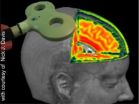
(Press-News.org) Tinnitus, migraine, epilepsy, depression, schizophrenia, Alzheimer's: all these are examples of diseases with neurological causes, the treatment and study of which is more and more frequently being carried out by means of magnetic stimulation of the brain. However, the method's precise mechanisms of action have not, as yet, been fully understood. The work group headed by PD Dr Dirk Jancke from the Institut für Neuroinformatik was the first to succeed in illustrating the neuronal effects of this treatment method with high-res images.
Painless Therapy
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a painless, non-invasive stimulation method, where an electromagnetic coil held above the head is used to generate a strong magnetic field. This method is deployed to activate or inhibit specific brain regions. Even though the number of its medical applications is constantly on the increase, TMS' precise neuronal mechanisms of action are not, as yet, very well understood. That is because imaging used for humans, such as fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging), do not possess the temporal resolution necessary for recording neural activities in milliseconds. More rapid measurement methods, such as EEG or MEG, on the other hand, are affected by the induced magnetic field, with the results that strong interferences are generated that cover important information regarding immediate TMS-based changes to brain activities.
Observing Effect on Neurons in Real Time
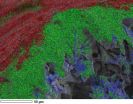
High-res images of TMS effects have now for the first time been successfully generated by RUB researchers in animal testing. The work group headed by PD Dr Dirk Jancke, Institut für Neuroinformatik, utilises voltage-sensitive dyes which, anchored in cell membranes, send out fluorescent light signals once neurons get activated or inhibited. By using light, the researchers avoided the problem of measurement of artefacts occurring due to magnetic fields. "We can now demonstrate in real time how one single TMS pulse suppresses brain activity across a considerable region, most likely through mass activation of inhibiting brain cells," says Dr Jancke. With higher TMS frequencies, each additional TMS pulse generates an incremental increase in brain activity. "This results in a higher cortical activation state, which opens up a time window for plastic changes," explains Dr Vladislav Kozyrev, the first author of the study.
Chances for Patients
The increased neuronal excitability may be utilised to effect specific reorganisation of cell connections by means of targeted learning processes. For example, through visual training after TMS, the ability to identify image contours improves; moreover, a combination of these methods enhances contrast perception in patients with amblyopia - a disorder of sight acquired during child development.
For many neurological diseases of the brain, such as epilepsy, depression and stroke, specific models have been developed. "Deployed in animal testing, our technology has delivered high spatiotemporal resolution imaging data of cortical activity changes," says Dirk Jancke. "We are hoping that these data will enable us to optimise TMS parameters and learning processes in a targeted manner, which are going to be used in future to adapt this technology for medical treatment of humans."
INFORMATION:
Funding
The German Research Foundation has financed the study, e.g. under the framework of Bochum's SFB 874 "Integration and Representation of Sensory Processes (Project A2, Eysel/Jancke)".
Title Catalogue
V. Kozyrev, U.T. Eysel, D. Jancke (2014): Voltage-sensitive dye imaging of transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced intracortical dynamics, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.1405508111
Visualising plastic changes to the brain
Effects of novel treatment method demonstrated
2014-09-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Harvard & Cornell researchers develop untethered, autonomous soft robot
2014-09-04
New Rochelle, NY, September 4, 2014--Imagine a non-rigid, shape-changing robot that walks on four "legs," can operate without the constraints of a tether, and can function in a snowstorm, move through puddles of water, and even withstand limited exposure to flames. Harvard advanced materials chemist George Whitesides, PhD and colleagues describe the mobile, autonomous robot they have created in Soft Robotics, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Soft Robotics website.
In "A Resilient, Untethered Soft Robot," ...
Intestinal barrier damage in multiple sclerosis
2014-09-04
Researchers at Lund University have published new research findings on the role of the intestinal barrier in the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis (MS).
Within medical science, it is not known for certain how MS develops or why the body's immune system attacks cells in the central nervous system. Inflammation develops for an unknown reason, which hinders transport of neural impulses. This can produce various physical and mental symptoms, including a loss of sensation, motor difficulties, blurred vision, dizziness and tiredness.
The present study investigates whether ...
Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology specialists studied jet fuel ignition
2014-09-04
Researchers from Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Viktor Zhukov, Vladislav Sechenov and Andrei Starikovsky, have published experimental data on the combustion of jet fuel in the journal Fuel. The results of their research are important for simulating processes in jet engines.
