(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
In this movie, the Dbr1 enzyme rotates 360 degrees. Partially inhibiting Dbr1 could represent a new way to treat most cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), according to a new...
Click here for more information.
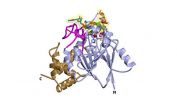
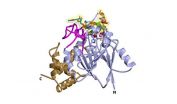
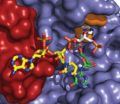
SAN ANTONIO, Texas, U.S.A. (Sept. 10, 2014) — Investigators from the School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio have determined the first high-resolution structure of an enzyme that, if partially inhibited, could represent a new way to treat most cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, also called Lou Gehrig's disease).
Dbr1 is the only enzyme known to break loops of ribonucleic acids (RNAs) called intron lariats. When Dbr1 activity is high, very few of these lariats remain in cells.
"This is relevant to ALS because another protein called TDP-43 aggregates to form clumps in motor neurons in 50 percent to 80 percent of all ALS cases," said senior author P. John Hart, Ph.D., professor of biochemistry and director of the X-ray Crystallography Core Laboratory at the UT Health Science Center San Antonio. "Decreasing Dbr1 activity will cause some of these lariats to remain and when TDP-43 binds these lariats, it is prevented from forming clumps in motor neurons."
ALS is characterized by death of motor neurons, resulting in progressive paralysis.
"This is the first picture of this enzyme to be obtained," Dr. Hart said. "We can see all the details, which will help us to develop small molecules (drugs) to inhibit Dbr1 activity."
The other lead investigators on the paper, published as a "Breakthrough Manuscript" in Nucleic Acids Research, are Masad Dahma, Ph.D., professor and chair of the Department of Chemistry at McGill University in Montreal, and Scott Stevens, Ph.D., associate professor of molecular genetics and microbiology at The University of Texas at Austin.
INFORMATION:
Visuals: the image below in high resolution and a movie that rotates the Dbr1 enzyme 360 degrees
On the Web and social media
For current news from the UT Health Science Center San Antonio, please visit our news release website, like us on Facebook or follow us on Twitter.
About the UT Health Science Center at San Antonio
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, one of the country's leading health sciences universities, ranks in the top 3 percent of all institutions worldwide receiving National Institutes of Health funding. The university's schools of medicine, nursing, dentistry, health professions and graduate biomedical sciences have produced more than 29,000 graduates. The $765 million operating budget supports eight campuses in San Antonio, Laredo, Harlingen and Edinburg. For more information on the many ways "We make lives better®," visit http://www.uthscsa.edu.
Structure of enzyme seen as target for ALS drugs
2014-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hold the mayo
2014-09-11
You are what you eat, the saying goes, and now a study conducted by researchers at UC Santa Barbara and the University of Pittsburgh suggests that the oft-repeated adage applies not just to physical health but to brain power as well.
In a paper published in the early online edition of the journal Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids, the researchers compared the fatty acid profiles of breast milk from women in over two dozen countries with how well children from those same countries performed on academic tests.
Their findings show that the amount of ...
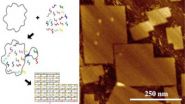
Researchers create world's largest DNA origami
2014-09-11
Researchers from North Carolina State University, Duke University and the University of Copenhagen have created the world's largest DNA origami, which are nanoscale constructions with applications ranging from biomedical research to nanoelectronics.
"These origami can be customized for use in everything from studying cell behavior to creating templates for the nanofabrication of electronic components," says Dr. Thom LaBean, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and senior author of a paper describing the work.
DNA origami are self-assembling ...
New superfoods could help key protein keep bodies healthy
2014-09-11
A new generation of new superfoods that tackle heart disease and diabetes could be developed following research into a protein that helps keep cells in our bodies healthy.
Researchers at the University of Warwick found that the protein, called Nrf2, continually moves in and out of the nuclei of human cells to sense the cell's health and vitality.
When Nrf2 is exposed to threats to the cell's health it oscillates faster and activates an increase in the cell's defence mechanism, including raising the levels of antioxidant.
The researchers, from the University's Warwick ...
Childhood mentors have positive impact on career success
2014-09-11
New research from North Carolina State University finds that young people who have had mentors are more likely to find work early in their careers that gives them more responsibility and autonomy – ultimately putting them on a path to more financially and personally rewarding careers.
"We wanted to look at the long-term impacts on mentees in naturally occurring mentorship relationships, rather than participants in formal mentorship programs," says Dr. Steve McDonald, an associate professor of sociology at NC State and lead author of a paper on the work. "And we found ...
Graphene paints a corrosion-free future
2014-09-11
The surface of graphene, a one atom thick sheet of carbon, can be randomly decorated with oxygen to create graphene oxide; a form of graphene that could have a significant impact on the chemical, pharmaceutical and electronic industries. Applied as paint, it could provide an ultra-strong, non-corrosive coating for a wide range of industrial applications.
Graphene oxide solutions can be used to paint various surfaces ranging from glass to metals to even conventional bricks. After a simple chemical treatment, the resulting coatings behave like graphite in terms of chemical ...
Lurking bright blue star caught!
2014-09-11
This release is available in Japanese.
A team led by Gastón Folatelli at the Kavli IPMU, the University of Tokyo, has found evidence of a hot binary companion star to a yellow supergiant star, which had become a bright supernova. The existence of the companion star had been predicted by the same team on the basis of numerical calculations. This finding provides the last link in a chain of observations that have so far supported the team's theoretical picture for this supernova. The results are published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters and have wide implications for ...
High levels of physical activity linked to better academic performance in boys
2014-09-11
A recent Finnish study shows that higher levels of physical activity are related to better academic achievement during the first three school years particularly in boys. The study published in PLOS ONE was conducted in collaboration with the Physical Activity and Nutrition in Children (PANIC) Study conducted at the University of Eastern Finland and the First Steps Study at the University of Jyväskylä.
The study investigated the relationships of different types of physical activity and sedentary behavior assessed in the first grade to reading and arithmetic skills in grades ...
Smokers who consume too much sodium at greater risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis
2014-09-11
A new study published online in the journal Rheumatology today indicates that the interaction between high sodium intake and smoking is associated with a more than doubled risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
The study, carried out by Björn Sundström and colleagues from the Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Rheumatology at Umeå University, Sweden, was carried out to see whether recent animal and human cell study results that showed a link between a high sodium intake and RA would yield similar results in a nested case-control study of data from ...
'Fat shaming' doesn't encourage weight loss
2014-09-11
Discrimination against overweight and obese people does not help them to lose weight, finds new UCL research funded by Cancer Research UK.
In a study of 2,944 UK adults over four years, those who reported experiencing weight discrimination gained more weight than those who did not. On average, after accounting for baseline differences, people who reported weight discrimination gained 0.95kg whereas those who did not lost 0.71kg, a difference of 1.66kg.
The research, published in the journal Obesity, contradicts the common perception that discrimination or 'fat shaming' ...
More needed to protect our sportspeople from brain injury, say Birmingham experts
2014-09-11
Two University of Birmingham academics are calling for more research to be carried out looking at how the brains of sportspeople – including children – react when they receive a blow to the head.
Their call is echoed by Dawn Astle and Peter Robinson. Dawn Astle, is the daughter of former West Bromwich Albion player Jeff Astle who, an inquest found, died from brain trauma caused by heading heavy footballs - a condition known as Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE). Peter Robinson is the father of Ben Robinson, whose son died as a result of repeated concussions during ...