(Press-News.org) The U.S. government is doing a better job of communicating on Twitter with people in sensitive areas like the Middle East and North Africa without the participation of media organizations, according to a study co-authored by a University of Georgia researcher.
The study looked at the U.S. State Department's use of social media and identified key actors who drive its messages to audiences around the world. In particular, it examined the role played by news media and the government in bridging the State Department communication with people domestically and internationally.
Published in the latest issue of the Journal of Public Relations Research, the study's authors say the main reason is that the government is making an effective use of "social mediators" critical to the communication process.
"News media tend to use social media in the old fashioned way," explained Itai Himelboim, an associate professor of telecommunications in the UGA Grady College of Journalism and Mass Communication. "They send out their reports like it was a broadcast—going one way. Communication on social media is a two-way street."
"They need to engage people in the conversation," added Guy Golan, an associate professor of public relations in the S.I. Newhouse School of Public Communications at Syracuse University. "They need to recognize that not all users yield equal influence. Organizations need to strategically identify and empower social mediators as bridges that connect their various publics."
The study defines social mediators as the entities that mediate the relations between an organization and its publics through social media. They are the people and organizations who re-tweet, re-blog and re-post material published online.
"Communication via these social spaces, such as Twitter, depends more than ever upon the willingness of third parties to participate in content distribution in the form of retweets or content endorsement," said Himelboim. "Twitter is a hybrid between mass communication and personal communication."
The study examined the U.S. State Department's use of #SecClinton on Twitter. It analyzed the engagement and curation techniques used with that account. In the process, it identified social mediators who control the flow of information between the Department of State and its publics worldwide.
The key findings are:
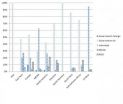
Engagement with users was medium-high for both formal and informal social mediators, but low for news media. Government-related formal and informal social mediators showed similar levels of bilateral relationships. In contrast, news media, the most traditional public relations mediators, were rarely found as social mediators and demonstrated the most unilateral relationships.
Social mediators vary in terms of their formality and interdependence. Formal social mediators were primarily U.S. government agencies while informal social mediators were nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) and individuals (bloggers).
Different types of social mediators influence the State Department's relationships with stakeholders in different parts of the world. The results showed that relationships with populations in the Middle East and North Africa were mediated primarily by informal actors, and formal mediators played a key role in connecting with the public everywhere else in the world.
The authors of the study note that the social mediators—the people retweeting those posts—will add their own message and their own comments and may disagree with the original posting. But the message is still getting out. They say government agencies in these sensitive areas are beginning to recognize that social media is playing a growing role in how they communicate with their publics, domestically and internationally. It is a lesson that news media groups need to recognize as well, the researchers said.
"Based on our findings, the news media could take a lesson from the federal government," Himelboim said.
INFORMATION:
For more information about the study, contact Itai Himelboim at 612-987-1585 or Guy J. Golan at 305-450-5066. The article is available online at http://tinyurl.com/qepmobg.
News media losing role as gatekeepers to new 'social mediators' on Twitter, study finds
2014-09-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists identify rare stem cells that hold potential for infertility treatments
2014-09-04
DALLAS – Sept. 4, 2014 – Rare stem cells in testis that produce a biomarker protein called PAX7 help give rise to new sperm cells — and may hold a key to restoring fertility, research by scientists at UT Southwestern Medical Center suggests.
Researchers studying infertility in mouse models found that, unlike similar types of cells that develop into sperm, the stem cells that express PAX7 can survive treatment with toxic drugs and radiation. If the findings hold true in people, they eventually could lead to new strategies to restore or protect fertility in men undergoing ...
Sugar substitutes not so super sweet after all
2014-09-04
The taste of common sugar substitutes is often described as being much more intense than sugar, but participants in a recent study indicated that these non-nutritive sugar substitutes are no sweeter than the real thing, according to Penn State food scientists.
In the study, participants compared the taste of non-nutritive sweeteners that are often used as low- or no-calorie sugar substitutes with those of nutritive sweeteners, such as sugar, maple syrup and agave nectar. The participants indicated they could perceive the non-nutritive sweeteners -- such as aspartame, ...