In their paper, the scientists described how quickly a mixture of jet fuel and oxygen ignites depending on different conditions. This value, called the induction period or combustion delay period, was defined for different temperatures, pressure values and blending ratios. The data obtained ...
Should scientists handle retractions differently?
2014-09-04
It is one of the highest-profile cases of scientific fraud in memory: In 2005, South Korean researcher Woo-Suk Hwang and colleagues made international news by claiming that they had produced embryonic stem cells from a cloned human embryo using nuclear transfer. But within a year, the work had been debunked, soon followed by findings of fraud. South Korea put a moratorium on stem-cell research funding. Some scientists abandoned or reduced their work in the field.
But the case is not so simple: By 2007, other stem-cell researchers had found that the debunked research ...
Students report greater learning gains in traditional science courses
2014-09-04
Students taking traditional, in-class science courses reported higher perceived learning gains than students enrolled in online distance education science courses. Notably, African-American students taking traditional science courses self-reported greater affective and psychomotor learning gains than students taking online science courses.
These are the key findings of a new study co-authored by a Clemson University researcher and published in the most recent issue of Black History Bulletin.
The purpose of the study, funded by a grant from the National Science Foundation ...
Drexel team unveils Dreadnoughtus: A gigantic, exceptionally complete sauropod dinosaur
2014-09-04
This news release is available in Spanish.
PHILADELPHIA (September 4, 2014) – Scientists have discovered and described a new supermassive dinosaur species with the most complete skeleton ever found of its type. At 85 feet (26 m) long and weighing about 65 tons (59,300 kg) in life, Dreadnoughtus schrani is the largest land animal for which a body mass can be accurately calculated. Its skeleton is exceptionally complete, with over 70 percent of the bones, excluding the head, represented. Because all previously discovered supermassive dinosaurs are known only from relatively ...
Phase III FIRST™ (MM-020/IFM 07-01) trial of REVLIMID® (lenalidomide) plus dexamethasone in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients who are not candidates for stem cell transplant published in New E
2014-09-04
SUMMIT, N.J. (Sept. 4, 2014) – Celgene Corporation (NASDAQ:CELG) today announced that data from FIRST (MM-020/IFM 07-01)—an open-label phase III randomized study of continuous REVLIMID (lenalidomide) in combination with dexamethasone in patients newly diagnosed with multiple myeloma (NDMM) who are not candidates for stem cell transplant—have been published in the Sept. 4 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Initial findings, including that the trial had met its primary endpoint of progression free survival (PFS), were reported during the plenary session at the ...
Nano-pea pod model widens electronics applications
2014-09-04
New York | Heidelberg, 4 September 2014 -- Periodic chain-like nanostructures are widely used in nanoelectronics. Typically, chain elements include the likes of quantum rings, quantum dots, or quantum graphs. Such a structure enables electrons to move along the chain, in theory, indefinitely. The trouble is that some applications require localised electrons—these are no longer in a continuous energy spectrum but in a discrete energy spectrum, instead. Now, a new study by Russian scientists identifies ways of disturbing the periodicity of a model nanostructure to obtain ...
Speaking of chemistry: Rethinking football head injuries (video)
2014-09-04
WASHINGTON, Sept. 4, 2014 — Football season is here, and along with thousands of lost hours of productivity from fantasy teams, there's a renewed discussion on the impact of head injuries on players. This week's Speaking of Chemistry focuses on a brain disorder called chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), whose symptoms include memory loss, depression and aggressive or violent behavior. Current detection methods can only identify CTE after a patient has died, leaving many NFL players with a diagnosis that came too late. Now doctors are developing a way to spot CTE in ...
Titania-based material holds promise as new insulator for superconductors
2014-09-04
Research from North Carolina State University shows that a type of modified titania, or titanium dioxide, holds promise as an electrical insulator for superconducting magnets, allowing heat to dissipate while preserving the electrical paths along which current flows. Superconducting magnets are being investigated for use in next-generation power generating technologies and medical devices.
Regular conductors conduct electricity, but a small fraction of that energy is lost during transmission. Superconductors can handle much higher currents per square centimeter and lose ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
[Press-News.org] Visualising plastic changes to the brainEffects of novel treatment method demonstrated