(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, PA, September 15, 2014 – Schizophrenia is generally considered to be a disorder of brain development and it shares many risk factors, both genetic and environmental, with other neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism and intellectual disability.
The normal path for brain development is determined by the combined effects of a complex network of genes and a wide range of environmental factors.
However, longitudinal brain imaging studies in both healthy and patient populations are required in order to map the disturbances in brain structures as they emerge, i.e., the disturbed trajectories of brain development.
A new study by an international, collaborative group of researchers has measured neurodevelopment in schizophrenia, by studying brain development during childhood and adolescence in people with and without this disorder. With access to new statistical approaches and long-term follow-up with participants, in some cases over more than a decade, the researchers were able to describe brain development patterns associated with schizophrenia.
"Specifically, this paper shows that parts of the brain's cortex develop differently in people with schizophrenia," said first author Dr. Aaron F. Alexander-Bloch, from the National Institute of Mental Health.
"The mapping of the path that the brain follows in deviating from normal development provides important clues to the underlying causes of the disorder," said Dr. John Krystal, Editor of Biological Psychiatry.
The findings were derived by investigating the trajectory of cortical thickness growth curves in 106 patients with childhood-onset schizophrenia and a comparison group of 102 healthy volunteers.
Each participant, ranging from 7 years of age, had repeated imaging scans over the course of several years. Then, using over 80,000 vertices across the cortex, the researchers modeled the effect of schizophrenia on the growth curve of cortical thickness.
This revealed differences that occur within a specific group of highly-connected brain regions that mature in synchrony during typical development, but follow altered trajectories of growth in schizophrenia.
"These findings show a relationship between the hypothesis that schizophrenia is a neurodevelopmental disorder and the longstanding hypothesis – first articulated by the German anatomist Karl Wernicke in the late 19th century – that it is a disease of altered connectivity between regions of the brain," added Alexander-Bloch.
This theoretical consistency is important, as it allows researchers to better focus future studies of brain connectivity in schizophrenia, by targeting the brain regions known to be affected.
INFORMATION:
The article is "Abnormal Cortical Growth in Schizophrenia Targets Normative Modules of Synchronized Development" by Aaron F. Alexander-Bloch, Philip T. Reiss, Judith Rapoport, Harry McAdams, Jay N. Giedd, Ed T. Bullmore, and Nitin Gogtay (doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.02.010). The article appears in Biological Psychiatry, Volume 76, Issue 6 (September 15, 2014), published by Elsevier.
Notes for Editors
Full text of the article is available to credentialed journalists upon request; contact Rhiannon Bugno at +1 214 648 0880 or Biol.Psych@utsouthwestern.edu. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Dr. Aaron F. Alexander-Bloch or aalexanderbloch@gmail.com.
The authors' affiliations, and disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available in the article.
John H. Krystal, M.D., is Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry at the Yale University School of Medicine, Chief of Psychiatry at Yale-New Haven Hospital, and a research psychiatrist at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. His disclosures of financial and conflicts of interests are available here.
About Biological Psychiatry
Biological Psychiatry is the official journal of the Society of Biological Psychiatry, whose purpose is to promote excellence in scientific research and education in fields that investigate the nature, causes, mechanisms and treatments of disorders of thought, emotion, or behavior. In accord with this mission, this peer-reviewed, rapid-publication, international journal publishes both basic and clinical contributions from all disciplines and research areas relevant to the pathophysiology and treatment of major psychiatric disorders.
The journal publishes novel results of original research which represent an important new lead or significant impact on the field, particularly those addressing genetic and environmental risk factors, neural circuitry and neurochemistry, and important new therapeutic approaches. Reviews and commentaries that focus on topics of current research and interest are also encouraged.
Biological Psychiatry is one of the most selective and highly cited journals in the field of psychiatric neuroscience. It is ranked 5th out of 135 Psychiatry titles and 14th out of 251 Neurosciences titles in the Journal Citations Reports® published by Thomson Reuters. The 2013 Impact Factor score for Biological Psychiatry is 9.472.
About Elsevier
Elsevier is a world-leading provider of information solutions that enhance the performance of science, health, and technology professionals, empowering them to make better decisions, deliver better care, and sometimes make groundbreaking discoveries that advance the boundaries of knowledge and human progress. Elsevier provides web-based, digital solutions — among them ScienceDirect, Scopus, Elsevier Research Intelligence, and ClinicalKey — and publishes nearly 2,200 journals, including The Lancet and Cell, and over 25,000 book titles, including a number of iconic reference works.
The company is part of Reed Elsevier Group PLC, a world leading provider of professional information solutions in the Science, Medical, Legal and Risk and Business sectors, which is jointly owned by Reed Elsevier PLC and Reed Elsevier NV. The ticker symbols are REN (Euronext Amsterdam), REL (London Stock Exchange), RUK and ENL (New York Stock Exchange).
Brain Development in Schizophrenia Strays from the Normal Path
Reports new study in Biological Psychiatry
2014-09-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sleep disorders widely undiagnosed in individuals with multiple sclerosis
2014-09-15
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) —In what may be the largest study of sleep problems among individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS), researchers at UC Davis have found that widely undiagnosed sleep disorders may be at the root of the most common and disabling symptom of the disease: fatigue.
