(Press-News.org) This news release is available in French.
Dairy is considered part of a healthy diet and dietary guidelines recommend the daily consumption of 2-4 portions of milk-based products such as milk, yogurt, cheese, cream and butter.
It's well known that dairy products contain calcium and minerals good for bones, but new research has shown that dairy consumption may also have beneficial effects on metabolic health and can reduce risk of metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Curious about these impacts, researchers from CHU de Québec Research Center and Laval University studied the dairy-eating habits of healthy French-Canadians' and monitored how dairy consumption may have an effect on their overall metabolic health. They published their findings today in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.
The aim of this study was to determine associations between dairy intake and specific metabolic risk factors, including anthropometric status, plasma glucose, plasma lipid profile, inflammatory markers and blood pressure, in a healthy population.
A total of 254 participants from the greater Quebec City metropolitan area were recruited; 233 participants (105 men and 128 women) met all the eligibility criteria for the study ‒ subjects had healthy metabolic profiles.
The study showed that the average individual consumed 2.5 ± 1.4 portions of dairy per day. However, nearly 45% of the population in this study did not meet Canada's Food Guide recommendations of at least 2 portions of dairy products a day. These findings are supported by recent Canadian surveys that highlighted an under consumption of dairy products by Canadians.
Data suggest that trans-palmitoleic acid found in plasma may be potentially used as a biomarker to evaluate dairy consumption. Trans-palmitoleic acid, is naturally present in milk, cheese, yogurt, butter, and meat fat but cannot be synthetized by the body. This fatty acid has been recently shown to have health-promoting effects. In this study, that trans-palmitoleic acid level was related to lower blood pressure in men and women, and to lower body weight in men.
Dairy intake is associated with lower blood glucose and blood pressure in the population studied, though no causal relationships can be made due to the cross-sectional design. This study adds to a growing body of literature demonstrating a lack of detrimental health effects with higher dairy intake.
Dr. Iwona Rudkowska, a research scientist at the Endocrinology and Nephrology Department, at the CHU de Québec Research Center and assistant professor at Laval University , says "additional well-designed intervention studies are needed to ascertain the effects of increased dairy consumption on metabolic health in healthy and in metabolically deteriorated populations."
INFORMATION:
The paper "Associations between dairy intake and metabolic risk parameters in a healthy French-Canadian population" was published today in Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.
Please cite Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism as the source of this story and include hyperlink to paper: http://www.nrcresearchpress.com/doi/abs/10.1139/apnm-2014-0154
More cheese, please! New study shows dairy is good for your metabolic health
Almost half of those surveyed not getting enough dairy
2014-09-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neuroimaging technique identifies concussion-related brain disease in living brain
2014-09-16
An experimental positron emission tomography (PET) tracer is effective in diagnosing concussion-related brain disease while a person is still alive, according to a case study conducted at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and at Molecular Neuroimaging (MNI) LLC in New Haven, and published September 16 in the journal Translational Psychiatry.
Specifically, the study results suggest that an experimental radiolabeled compound called [18 F]-T807, which is designed to latch onto a protein called tau that accumulates in the brain with repetitive blows to the head, ...
Lactation linked to reduced estrogen receptor-negative, triple-negative breast cancer risk
2014-09-16
(Boston) — Women who have had children (parous women) appear to have an increased risk of developing estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer, the subtype that carries a higher mortality rate and is more common in women of African ancestry. A similar relationship was found for triple-negative breast cancer. However, the association between childbearing and increased risk of estrogen receptor-negative and triple-negative breast cancer was largely confined to the women who had never breastfed. These findings, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, suggest ...
Select group of stage IV lung cancer patients achieve long-term survival after aggressive treatments
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 16, 2014—A large, international analysis of patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) indicates that a patient's overall survival (OS) rate can be related to factors including the timing of when metastases develop and lymph node involvement, and that aggressive treatment for "low-risk" patients leads to a five-year OS rate of 47.8 percent, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting.
When lung cancer has spread from an original tumor to other sites of the ...
New gene research helps pinpoint prostate cancer risk
2014-09-16
Scientists could soon better predict a man's risk of getting prostate cancer after a worldwide team of researchers carried out the largest-ever analysis of the cancer's genetic biomarkers, reported in Nature Genetics today.
QUT Institute of Health and Biomedical Innovation's Dr Jyotsna Batra and Distinguished Professor Judith Clements, who led the Australian researchers in the large consortia of research hubs around the world, said the teams analysed more than 10 million genetic markers in 80,000 men.
"It's the largest analysis of genetic biomarkers ever done. We found ...
Scientists create therapy-grade stem cells using new cocktail to reprogram adult cells
2014-09-16
Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have developed a new cocktail that is highly effective at coaxing adult cells to become quality pluripotent stem cells.
Regenerative medicine is a new and expanding area that aims to replace lost or damaged cells, tissues or organs through cellular transplantation. Because stem cells derived from human embryos can trigger ethical concerns, a good solution is reprogramming adult cells back to an embryo-like state using a combination of reprogramming factors.
The resulting cells, called induced pluripotent stem cells ...
NSCLC patients who never smoked or who quit smoking have lower risk of developing secondary cancers
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 16, 2014— Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) survivors who never smoked or who are former smokers at the time of diagnosis have a lower risk of developing secondary primary lung cancers (SPLC) compared to those who are current smokers, suggesting that increased tobacco exposure is associated with a higher risk of SPLC, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting.
The analysis studied the association between patients' smoking histories and their risks of developing SPLC, which ...
Poor body size judgement can lead to increased tolerance of obesity
2014-09-16
Size is relative, especially to people who tend to be on the heavy side. Researchers at the Columbia University Medical Center in the US found that seven in every ten obese adults underestimate how much someone weighs. People of normal weight make this mistake much less often. Mothers of overweight or obese children also tend to misjudge their children's size, as youngsters misjudge their obese mothers' size, says lead author Tracy Paul, now at Weill-Cornell Medical College, in a study¹ in the Journal of General Internal Medicine², published by Springer.
If abnormal weight ...
Prostate cancer patients who receive hypofractionated RT report consistent QoL
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—Prostate cancer patients who received hypofractionated (HPFX) radiation therapy (RT) reported that their quality of life, as well as bladder and bowel function were at similar levels before and after RT, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting. Additionally, results indicate that parallel quality of life outcomes occurred between groups of patients who receive different regimens of HPFX RT.
The phase I/II trial enrolled 343 patients with low-to-intermediate risk ...
Prostate cancer patients surveyed 5 years after vessel-sparing RT report preserved sexual function
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—A comparison of five-year sexual function outcomes, as reported by patients treated with external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) versus combination EBRT plus brachytherapy, indicates that the utilization of vessel-sparing radiation therapy makes cure possible without compromising long-term sexual function, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting.
The study examined the patient-reported outcomes of 91 men with prostate cancer who received MRI-guided, vessel-sparing ...
Keystone XL would likely raise oil sands production and greenhouse gas emissions
2014-09-16
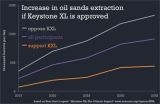
Approval of the Keystone XL pipeline (KXL) would likely increase oil sands extraction, according to 26 oil sands professionals and researchers surveyed by the non-profit organization Near Zero. The results are detailed in the report, "Keystone XL: The Climate Impact," and includes both supporters and opponents of the pipeline.
This additional extraction of oil sands could lead to significantly higher greenhouse gas emissions, with the exact amount depending largely on how markets respond.
"This report examines three main scenarios discussed by participants in our ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
[Press-News.org] More cheese, please! New study shows dairy is good for your metabolic healthAlmost half of those surveyed not getting enough dairy