 20 years, China's R&D expenditure as a percentage of its gross domestic product has more than tripled, reaching 1.98 per cent in 2012. This figure surpasses the 28 member states of the EU, which collectively managed 1.96 per cent.
However, despite this, China saw a sharp decline in money spent on scientific research, in particular applied research. Basic research funding plummeted from 5.2 per cent in 1995 to 4.7 per cent in 2011, and applied research funding fell from 26.4 per cent to 11.8 per cent in the same years.
This is Dr Cao's second Science article ...
Snails tell of the rise and fall of the Tibetan Plateau
2014-08-29
Boulder, Colo., USA - The rise of the Tibetan plateau -- the largest topographic anomaly above sea level on Earth -- is important for both its profound effect on climate and its reflection of continental dynamics. In this study published in GSA Bulletin, Katharine Huntington and colleagues employ a cutting-edge geochemical tool -- "clumped" isotope thermometry -- using modern and fossil snail shells to investigate the uplift history of the Zhada basin in southwestern Tibet.
Views range widely on the timing of surface uplift of the Tibetan Plateau to its current high ...
Science advice to governments comes of age at Auckland conference
2014-08-29
Auckland, New Zealand (29 August) — Science advice to governments has emerged as a discipline in its own right, which is both art and science. This is what delegates to the world's first summit of science advice heard at a meeting in Auckland, which closed today with a strong call to strengthen international collaboration, an agreement to formalise the network and meet again in 2016.
Convened by the International Council for Science (ICSU) and hosted by New Zealand's Chief Science Advisor, Sir Peter Gluckman, this historic summit marks a turning point in the global awareness ...
Intervention needed for survivors of childhood burns
2014-08-29
Adults who have been hospitalized for a burn as a child experience higher than usual rates of depression and suicidal thoughts, according to new research at the University of Adelaide.
A 30-year follow up of childhood burns victims has been conducted by the University's Centre for Traumatic Stress Studies. They found that 42% of people surveyed had suffered some form of mental illness and 30% suffered depression at some stage in their lives.
The results, now published in the journal Burns, also found that long-term depression was an issue among the group, and 11% had ...
Can YouTube save your life?
2014-08-29
Only a handful of CPR and basic life support (BLS) videos available on YouTube provide instructions which are consistent with recent health guidelines, according to a new study published in Emergency Medicine Australasia, the journal for the Australasian College for Emergency Medicine (ACEM).
Early recognition and treatment of sudden cardiac arrest are known to improve survival for
victims.
A team of Turkish emergency medicine specialists put together the study, which reviewed educational videos from the last three years accessed via YouTube when the search terms ...
Rapamycin or FK506, which is better for SCs migration and peripheral nerve repair
2014-08-29
FK506 possesses a well-studied neuroregenerative effect, stimulating neurite extension in the presence of nerve growth factor in vitro, and enhancing nerve regeneration following nerve crush injury and isografting. However, the use of FK506 to stimulate nerve regeneration is limited because of the risk of renal failure and hypertension, and its considerable cost. With long-term allografts, FK506 alone or combined with other drugs reportedly cause life-threatening infections. Like FK506, rapamycin is an immunosuppressant and FKBP-12-binding ligand, and has a neuroregenerative ...