(Press-News.org) International research involving the University of Adelaide has found that the risk of preterm birth could be halved for a specific group of "super high-risk" twin pregnancies.
The results could help to save babies' lives throughout the world and prevent serious health complications after birth.
The study, involving researchers from the University of Adelaide's Robinson Research Institute, reviewed all of the previous large studies conducted into the use of progestogen hormones, which have been trialed over the past 10 years to help prevent preterm birth in twins. In total, 13 studies covering more than 3700 women and 7500 babies were reviewed.
The results, published in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, show that an important discovery had been missed in each of those previous studies.
"Until now the research has demonstrated that there has been no benefit from the use of progestogen hormones in preventing preterm birth for women with a twin pregnancy," says co-author Professor Ben Mol from the University's Robinson Research Institute.
"Thanks to this international review, we can now see that there is a very specific benefit to one group of high-risk pregnancies: women who have a short cervix, who are pregnant with twins.
"Twin pregnancies are very much at risk of preterm birth, with half of these pregnancies delivering before 37 weeks' gestation. For women with a short cervix who are also pregnant with twins, this is what I would call a 'super high risk' category for adverse outcomes, either for infant death or for serious health problems after birth.
"We found that by using progestogen hormones, there was a 50% reduction in risk of preterm birth for this group of pregnancies. That's a very significant result, and one that we hope will help to save lives and prevent future heartache for couples who are trying to have children," he says.
Professor Mol says preterm birth remains the biggest problem in modern Western obstetrics.
"Anything that can help to prevent preterm birth will be of interest to clinicians and families throughout the world, and that's why this finding is important. While it does not help to reduce risk in all twin pregnancies, it does help to significantly reduce poor outcomes for those twin pregnancies in a very high risk group," he says.
"This work also highlights the need for further collaboration between researchers and countries."
INFORMATION:
Media contact:
Professor Ben Mol
Robinson Research Institute
The University of Adelaide
Cell phone: + 61 (0)434 122 170
ben.mol@adelaide.edu.au END
Halving the risk of preterm birth for some twin pregnancies
2014-09-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA tracks Norbert moisture to Arizona's drenching thunderstorms
2014-09-10
VIDEO:
This simulated flyby of NASA's TRMM satellite on Sept. 8 saw rain falling at a rate of over 62 mm (2.4 inches) per hour in some downpours over Arizona. Some...
Click here for more information.
Post-tropical storm Norbert may have been centered a couple of hundred miles off the northwestern coast of Mexico's Baja California, but the flow of warm, moist air that spun around it generated drenching thunderstorms over Arizona. NASA's TRMM satellite saw Norbert's remnants and ...
Where to grab space debris
2014-09-10
Objects in space tend to spin — and spin in a way that's totally different from the way they spin on earth. Understanding how objects are spinning, where their centers of mass are, and how their mass is distributed is crucial to any number of actual or potential space missions, from cleaning up debris in the geosynchronous orbit favored by communications satellites to landing a demolition crew on a comet.
In a forthcoming issue of the Journal of Field Robotics, MIT researchers will describe a new algorithm for gauging the rotation of objects in zero gravity using only ...
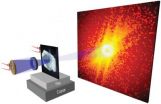
Advanced light source sets microscopy record
2014-09-10
A record-setting X-ray microscopy experiment may have ushered in a new era for nanoscale imaging. Working at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), a collaboration of researchers used low energy or "soft" X-rays to image structures only five nanometers in size. This resolution, obtained at Berkeley Lab's Advanced Light Source (ALS), a DOE Office of Science User Facility, is the highest ever achieved with X-ray microscopy.
Using ptychography, a coherent diffractive imaging technique based on high-performance scanning ...
Missing piece found to help solve concussion puzzle
2014-09-10
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 10, 2014 – Researchers at UPMC and the University of Pittsburgh have created a new, 5- to 10-minute test that could be added to a clinician's concussion evaluation toolkit for a more comprehensive assessment of the injury.
In a recent study published online first by the American Journal of Sports Medicine, researchers from the UPMC Sports Medicine Concussion Program demonstrated that clinicians could use their novel Vestibular/Ocular Motor Screening (VOMS) examination to be 90 percent accurate in identifying patients with concussion. The VOMS, which ...
Nerve impulses can collide and continue unaffected
2014-09-10
According to the traditional theory of nerves, two nerve impulses sent from opposite ends of a nerve annihilate when they collide. New research from the Niels Bohr Institute now shows that two colliding nerve impulses simply pass through each other and continue unaffected. This supports the theory that nerves function as sound pulses. The results are published in the scientific journal Physical Review X.
Nerve signals control the communication between the billions of cells in an organism and enable them to work together in neural networks. But how do nerve signals work? ...
Non-dominant hand vital to the evolution of the thumb
2014-09-10
New research from biological anthropologists at the University of Kent has shown that the use of the non-dominant hand was likely to have played a vital role in the evolution of modern human hand morphology.
In the largest experiment ever undertaken into the manipulative pressures experienced by the hand during stone tool production, researchers analysed the manipulative forces and frequency of use experienced by the thumb and fingers on the non-dominant hand during a series of stone tool production sequences that replicated early tool forms.
It is well known that ...
Living liver donors ambivalent with donation
2014-09-10
Living donors are important to increasing the number of viable grafts for liver transplantation. A new study published in Liver Transplantation, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society, found that ambivalence is common among donor candidates. However, providing social support may help minimize the donors' concerns regarding donation.
There is much demand for organs and a shortage of deceased organ donations. One solution to this shortage is the use of living donors for liver transplantation. ...
How skin falls apart: Pathology of autoimmune skin disease is revealed at the nanoscale
2014-09-10
BUFFALO, N.Y. –University at Buffalo researchers and colleagues studying a rare, blistering disease have discovered new details of how autoantibodies destroy healthy cells in skin. This information provides new insights into autoimmune mechanisms in general and could help develop and screen treatments for patients suffering from all autoimmune diseases, estimated to affect 5-10 percent of the U.S. population.
The research, published in PLoS One on Sept. 8, has the potential to help clinicians identify who may be at risk for developing Pemphigus vulgaris (PV), an autoimmune ...
CNIO successfully completes its fisrt clinical trial on HER-2-negative breast cancer with nintedanib
2014-09-10
The experimental drug nintedanib, combined with standard chemotherapy with paclitaxel, causes a total remission of tumours in 50% of patients suffering from early HER-2- negative breast cancer, the most common type of breast cancer. These are the conclusions of the Phase I Clinical Trial, sponsored by the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) and carried out by CNIO ́s Breast Cancer Clinical Research Unit. The study has been published today in British Journal of Cancer, which belongs to Nature Publishing Group.
According to Miguel Ángel Quintela, ...
Monitoring the response of bone metastases to treatment using MRI and PET
2014-09-10
Imaging technologies are very useful in evaluating a patient's response to cancer treatment, and this can be done quite effectively for most tumors using RECIST, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors. However, RECIST works well for tumors located in soft tissue, but not so well for cancers that spread to the bone, such as is the case for prostate and breast cancers. More effort, therefore, is needed to improve our understanding of how to monitor the response of bone metastases to treatment using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), ...