Artworks are people!
Study finds 'magical contagion' spreads creator's essence to pieces, adding value
2014-09-16
(Press-News.org) Not all things are created equally. We don't view a Picasso sculpture in the same way we look at a hammer, for example — no matter how fancy the hammer.
The reason? We see the Picasso more as a person than an object, according to new research from the University of Chicago Booth School of Business.
And in some cases, we make distinctions between artworks — say, an exact replica of a piece created by the artist, versus one created by a different artist.
Art, in other words, is an extension of the creator, write Professor Daniel M. Bartels of Chicago Booth, and Professor George E. Newman and Rosanna K. Smith, a doctoral student, both of Yale University School of Management.
In their paper, "Are Artworks More Like People Than Artifacts? Individual Concepts and Their Extensions," published in the journal Topics in Cognitive Science, the researchers build on previous studies that looked at the continuity of people. For example, if you transplant someone's brain into another body and the memories remain stored in the body, is that the same person? Identity is determined by the sameness of physical and mental states — and this view applies to art, as well.
"We have intuitions about the continuity of people and other kinds of one-of-a-kind objects," Bartels said.
They found that people viewed copies of tools the same as the original, no matter who manufactured them. But with art, replicas created by the original artist were viewed similarly to the original, whereas they were not when another artist made the re-creations.
This has to do with "magical contagion" — the idea that the essence of the artist rubs off on the creation.
"If the artist made physical contact with the replica, it's as if the artist imbued the work with her/his essence by having worked with the (new, replica) piece — it seems like others who might make the copy or other processes by which a copy could be made can't transmit this essence in this way," Bartels said.
Newman added: "One prediction that comes out of this idea is that artwork that seems like it has really had a lot of close physical contact with the artist, i.e., you can see evidence of his or her 'hand,' may be preferred to art where that direct physical connection is less obvious."
INFORMATION:
Contact: Professor Bartels is available for further comment at Daniel.Bartels@chicagobooth.edu.
From: Ethan Grove, Chicago Booth Office of Media Relations, 773.834.5161 (office), 773.420.8670 (cell), Ethan.Grove@chicagobooth.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
For electronics beyond silicon, a new contender emerges
2014-09-16
Cambridge, Mass. – September 16, 2014 – Silicon has few serious competitors as the material of choice in the electronics industry. Yet transistors, the switchable valves that control the flow of electrons in a circuit, cannot simply keep shrinking to meet the needs of powerful, compact devices; physical limitations like energy consumption and heat dissipation are too significant.
Now, using a quantum material called a correlated oxide, Harvard researchers have achieved a reversible change in electrical resistance of eight orders of magnitude, a result the researchers ...
NASA's Global Hawk and satellites investigating Hurricane Edouard today
2014-09-16
The unmanned Global Hawk aircraft that's part of NASA's airborne Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel, or HS3 mission was winging its way to Hurricane Edouard on September 16. In addition to the Global Hawk, various NASA satellites are continually providing data on the Atlantic hurricane.
Scientific instruments aboard NASA's remotely piloted Global Hawk aircraft have been studying the hurricane over the last couple of days, and the Global Hawk returned to Edouard again today, September 16. Two of the instruments aboard the Global Hawk that will study Edouard are the S-HIS ...
Cancer patients with malignant spinal cord compression have preserved mobility
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—Mobility is equally preserved in cancer patients suffering from malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) who receive a single dose of 10 Gy of radiation therapy (RT), compared to patients who receive five daily doses of 4 Gy of RT each, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting.
Malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) is a complication of metastatic cancer mostly with bone involvement that occurs when a tumor's secondary deposit presses on the spinal cord and ...
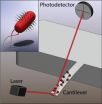
And so they beat on, flagella against the cantilever
2014-09-16
WASHINGTON D.C., September 16, 2014 – A team of researchers at Boston University and Stanford University School of Medicine has developed a new model to study the motion patterns of bacteria in real time and to determine how these motions relate to communication within a bacterial colony.
The researchers chemically attached colonies of Escherichia coli bacteria to a microcantilever – a microscopic beam anchored at one end, similar to a diving board – thus coupling its motion to that of the bacteria. As the cantilever itself isn't doesn't generate any vibrations, or 'noise,' ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Odile knocking at US Southwest
2014-09-16
Tropical Storm Odile continues to drench western Mexico and has now entered into the U.S. Southwest. On September 15, NASA's Terra satellite saw Odile's northernmost edge crossing the Mexican border into southern California. NOAA's GOES-East satellite on September 16 showed Odile's outer bands were already bringing storms to southern Arizona.
NASA Sees Odile Knocking on U.S. Border
On Sept. 15 at 2:35 p.m. EDT, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite saw the northern fringes of Hurricane Odile straddling the border ...
Scientists twist radio beams to send data
2014-09-16
Building on previous research that twisted light to send data at unheard-of speeds, scientists at USC have developed a similar technique with radiowaves, reaching high speeds without some of the hassles that can go with optical systems.
The researchers, led by electrical engineering professor Alan Willner of the USC Viterbi School of Engineering, reached data transmission rates of 32 gigabits per second across 2.5 meters of free space in a basement lab at USC.
For reference, 32 gigabits per second is fast enough to transmit more than 10 hour-and-a-half-long HD movies ...
Kessler Foundation scientists link slowed processing speed with executive deficits in MS
2014-09-16
West Orange, NJ. September 16, 2014. Kessler Foundation researchers have published a study supporting the role of slowed processing speed in the executive deficits found in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS). "Does slowed processing speed account for executive deficits in multiple sclerosis? Evidence from neuropsychological performance and structural neuroimaging," was published online ahead of print on August 18 by Rehabilitation Psychology The authors are Victoria Leavitt, PhD, of the Manhattan Memory Center, formerly of Kessler Foundation. Co-authors are Foundation ...
Tornadoes occurring earlier in 'Tornado Alley'
2014-09-16
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Peak tornado activity in the central and southern Great Plains of the United States is occurring up to two weeks earlier than it did half a century ago, according to a new study whose findings could help states in "Tornado Alley" better prepare for these violent storms.
Tornado records from Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and northern Texas – an area of high tornado activity dubbed "Tornado Alley" -- show that peak tornado activity is starting and ending earlier than it did 60 years ago.
Peak tornado activity, which occurs in the region from early ...
Water-based nuclear battery developed by MU can be used to generate electrical energy
2014-09-16
COLUMBIA, Mo. – From cell phones to cars and flashlights, batteries play an important role in everyday life. Scientists and technology companies constantly are seeking ways to improve battery life and efficiency. Now, for the first time using a water-based solution, researchers at the University of Missouri have created a long-lasting and more efficient nuclear battery that could be used for many applications such as a reliable energy source in automobiles and also in complicated applications such as space flight.
"Betavoltaics, a battery technology that generates power ...
Patients waiting too long to see doctor? Try 'just-in-time' management methods, researchers urge
2014-09-16
Using a pain clinic as a testing ground, researchers at Johns Hopkins have shown that a management process first popularized by Toyota in Japan can substantially reduce patient wait times and possibly improve the teaching of interns and residents.
In a report on the pilot study, published online Sept. 9, in Pain Medicine, the researchers adopted the so-called "Just-in-Time" training and inventory process used now by many manufacturers and service industries to stem waste and keep complicated operations from bottlenecking.
"We realized that a significant amount of time ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] Artworks are people!Study finds 'magical contagion' spreads creator's essence to pieces, adding value