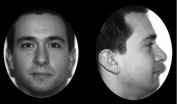
(Press-News.org) Contrary to what one might expect, facial masculinity was negatively associated with semen quality in a recent Journal of Evolutionary Biology study. As increased levels of testosterone have been demonstrated to impair sperm production, this finding may indicate a trade-off between investments in secondary sexual signaling (i.e. facial masculinity) and fertility.
Interestingly, males estimated facial images generally more attractive than females did, suggesting that males may generally overestimate the attractiveness of other men to females.
INFORMATION: END
A handsome face could mean lower semen quality
2014-09-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Underwater grass comeback bodes well for Chesapeake Bay
2014-09-02
CAMBRIDGE, MD (September 2, 2014)—The Susquehanna Flats, a large bed of underwater grasses near the mouth of the Susquehanna River, virtually disappeared from the upper Chesapeake Bay after Tropical Storm Agnes more than 40 years ago. However, the grasses mysteriously began to come back in the early 2000s. Today, the bed is one of the biggest and healthiest in the Bay, spanning some 20 square miles. A new study by scientists at the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science explores what's behind this major comeback.
"This is a story about resilience," said ...
Men who exercise less likely to wake up to urinate
2014-09-02
MAYWOOD, Ill – Men who are physically active are at lower risk of nocturia (waking up at night to urinate), according to a study led by a Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine researcher.
The study by Kate Wolin, ScD, and colleagues is published online ahead of print in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, the official journal of the American College of Sports Medicine.
Nocturia is the most common and bothersome lower urinary tract symptom in men. It can be due to an enlarged prostate known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) -- as the prostate ...
Observing the onset of a magnetic substorm
2014-09-02
Magnetic substorms, the disruptions in geomagnetic activity that cause brightening of aurora, may sometimes be driven by a different process than generally thought, a new study in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics shows.
Hwang et al. report observations using the Cluster spacecraft and ground-based magnetometers associated with the onset of a substorm. They saw two consecutive sudden jumps in the current sheet normal component of the magnetic field in the plasma sheet (the surface of dense plasma that lies approximately in Earth's equatorial plane), separated ...
Researchers uncover hidden infection route of major bacterial pathogen
2014-09-02
Researchers at the University of Liverpool's Institute of Infection and Global Health have discovered the pattern of infection of the bacterium responsible for causing severe lung infections in people with cystic fibrosis.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is usually harmless to humans, but in people with cystic fibrosis (CF) or who have weakened immune systems – such as those who have had an operation or treatment for cancer – it can cause infections that are resistant to antibiotics. In CF patients in particular, infections can be impossible to eradicate from the lungs.
The ...
Aging gracefully: Diving seabirds shed light on declines with age
2014-09-02
Scientists who studied long-lived diving birds, which represent valuable models to examine aging in the wild, found that blood oxygen stores, resting metabolism and thyroid hormone levels all declined with age, although diving performance did not. Apparently, physiological changes do occur with age in long-lived species, but they may have no detectable effect on behavioral performance.
The Functional Ecology findings suggest that reductions in metabolism with age can be viewed as strategic restraint on the part of individuals who are likely to encounter energy-related ...
Could poor stomach absorption of drugs reduce autism medications' effectiveness?
2014-09-02
Recent research has revealed that many children and adults with autism experience gastrointestinal symptoms and that such symptoms can impact the absorption and availability of medications.
Because approximately 35% of people with autism take at least one psychotropic medication to help control their symptoms, the authors of a Journal of Clinical Pharmacology commentary are calling for a formal evaluation of the potential relationship between gastrointestinal symptoms and the effectiveness of autism medications. Alternative modes of drug administration may be needed to ...
Modern population boom traced to pre-industrial roots
2014-09-02
The foundation of the human population explosion, commonly attributed to a sudden surge in industrialization and public health during the 18th and 19th centuries, was actually laid as far back as 2,000 years ago, suggests an extended model of detailed demographic and archeological data.
The Public Library of Science One (PLOS ONE) recently published the analytical framework developed by Aaron Stutz, an associate professor of anthropology at Emory University's Oxford College.
"The industrial revolution and public health improvements were proximate reasons that more people ...
New name for symptoms associated with menopause
2014-09-02
Experts who reviewed the terminology associated with genitourinary tract symptoms related to menopause—currently referred to as vulvovaginal atrophy—have agreed that the term genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) is a medically more accurate, all-encompassing, and a more publicly acceptable term. Their thoughts are published in a recent Journal of Sexual Medicine article.
Going forward, GSM will encompass a collection of symptoms and signs associated with a decrease in estrogen and other sex steroids and may include genital symptoms of dryness, burning, and irritation; ...
Extinctions during human era worse than thought
2014-09-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — It's hard to comprehend how bad the current rate of species extinction around the world has become without knowing what it was before people came along. The newest estimate is that the pre-human rate was 10 times lower than scientists had thought, which means that the current level is 10 times worse.
Extinctions are about 1,000 times more frequent now than in the 60 million years before people came along. The explanation from lead author Jurriaan de Vos, a Brown University postdoctoral researcher, senior author Stuart Pimm, a Duke ...
Time to take notice and tackle heart failure
2014-09-02
Experts have sounded a call to action for policy makers at local, national, and international levels to promote heart failure prevention, improve heart failure awareness among healthcare professionals, ensure equity of care for all patients with heart failure, support and empower patients and their caregivers, and promote heart failure research.
Despite the increasing numbers of people living with and dying from heart failure, awareness of the disease is low among the public, politicians, and even some healthcare professionals. Although there is no cure for heart failure, ...