(Press-News.org) ARLINGTON, Texas -- A high school senior who lives with two college-educated parents is significantly less likely to drink alcohol or smoke marijuana than a teenager who lives with one parent, a new University of Texas at Arlington study has found.
For example, teens living with their mother only are 54 percent more likely to use alcohol, and 58 percent more likely to smoke if they live only with their father.
Eusebius Small, an assistant professor in the UT Arlington School of Social Work, analyzed data on 14,268 teenagers to determine the impact of family structure and parental education on adolescents' substance use. He concluded that family structure and parental education had a more substantial influence on the teen's well-being than other factors such as gender, age or where the teen lived.
In terms of race, researchers found the presence of both parents is an especially strong protective factor for African-American adolescents. When both groups live in two parent homes, white teenagers are 69 percent more likely to engage in substance abuse than black teens. Hispanic teens who live with both parents are 74 percent more likely to use alcohol than their African-American peers who live with both parents.
"We know from previous research that early drinking and drug use is linked to social, economic, emotional and behavioral problems including violence, depression and precarious sexual activity," said Small, whose work focuses on reducing incidents of sexually transmitted infections among adolescents. "Addressing these environmental concerns in concert with related individual problems could reduce substance use occurrences among our young people."
Small co-authored the research with Arati Maleku, a doctoral student and adjunct assistant professor in the UT Arlington School of Social Work, and Rie Suzuki, an assistant professor of public health and health sciences at the University of Michigan-Flint.
The study, called "The Impact of Family and Parental Education on Adolescents' Substance Use: A Study of U.S. High School Seniors," is published online in the journal, Social Work in Public Health.
Scott Ryan, dean of the UT Arlington School of Social Work, said Small's work enhances the conversation about teen substance use and furthers understanding of research to combat the problem.
"Addressing high-risk behaviors means understanding the underlying mechanisms and contextual factors that influence our youths," Ryan said. "Dr. Small's research accomplishes that goal and contributes greatly to ongoing efforts to help families make healthier choices."
The team reviewed data from the ongoing Monitoring the Future study, which is conducted each year by the Institute for Social Research at the University of Michigan. Approximately 50,000 eighth, 10th and 12th grade students are surveyed across the nation. Small and his team used only 12th grade samples addressing demographic variables, beliefs concerning personal lifestyle, school performance and satisfaction, intergroup and interpersonal attitudes and behaviors, attitudes, and beliefs related to alcohol and other substance use, such as tobacco and marijuana.
Previous studies have affirmed that youths who use drugs and alcohol early often reside in families with poor family structure, lower parental education and are from ethnic minority families. But studies focusing on teen substance abuse and family factors, especially among minority ethnic populations, are sparse and fragmented, the researchers said.
Previous studies have recommended the exploration of family structure, parental education and ethnicity to address key risk factors that involve adolescents' substance use, and as a first step in unlocking the complexities of health disparities among diverse populations.
"Our study should re-emphasize the direction for practice and policy, for example, examining the elements in the family structure that are deemed protective and can enhance the well-being of children," Small said.
INFORMATION:
Teens living with 2 college-educated parents less likely to use alcohol and marijuana
2014-09-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ohio University paleontologists discover new species of titanosaurian dinosaur in Tanzania
2014-09-08
ATHENS, Ohio (Sept. 8, 2014)—Ohio University paleontologists have identified a new species of titanosaurian, a member of the large-bodied sauropods that thrived during the final period of the dinosaur age, in Tanzania. Although many fossils of titanosaurians have been discovered around the globe, especially in South America, few have been recovered from the continent of Africa.
The new species, named Rukwatitan bisepultus, was first spotted by scientists embedded in a cliff wall in the Rukwa Rift Basin of southwestern Tanzania. Using the help of professional excavators ...
In one of nature's innovations, a single cell smashes and rebuilds its own genome
2014-09-08
Life can be so intricate and novel that even a single cell can pack a few surprises, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers.
The pond-dwelling, single-celled organism Oxytricha trifallax has the remarkable ability to break its own DNA into nearly a quarter-million pieces and rapidly reassemble those pieces when it's time to mate, the researchers report in the journal Cell. The organism internally stores its genome as thousands of scrambled, encrypted gene pieces. Upon mating with another of its kind, the organism rummages through these jumbled genes ...