UCSB researchers develop ultra sensitive biosensor from molybdenite semiconductor
2014-09-04
Move over, graphene. An atomically thin, two-dimensional, ultrasensitive semiconductor material for biosensing developed by researchers at UC Santa Barbara promises to push the boundaries of biosensing technology in many fields, from health care to environmental protection to forensic industries.
Based on molybdenum disulfide or molybdenite (MoS2), the biosensor material — used commonly as a dry lubricant — surpasses graphene's already high sensitivity, offers better scalability and lends itself to high-volume manufacturing. Results of the researchers' study have been ...
A minimally invasive, high-performance intervention for staging lung cancer
2014-09-04
Endoscopic biopsy of lymph nodes between the two lungs (mediastinum) is a sensitive and accurate technique that can replace mediastinal surgery for staging lung cancer in patients with potentially resectable tumours. Such were the conclusions of a prospective controlled trial conducted under Dr. Moishe Liberman, a researcher at the CHUM Research Centre (CRCHUM) and an Associate Professor at the Université de Montréal. Moreover, the study showed that it is not necessary to perform surgery to confirm negative results obtained through the endoscopic approach during the pre-operative ...
Breakthrough study identifies genetic link between the circadian clock and seasonal timing
2014-09-04
Researchers from the University of Leicester have for the first time provided experimental evidence for a genetic link between two major timing mechanisms, the circadian clock and the seasonal timer.
New research from the Tauber laboratory at the University of Leicester, which will be published in the academic journal PLOS Genetics on 4 September, has corroborated previous observations that flies developed under short days become significantly more cold-resistant compared with flies raised in long-days, suggesting that this response can be used to study seasonal photoperiodic ...
The yin and yang of overcoming cocaine addiction
2014-09-04
PITTSBURGH—Yaoying Ma says that biology, by nature, has a yin and a yang—a push and a pull.
Addiction, particularly relapse, she finds, is no exception.
Ma is a research associate in the lab of Yan Dong, assistant professor of neuroscience in the University of Pittsburgh's Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences. She is the lead author of a paper published online today in the journal Neuron that posits that it may be possible to ramp up an intrinsic anti-addiction response as a means to fight cocaine relapse and keep the wolves of relapse at bay.
This paper ...
A metallic alloy that is tough and ductile at cryogenic temperatures
2014-09-04
A new concept in metallic alloy design – called "high-entropy alloys" - has yielded a multiple-element material that not only tests out as one of the toughest on record, but, unlike most materials, the toughness as well as the strength and ductility of this alloy actually improves at cryogenic temperatures. This multi-element alloy was synthesized and tested through a collaboration of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley and Oak Ridge National Laboratories (Berkeley Lab and ORNL).
"We examined CrMnFeCoNi, a high-entropy alloy that contains ...
Rosetta-Alice spectrograph obtains first far ultraviolet spectra of a cometary surface
2014-09-04
Boulder, Colo. — Sept. 4, 2014 — NASA's Alice ultraviolet (UV) spectrograph aboard the European Space Agency's Rosetta comet orbiter has delivered its first scientific discoveries. Rosetta, in orbit around comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, is the first spacecraft to study a comet up close.
As Alice began mapping the comet's surface last month, it made the first far ultraviolet spectra of a cometary surface. From these data, the Alice team discovered that the comet is unusually dark at ultraviolet wavelengths and that the comet's surface — so far — shows no large water-ice ...
Avian influenza virus isolated in harbor seals poses a threat to humans
2014-09-04
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – September 4, 2014) A study led by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists found the avian influenza A H3N8 virus that killed harbor seals along the New England coast can spread through respiratory droplets and poses a threat to humans. The research appears in the current issue of the scientific journal Nature Communications.
The avian H3N8 virus was isolated by scientists investigating the 2011 deaths of more than 160 harbor seals. Researchers discovered the virus had naturally acquired mutations in a key protein that previous laboratory research ...
2-D or 3-D? That is the question
2014-09-04
The increased visual realism of 3-D films is believed to offer viewers a more vivid and lifelike experience—more thrilling and intense than 2-D because it more closely approximates real life. However, psychology researchers at the University of Utah, among those who use film clips routinely in the lab to study patients' emotional conditions, have found that there is no significant difference between the two formats. The results were published recently in PLOS ONE.
The study aimed to validate the effectiveness of 3-D film, a newer technology, as compared to 2-D film that ...