Conducted in over 2,300 individuals in Northern California with multiple sclerosis, the large, population-based study found that, overall, more than 70 percent of participants screened positive for one or more sleep disorders.
The research highlights the importance of diagnosing the root causes ...
How evolutionary principles could help save our world
2014-09-15
The age of the Anthropocene--the scientific name given to our current geologic age--is dominated by human impacts on our environment. A warming climate. Increased resistance of pathogens and pests. A swelling population. Coping with these modern global challenges requires application of what one might call a more-ancient principle: evolution.
That's the recommendation of a diverse group of researchers, in a paper published today in the online version of the journal Science. A majority of the nine authors on the paper have received funding from the National Science Foundation ...
Boosting armor for nuclear-waste eating microbes
2014-09-15
EAST LANSING, Mich. – A microbe developed to clean up nuclear waste and patented by a Michigan State University researcher has just been improved.
In earlier research, Gemma Reguera, MSU microbiologist, identified that Geobacter bacteria's tiny conductive hair-like appendages, or pili, did the yeoman's share of remediation. By increasing the strength of the pili nanowires, she improved their ability to clean up uranium and other toxic wastes.
In new research, published in the current issue of Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Reguera has added an additional layer ...
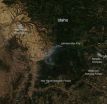
Selway complex and Johnson Bar fires in Idaho
2014-09-15
Two fires are seen burning in this satellite image taken by the Aqua satellite on September 11, 2014. The Selway complex of fires had been previously reported located 30 miles west of Darby, MT. It appears a new fire may have started again in this complex. Currently the size of the complex is 1,659 fires. The fire is mostly contained and there will be no additional reporting on this fire unless activity increases. It is, for the most part, contained.
The Johnson Bar fire started with a lightning strike on August 03, 2014. To date, 8,867 acres have been affected. ...
New glaucoma culprit is found
2014-09-15
Glaucoma, a leading cause of irreversible blindness, is associated with elevated pressure in the eye. This elevated pressure essentially is due to a plumbing problem. Fluid builds up in the eye, increasing pressure and eventually damaging the optic nerve. For nearly 150 years, researchers have been trying to understand what causes the blockage that prevents the eye from draining properly.
In a unique study of human ocular cells, a multi-institution research team led by a biomedical engineer at Northwestern University has found a new culprit. Glaucoma appears to be a consequence ...
Getting hot and wet in Vermont
2014-09-15
Here's your northern Vermont forecast for the rest of this century: annual precipitation will increase by between a third and half an inch per decade, while average temperatures will rise some five degrees Fahrenheit by midcentury. By late in the century, average temperatures will have spiked more than eight degrees. In July, by 2100, the City of Burlington will have at least ten additional days above ninety degrees. The growing season picks up 43 more days. Looking at ski conditions, expect annual snowfall at six major ski resorts to decline about fifty percent by century's ...
Mayo finds many liver transplant patients can avoid costly stay in ICU after surgery
2014-09-15
JACKSONVILLE, Fla., Sept. 12, 2014 — The liver transplant team at Mayo Clinic in Florida has found, based on 12 years of experience, that more than half of patients receiving a new liver can be "fast-tracked" to return to a surgical ward room following their transplant, bypassing a one- or two-day stay in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU).
In the September issue of the American Journal of Transplantation, the physicians and researchers have turned their knowledge of who can be safely fast-tracked into a scoring system that other transplant centers can also use — thus sparing ...
The shadow of a disease
2014-09-15
This news release is available in German.
In future, some diseases might be diagnosed earlier and treated more effectively. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light in Erlangen have developed an optical method that makes individual proteins, such as the proteins characteristic of some cancers, visible. Other methods that achieve this only work if the target biomolecules have first been labelled with fluorescent tags; In general, however, that approach is difficult or even impossible. By contrast, with their method, coined iSCAT, the researchers ...
Unemployment for doctoral scientists and engineers below national average in 2013
2014-09-15
A new National Science Foundation (NSF) report says the 2013 unemployment rate for individuals with research doctoral degrees in science, engineering and health (SEH) fields was one-third the rate for the general population aged 25 and older--2.1 percent versus 6.3 percent.
According to the report, an estimated 837,900 individuals in the United States held SEH research doctoral degrees in 2013, and nearly 735,900 of them were in the labor force; this includes those employed full time or part time and unemployed individuals actively seeking work.
Statistics show that ...
USC researchers discover the healing power of 'rib-tickling'
2014-09-15
Unlike salamanders, mammals can't regenerate lost limbs, but they can repair large sections of their ribs.
In a new study in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, a team directed by USC Stem Cell researcher Francesca Mariani takes a closer look at rib regeneration in both humans and mice.
The first author of the paper, USC medical student Marissa K. Srour, was a USC undergraduate when she started the project, which earned a 2011 USC Discovery Scholar Prize. Each year, 10 graduating seniors win these coveted prizes, which recognize exceptional new scholarship.
Using ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Brain Development in Schizophrenia Strays from the Normal PathReports new study in Biological Psychiatry