(Press-News.org) September 15, 2014 – An educational program for nurses can help address knowledge gaps related to advance health care directives (AHCDs)—thus helping to ensure that patients' wishes for care at the end of life are known and respected, reports a paper in the October/December Journal of Christian Nursing, official journal of the Nurses Christian Fellowship. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Maureen Kroning, EdD, RN, of Nyack (N.Y.) College and Good Samaritan Hospital presents her hospital's experience with developing an inservice educational program to provide nurses with needed information on advance directives. She writes, "It is vital to recognize and address problems associated with AHCD so nurses can provide competent and compassionate care."
Program Meets Nurses' Need for Knowledge on Advance Directives
Research shows that, while most adults want their wishes for end-of-life care response, only about one-third have completed AHCDs. Despite the growing need for advance care planning, many health care professionals lack the knowledge to teach patients about advance directives.
At the study hospital, there was a "recognized problem" with AHCD education. On admission, patients were provided with an AHCD information packet and told to ask a nurse if they had any questions. "However," Maureen Kroning writes, "nurses expressed not fully understanding AHCDs, feeling incompetent to educate patients, nor did they believe AHCD education was an important part of their role."
A subsequent survey of 49 nurses found significant deficits in knowledge regarding AHCDs, especially among less-experienced nurses. Nurses "specifically and repeatedly" addressed the need for more AHCD education.
In response, the hospital developed an AHCD inservice education program, specifically addressing the knowledge gaps uncovered by the survey and tailored to the needs of adult learners. The two-hour program included information on AHCDs and living wills, and relevant federal and state laws. In addition to lecture and discussion, the program included role-playing opportunities and questions and answers. The online version of the article includes links to the author's lecture slides and an AHCD patient booklet.
The educational program led to significant improvements in nurses' knowledge of AHCDs. The hospital also saw vital changes in several areas related to AHCDs, including increased awareness of the problem by hospital leadership and the desire obtain further AHCD education by nurses.
Other hospitals have been provided with and are implementing the educational intervention. Providing time for nurses to attend the program during regular work hours is a key factor in ensuring access to the inservice program.
The experience highlights the need to provide nurses with practical and relevant information about AHCDs and end-of-life care, Maureen Kroning believes. She writes, "If nurses lack the education to effectively educate, how are patients going to make desired decisions about their wishes at the end of life?" She also highlights some key issues for further research related to AHCDs, including addressing patients' distress around end-of-life care, issues surrounding healthcare team relationships, and the optimal timing of conversations with patients and families about completing an advance directive.
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Advance Directives Education: A Critical Need."
About Journal of Christian Nursing
Journal of Christian Nursing is a peer-reviewed, quarterly, professional journal helping nurses integrate issues of faith with nursing practice and sustain excellence in nursing care since 1984. Our mission is to help nurses, students, and educators practice from a biblically-based, Christian perspective. JCN offers relevant peer-reviewed clinical and professional information, including original research, on current issues and trends, spirituality and spiritual care, ethics, values, healing and wholeness, faith community nursing, healthcare missions, nursing education, personal growth and self-care, health care for the poor and disenfranchised, and nursing care experiences which promote excellence and encourage nurses.
About Wolters Kluwer Health
Wolters Kluwer Health is a leading global provider of information, business intelligence and point-of-care solutions for the healthcare industry. Serving more than 150 countries worldwide, clinicians rely on Wolters Kluwer Health's market leading information-enabled tools and software solutions throughout their professional careers from training to research to practice. Major brands include Health Language®, Lexicomp®, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Medicom®, Medknow, Ovid®, Pharmacy OneSource®, ProVation® Medical and UpToDate®.
Wolters Kluwer Health is part of Wolters Kluwer, a market-leading global information services company. Wolters Kluwer had 2013 annual revenues of €3.6 billion ($4.7 billion), employs approximately 19,000 people worldwide, and maintains operations in over 40 countries across Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, and Latin America.maintains operations in over 40 countries across Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, and Latin America. Wolters Kluwer is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands. Its shares are quoted on Euronext Amsterdam (WKL) and are included in the AEX and Euronext 100 indices. Wolters Kluwer has a sponsored Level 1 American Depositary Receipt program. The ADRs are traded on the over-the-counter market in the U.S. (WTKWY).
Follow our official Twitter handle: @WKHealth.
Nurses need education on advance health care directives, reports Journal of Christian Nursing
Hospital shares effective training program on advance directives and end-of-life care
2014-09-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Skin cancer risks higher for soldiers serving abroad
2014-09-15
Soldiers deployed to tropical and sunny climates are coming home with increased risk factors for a threat far from the battlefield: skin cancer.
In a retrospective study of about 200 veterans seen at the post-deployment clinic of the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, researchers from Vanderbilt University Medical Center and the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System found that 62 percent of military personnel reported getting sunburned while deployed abroad, including cases of skin blistering. In addition, 29 percent noted a change ...
