(Press-News.org) Ageing of insulin-secreting cells is coupled to a progressive decline in signal transduction and insulin release, according to a recent study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. The finding, which is published in the journal Diabetes, provides a new molecular mechanism underlying age-related impairment of insulin-producing cells and diabetes.
Ageing is among the largest known risk factors for many diseases, and type 2 diabetes is no exception. People older than 65 years have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes if their insulin-producing cells in the pancreas fail to compensate for insulin resistance. A decline in insulin secretion from these so called beta cells is considered to be a major contributing factor to disease development, but little has been known about why this happens.
As the investigators behind the recent study searched for a link between ageing, beta cell dysfunction and diabetes, they took a closer look at calcium ions.
"Calcium ions as mediators of signals in the cell play a crucial role in regulating the function and survival of insulin-producing beta cells", says Luo-Sheng Li, at The Rolf Luft Research Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology at Karolinska Institutet, the study's first author.
The researchers studied three different types of mice that differ in age-induced deterioration. The first was a genetically modified mouse that accumulate DNA mutations in the cellular power plants, the mitochondria, and thus age prematurely. The second type of mouse represents naturally mature ageing, whereas the third is more resistant to age-induced deterioration. When comparing the mice, the investigators found that the function of the mitochondria is reduced with age. This age-dependent reduction of mitochondrial function in beta cells ultimately leads to reduced insulin release.
The study demonstrates that an impaired fine tuning of the free calcium concentration in the beta cell is the molecular mechanism linking mitochondrial dysfunction to impaired insulin release.
"The defective metabolism-induced deterioration in calcium ion dynamics reflects an important age-dependent phenotype that may have a critical role in the development of type 2 diabetes", says Principal Investigator Per-Olof Berggren at The Rolf Luft Research Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology. "This is important information that may lay the foundation for a novel treatment regimen for diabetes."
INFORMATION:
The work conducted at Karolinska Institutet was supported by, among others, the Swedish Research Council, the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Swedish Diabetes Association, and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation.
Publication: "Defects in β-Cell Ca2+ Dynamics in Age-Induced Diabetes", Li L, Trifunovic A, Köhler M, Wang Y, Berglund JP, Illies C, Juntti-Berggren L, Larsson NG, Berggren PO, Diabetes, epub ahead of print 1 July 2014, doi:10.2337/db13-1855.
Karolinska Institutet - a medical university: ki.se/english
Mechanism behind age-dependent diabetes discovered
2014-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds Great Barrier Reef is an effective wave absorber
2014-09-17
New research has found that the Great Barrier Reef, as a whole, is a remarkably effective wave absorber, despite large gaps between the reefs. This means that landward of the reefs, waves are mostly related to local winds rather than offshore wave conditions.
As waves break and reduce in height over reefs, this drives currents that are very important for the transport of nutrients and larvae. This reduction in wave height also has implications for shoreline stability.
The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is the largest coral reef system in the world, extending 2,300 ...
New MRI technique helps clinicians better predict outcomes following mild traumatic brain injury
2014-09-17
New Rochelle, NY, September 17, 2014—Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI), a specialized magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique that detects microstructural changes in brain tissue, can help physicians better predict the likelihood for poor clinical outcomes following mild traumatic brain injury compared to conventional imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT), according to a new study published in Journal of Neurotrauma, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Neurotrauma website until October ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Kalmaegi weakening over Vietnam
2014-09-17
Tropical Storm Kalmaegi made landfall on September 17 near the border of Vietnam and China and moved inland. Soon after the landfall as a typhoon, NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead and captured an image of the weaker tropical storm.
The MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua took a visible picture of Tropical Storm Kalmaegi on Sept. 17 at 03:35 UTC (Sept. 16 at 11:35 p.m. EDT). The image showed the center of the storm in northeastern Vietnam, just south of the China border. Kalmaegi's clouds extended north into southern China and west into Laos.
The Vietnamese ...
Size at birth affects risk of adolescent mental health disorders
2014-09-17
New research from the Copenhagen Centre for Social Evolution and Yale University offers compelling support for the general evolutionary theory that birth weight and -length can partially predict the likelihood of being diagnosed with mental health disorders such as autism and schizophrenia later in life. The study analyzed medical records of 1.75 million Danish births, and subsequent hospital diagnoses for up to 30 years, and adjusted for almost all other known risk factors. The study is published today in the Proceedings of the Royal Society, London B.
The number of ...
Artificial 'beaks' that collect water from fog: A drought solution?
2014-09-17
From the most parched areas of Saudi Arabia to water-scarce areas of the western U.S., the idea of harvesting fog for water is catching on. Now, a novel approach to this process could help meet affected communities' needs for the life-essential resource. Scientists describe their new, highly efficient fog collector, inspired by a shorebird's beak, in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Cheng Luo and his doctoral student, Xin Heng, explain that deserts and semi-arid areas cover about half of the Earth's land masses. In some of these places, trucks bring in ...
Parts of genome without a known function may play a key role in the birth of new proteins
2014-09-17
Researchers in Biomedical Informatics at IMIM (Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute) and at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) have recently published a study in eLife showing that RNA called non-coding (IncRNA) plays an important role in the evolution of new proteins, some of which could have important cell functions yet to be discovered.
Ribosomes produce proteins from the instructions found in an RNA molecule. However, only 2% of the human genome is RNA containing information for the synthesis of proteins, meaning it is coding. Other parts of the ...
Iberian pig genome remains unchanged after 5 centuries
2014-09-17
A team of Spanish researchers have obtained the first partial genome sequence of an ancient pig. Extracted from a sixteenth century pig found at the site of the Montsoriu Castle in Girona, the data obtained indicates that this ancient pig is closely related to today's Iberian pig. Researchers also discard the hypothesis that Asian pigs were crossed with modern Iberian pigs.
The study, published in Heredity, sheds new light on evolutionary aspects of pig species, and particularly on that of the Iberian breed, considered to be representative of original European Mediterranean ...
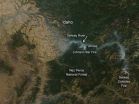
Smoke wafts over the Selway Valley in Idaho
2014-09-17
Smoke from the fires in the Selway Complex is wafting into the Selway River valley in this image taken by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Terra satellite on September 15, 2014. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red. All the fires began between August 10 and August 25, 2014 by lightning strikes. The following fires are part of the Selway Complex: Raven Creek, Elevator Mountain, Eagle Creek, Vance Mountain, Nick Wynn, and Jerusalem fires.
The Johnson Bar fire is also contributing to the smoke ...
Slimy fish and the origins of brain development
2014-09-17
Lamprey—slimy, eel-like parasitic fish with tooth-riddled, jawless sucking mouths—are rather disgusting to look at, but thanks to their important position on the vertebrate family tree, they can offer important insights about the evolutionary history of our own brain development, a recent study suggests.
The work appears in a paper in the September 14 advance online issue of the journal Nature.
"Lamprey are one of the most primitive vertebrates alive on Earth today, and by closely studying their genes and developmental characteristics, researchers can learn more about ...
Improved risk identification will aid fertility preservation in young male cancer patients
2014-09-17
(MEMPHIS, TENN. – September 16, 2014) A study led by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital investigators has found the chemotherapy dose threshold below which male childhood cancer survivors are likely to have normal sperm production. The study appears in September 17 edition of the journal Lancet Oncology.
By clarifying which patients are at highest risk for reduced sperm production as adults, researchers expect the findings to eventually increase use of pre-treatment fertility preservation methods such as sperm banking.
The study involved drugs called alkylating agents ...