(Press-News.org) Hurricane Polo still appears rounded in imagery from NOAA's GOES-West satellite, but forecasters at the National Hurricane Center expect that to change.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured data on Hurricane Polo on Sept. 18 at 10:15 a.m. EDT. An image using that data was created by the NASA/NOAA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The image showed thunderstorms wrapping tightly around the center of the storm while one broken band of thunderstorms extended to the northwest, while the other appeared on the eastern side of the center and paralleled the southern Mexican coastline.
Polo presents a threat to the coast of southwestern Mexico's coastline. A Tropical Storm Warning is in effect for Punta San Telmo to Playa Perula and a Tropical Storm Watch is in effect for west of Playa Perula to Cabo Corrientes.
Forecasters from the National Hurricane Center (NHC) examining satellite imagery today, Sept. 18 noted that "there is a small central dense overcast surrounded by a cyclonically curved convective band (a band of thunderstorms). Polo has the opportunity to strengthen before the northeasterly wind shear increases in 24 hours before it is expected to gradual weaken.
At 11 a.m. EDT on Sept. 18, the center of Hurricane Polo was located near latitude 17.3 north and longitude 105.7 west. That's about 150 miles (240 km) southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico. Maximum sustained winds were near 75 mph (120 kph) and some slight strengthening is possible in the next day, according to the NHC. Polo is moving toward the northwest near 8 mph (13 kph) and is expected to continue in that direction for the next couple of days.
NHC noted that Polo will move parallel to the southwestern coast of Mexico, although any deviation from the forecast track could mean stronger winds to the coast. After Sept. 19, Polo is expected to weaken.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA marks Polo for a hurricane
2014-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New Dartmouth smartphone app reveals users' mental health, performance, behavior
2014-09-18
Dartmouth researchers and their colleagues have built the first smartphone app that automatically reveals students' mental health, academic performance and behavioral trends. In other words, your smartphone knows your state of mind -- even if you don't -- and how that affects you.
The StudentLife app, which compares students' happiness, stress, depression and loneliness to their academic performance, also may be used in the general population – for example, to monitor mental health, trigger intervention and improve productivity in workplace employees.
"The StudentLife ...
Fall foliage season may be later, but longer on warmer Earth
2014-09-18
The fall foliage season that prompts millions of Americans to undertake jaunts into the countryside each year could come much later and possibly last a little longer within a century, according to new research.
Climate change could postpone fall leaf peeping in some areas of the United States as summer temperatures linger later into the year, Princeton University researchers report in the journal Global Ecology and Biogeography. For instance, the paper birch — a popular foliage tree that is the state tree of New Hampshire — could change color one to three weeks later ...
Want to link genes to complex traits? Start with more diversity
2014-09-18
Life is rarely simple. From crop yields to disease risks, the biological characteristics people care most about are usually those considered "complex traits." Just as for height—the textbook example of a complex trait—attributes like risk for a particular human disease are shaped by multiple genetic and environmental influences, making it challenging to find the genes involved. To track down such genes, geneticists typically mate two individuals that differ in key ways—for example, a large mouse and a small mouse—and then study their descendents, looking for genes that ...
Americans rate losing eyesight as having greatest impact on their lives
2014-09-18
ALEXANDRIA, Va.—Sept. 18, 2014—Many Americans across racial and ethnic groups describe losing eyesight as potentially having the greatest impact on their day-to-day life, more so than other conditions including: loss of limb, memory, hearing and speech (57% of African-Americans, 49% of non-Hispanic whites, 43% of Asians and 38% of Hispanics). When asked which disease or ailment is the worst that could happen to them, blindness ranked first among African-Americans followed by AIDS/HIV. Hispanics and Asians ranked cancer first and blindness second, while Alzheimer's disease ...
Living in a disadvantaged neighborhood worsens musculoskeletal pain outcomes after trauma
2014-09-18
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Individuals living in disadvantaged neighborhoods have worse musculoskeletal pain outcomes over time after stressful events such as motor vehicle collision than individuals from higher socioeconomic status neighborhoods, even after accounting for individual characteristics such as age, sex, income, education, and employment status.
These were the findings of a multi-site research study led by Samuel McLean, MD, MPH, associate professor of anesthesiology and emergency medicine at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine. The results of the ...
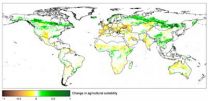
Global agriculture: More land, fewer harvests
2014-09-18
According to a simulation of the impact of climate change on agricultural production over the course of the 21st century, carried out by researchers led by Professor Wolfram Mauser at LMU's Department of Geography, some two-thirds of all land potentially suitable for agricultural use is already under cultivation. The study indicates that climate change will expand the supply of cropland in the high latitudes of the Northern hemisphere (Canada, Russia, China) over the next 100 years. However, in the absence of adaptation measures such as increased irrigation, the simulation ...
Withdrawal from the evolutionary race
2014-09-18
This news release is available in German. In ecology, disease tolerance is defined as a host strategy not to fight a pathogen tooth and nail, but rather tolerate it to live (and survive) better in the long term. One key feature of tolerance is that the disease only progresses very slowly – if at all – even if the host carries a high pathogen load.
Roland Regoes, a senior scientist at ETH Zurich's Institute of Theoretical Biology, has now transferred this approach to HIV. He set about investigating whether there are infected people who are more tolerant of the HI virus ...
Decision-support program helps keep seniors out of the emergency room
2014-09-18
New Rochelle, NY, September 18, 2014–An Emergency Room Decision-Support (ERDS) program can significantly reduce ER visits and hospital admissions among older adults on Medicare. This could have important economic implications, helping to reduce the nearly 33% of avoidable ER visits that contribute to about $18 billion in unnecessary healthcare costs each year. Details of a successful ERDS program that had a positive return on investment are published in an article in Population Health Management, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article ...
Language evolution: Quicker on the uptake
2014-09-18
The ability to acquire and creatively manipulate spoken language is unique to humans. "The genetic changes that occurred over the past 6 million years of human evolution to make this possible are largely unknown, but Foxp2 is the best candidate gene we now have," says Wolfgang Enard, Professor of Anthropology and Human Biology at LMU. In his efforts to understand the molecular biological basis of language Enard has now taken an important step forward. The results of his latest study, undertaken in collaboration with scientists at several universities, including the Massachusetts ...
First eyewitness accounts of mystery volcanic eruption
2014-09-18
This eruption occurred just before the 1815 Tambora volcanic eruption which is famous for its impact on climate worldwide, with 1816 given memorable names such as 'Eighteen-Hundred-and-Froze-to-Death', the 'Year of the Beggar' and the 'Year Without a Summer' because of unseasonal frosts, crop failure and famine across Europe and North America. The extraordinary conditions are considered to have inspired literary works such as Byron's 'Darkness' and Mary Shelley's Frankenstein.
However, the global deterioration of the 1810s into the coldest decade in the last 500 years ...