The science behind swimming
2014-09-15
At nearly 100 feet long and weighing as much as 170 tons, the blue whale is the largest creature on the planet, and by far the heaviest living thing ever seen on Earth. So there's no way it could have anything in common with the tiniest fish larvae, which measure millimeters in length and tip the scales at a fraction of a gram, right?
Not so fast, says L. Mahadevan, the Lola England de Valpine Professor of Applied Mathematics, of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, and of Physics.
Using simple hydrodynamics, a team of researchers led by Mahadevan was able to show ...
Brain Development in Schizophrenia Strays from the Normal Path
2014-09-15
Philadelphia, PA, September 15, 2014 – Schizophrenia is generally considered to be a disorder of brain development and it shares many risk factors, both genetic and environmental, with other neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism and intellectual disability.
The normal path for brain development is determined by the combined effects of a complex network of genes and a wide range of environmental factors.
However, longitudinal brain imaging studies in both healthy and patient populations are required in order to map the disturbances in brain structures as they emerge, ...
Sleep disorders widely undiagnosed in individuals with multiple sclerosis
2014-09-15
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) —In what may be the largest study of sleep problems among individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS), researchers at UC Davis have found that widely undiagnosed sleep disorders may be at the root of the most common and disabling symptom of the disease: fatigue.
Conducted in over 2,300 individuals in Northern California with multiple sclerosis, the large, population-based study found that, overall, more than 70 percent of participants screened positive for one or more sleep disorders.
The research highlights the importance of diagnosing the root causes ...
How evolutionary principles could help save our world
2014-09-15
The age of the Anthropocene--the scientific name given to our current geologic age--is dominated by human impacts on our environment. A warming climate. Increased resistance of pathogens and pests. A swelling population. Coping with these modern global challenges requires application of what one might call a more-ancient principle: evolution.
That's the recommendation of a diverse group of researchers, in a paper published today in the online version of the journal Science. A majority of the nine authors on the paper have received funding from the National Science Foundation ...
Boosting armor for nuclear-waste eating microbes
2014-09-15
EAST LANSING, Mich. – A microbe developed to clean up nuclear waste and patented by a Michigan State University researcher has just been improved.
In earlier research, Gemma Reguera, MSU microbiologist, identified that Geobacter bacteria's tiny conductive hair-like appendages, or pili, did the yeoman's share of remediation. By increasing the strength of the pili nanowires, she improved their ability to clean up uranium and other toxic wastes.
In new research, published in the current issue of Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Reguera has added an additional layer ...
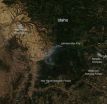
Selway complex and Johnson Bar fires in Idaho
2014-09-15
Two fires are seen burning in this satellite image taken by the Aqua satellite on September 11, 2014. The Selway complex of fires had been previously reported located 30 miles west of Darby, MT. It appears a new fire may have started again in this complex. Currently the size of the complex is 1,659 fires. The fire is mostly contained and there will be no additional reporting on this fire unless activity increases. It is, for the most part, contained.
The Johnson Bar fire started with a lightning strike on August 03, 2014. To date, 8,867 acres have been affected. ...
New glaucoma culprit is found
2014-09-15
Glaucoma, a leading cause of irreversible blindness, is associated with elevated pressure in the eye. This elevated pressure essentially is due to a plumbing problem. Fluid builds up in the eye, increasing pressure and eventually damaging the optic nerve. For nearly 150 years, researchers have been trying to understand what causes the blockage that prevents the eye from draining properly.
In a unique study of human ocular cells, a multi-institution research team led by a biomedical engineer at Northwestern University has found a new culprit. Glaucoma appears to be a consequence ...
Getting hot and wet in Vermont
2014-09-15
Here's your northern Vermont forecast for the rest of this century: annual precipitation will increase by between a third and half an inch per decade, while average temperatures will rise some five degrees Fahrenheit by midcentury. By late in the century, average temperatures will have spiked more than eight degrees. In July, by 2100, the City of Burlington will have at least ten additional days above ninety degrees. The growing season picks up 43 more days. Looking at ski conditions, expect annual snowfall at six major ski resorts to decline about fifty percent by century's ...
Mayo finds many liver transplant patients can avoid costly stay in ICU after surgery
2014-09-15
JACKSONVILLE, Fla., Sept. 12, 2014 — The liver transplant team at Mayo Clinic in Florida has found, based on 12 years of experience, that more than half of patients receiving a new liver can be "fast-tracked" to return to a surgical ward room following their transplant, bypassing a one- or two-day stay in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU).
In the September issue of the American Journal of Transplantation, the physicians and researchers have turned their knowledge of who can be safely fast-tracked into a scoring system that other transplant centers can also use — thus sparing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Nurses need education on advance health care directives, reports Journal of Christian NursingHospital shares effective training program on advance directives and end-of-life care