Gobbling up poison: A method for killing colon cancer
2014-09-08
(PHILADELPHIA) – These days, cancer researchers aim to design targeted and specific therapy – those that kill cancer but spare the surrounding tissue. Immunotoxins, which use cancer-targeted antibodies linked to deadly toxins such as ricin, are one such therapy. However, few have succeeded to date in part because cancer cells share many molecules with normal cells, and because it can be challenging to unlock the deadly chemical only after the antibody has homed to the diseased tissue.
Now researchers at Thomas Jefferson University have discovered the unique biological ...
Soft robot squirms over fire, ice, and withstands crushing force
2014-09-08
ITHACA, N.Y. – Engineers have created a shape-changing "soft" robot that can tread over a variety of adverse environmental conditions including snow, puddles of water, flames, and the crushing force of being run over by an automobile.
Videos: https://cornell.box.com/softrobot
The engineers from Cornell and Harvard Universities will detail the robot in an upcoming edition of the journal Soft Robotics. An early online version of the study can be found at: http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/soro.2014.0008
The pneumatically powered, fully untethered robot was ...
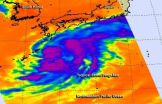
NASA sees large Tropical Storm Fengshen skirting eastern Japan's coastline
2014-09-08
Tropical Storm Fengshen is a large storm and infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows that it's about as long as the big island of Japan.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Fengshen on September 7 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument known as AIRS gathered temperature data about the storm's cloud tops and surrounding sea surface temperatures. The infrared data showed strong thunderstorms surrounded the center of circulation and also appeared in large bands south and northeast of the storm's center. Another large and fragmented band on ...
Yale study shows how conversion of forests to cropland affected climate
2014-09-08
The conversion of forests into cropland worldwide has triggered an atmospheric change that, while seldom considered in climate models, has had a net cooling effect on global temperatures, according to a new Yale study.
Writing in the journal Nature Climate Change, Professor Nadine Unger of the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies (F&ES) reports that large-scale forest losses during the last 150 years have reduced global emissions of biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs), which control the atmospheric distribution of many short-lived climate pollutants, ...
Brain damage caused by severe sleep apnea is reversible
2014-09-08
DARIEN, IL – A neuroimaging study is the first to show that white matter damage caused by severe obstructive sleep apnea can be reversed by continuous positive airway pressure therapy. The results underscore the importance of the "Stop the Snore" campaign of the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project, a collaboration between the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Sleep Research Society and other partners.
Results show that participants with severe, untreated sleep apnea had a significant reduction in white matter fiber integrity ...
A bird-pollinated flower with a rather ingenious twist
2014-09-08
VIDEO:
When a bird forages on nectar, the flower twists as the spur complies with the shape of the
bird's bill. In consequence, pollen is placed in an unusual location on...
Click here for more information.
When researchers studying several bird-pollinated species of Impatiens flowers in the mountains of western Cameroon noticed one with an odd, upwardly curving nectar spur, they couldn't imagine how any sunbird could ever sip from it. After recording visitors to the flower continuously ...
Coral trout pick their collaborators carefully
2014-09-08
VIDEO:
Coral trout are choosey about moray collaborators.
Click here for more information.
Coral trout not only work with moray eels to improve their chances of a meal, but they can also be choosy when it comes to picking the best moray partner. The findings reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 8 show that such sophisticated collaborative abilities are not limited to apes and humans.
The fish's behavior is remarkable in other ways too, the researchers ...
Fish as good as chimpanzees at choosing the best partner for a task
2014-09-08
Coral trout are fast when chasing prey above the reefs of their habitat, but can't pursue their quarry if it buries itself into a hard-to-reach reef crevice.
When this happens, the trout will team up with a snake-like moray eel to flush out the unfortunate fish in a remarkable piece of interspecies collaboration: either the eel takes the prey in the reef, or scares it back into the open so the trout can pounce.
Coral trout - along with close relative the roving coral grouper - will use gestures and signals to flag the location of prey to an eel, including head shakes ...