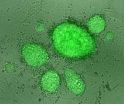
(Press-News.org) Stem cells hold great promise as a means of repairing cells in conditions such as multiple sclerosis, stroke or injuries of the spinal cord because they have the ability to develop into almost any cell type. Now, new research shows that stem cell therapy can also work through a mechanism other than cell replacement.
In a study published today in Molecular Cell, a team of researchers led by the University of Cambridge has shown that stem cells "communicate" with cells by transferring molecules via fluid filled bags called vesicles, helping other cells to modify the damaging immune response around them.
Although scientists have speculated that stem cells might act rather like drugs – in sensing signals, moving to specific areas of the body and executing complex reactions – this is the first time that a molecular mechanism for this process has been demonstrated. By understanding this process better, researchers can identify ways of maximising the efficiency of stem-cell-based therapies.
Dr Stefano Pluchino from the Wellcome Trust-Medical Research Council Cambridge Stem Cell Institute, who led the study, said: "These tiny vesicles in stem cells contain molecules like proteins and nucleic acids that stimulate the target cells and help them to survive – they act like mini "first aid kits".
"Essentially, they mirror how the stem cells respond to an inflammatory environment like that seen during complex neural injuries and diseases, and they pass this ability on to the target cells. We think this helps injured brain cells to repair themselves."
Mice with damage to brain cells – such as the damage seen in multiple sclerosis – show a remarkable level of recovery when neural stem/precursor cells (NPCs) are injected into their circulatory system. It has been suggested that this happens because the NPCs discharge molecules that regulate the immune system and that ultimately reduce tissue damage or enhance tissue repair.
The team of researchers from the UK, Australia, Italy, China and Spain has now shown that NPCs make vesicles when they are in the vicinity of an immune response, and especially in response to a small protein, or cytokine, called Interferon-gamma which is released by immune cells. This protein has the ability to regulate both the immune responses and intrinsic brain repair programmes and can alter the function of cells by regulating the activity of scores of genes.
Their results show that a highly specific pathway of gene activation is triggered in NPCs by IFN-gamma, and that this protein also binds to a receptor on the surface of vesicles. When the vesicles are released by the NPCs, they adhere and are taken up by target cells. Not only does the target cell receive proteins and nucleic acids that can help them self-repair, but it also receives the IFN-gamma on the surface of the vesicles, which activates genes within the target cells.
The researchers, who were funded by the European Research Council and the Italian MS Society, used electron microscopy and superresolution imaging to visualise the vesicles moving between the NPCs and target cells in vitro.
"Our work highlights a surprising novel role for stem-cell-derived vesicles in propagating responses to the environment," added Pluchino. "It represents a significant advance in understanding the many levels of interaction between stem cells and the immune system, and a new molecular mechanism to explain how stem-cell therapy works."
INFORMATION:
Stem cells use 'first aid kits' to repair damage
2014-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NYU Langone scientists report reliable and highly efficient method for making stem cells
2014-09-18
NEW YORK, September 18, 2014 – Scientists at NYU Langone Medical Center have found a way to boost dramatically the efficiency of the process for turning adult cells into so-called pluripotent stem cells by combining three well-known compounds, including vitamin C. Using the new technique in mice, the researchers increased the number of stem cells obtained from adult skin cells by more than 20-fold compared with the standard method. They say their technique is efficient and reliable, and thus should generally accelerate research aimed at using stem cells to generate virtually ...
The war on leukemia: How the battle for cell production could be decisive
2014-09-18
A key step in understanding the nature of the fight for superiority between mutated genes and normal genes could lead to new therapies to combat leukaemia, say researchers from the University of Birmingham and Newcastle University.
The study, published in Cell Reports, investigated Acute Myeloid Leukaemia to understand why leukemic cells are not able to develop normally into mature blood cells.
Stem cells in the bone marrow generate billions of different blood cells each day. The process resembles a production line with genes acting as regulators to control each step ...
NASA sees Hurricane Edouard enter cooler waters
2014-09-18
VIDEO:
On Sept. 17 at 03:39 UTC, the TRMM satellite saw a newer outer eyewall forming around Edouard's original eyewall creating a double eye-wall structure. Red indicates heavy rainfall....
Click here for more information.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite and Aqua satellite gathered data on Hurricane Edouard's rainfall, clouds and waning power is it continued moving northward in the Atlantic into cooler waters. On Sept. 18, NASA's Global Hawk #872 ...
Scientists find how mysterious 'circular RNA' is formed, claim muscular dystrophy link
2014-09-18
Our genetic information is stored in DNA, tiny strands of nucleic acid that contain instructions for the functioning of our bodies. To express this genetic data, our DNA is copied into RNA molecules, which then translate the instructions into proteins that perform tasks in our cells.
Several years ago, scientists discovered a new type of RNA molecule. Unlike all other known RNAs, this molecule is circular, and was labeled circular RNA. Although circRNA molecules are abundant, little has been known about how they are produced. Moreover, little has been known about the ...
Flu vaccine for expectant moms a top priority
2014-09-18
WHITE PLAINS, NY, SEPT. 18, 2014 -- Only about half of all pregnant women in the U.S. get a flu shot each season, leaving thousands of moms-to-be and their babies at increased risk of serious illness.
"Getting a flu shot should be a routine part of prenatal care," said Edward McCabe, MD, March of Dimes chief medical officer. "Health care providers should offer their pregnant patients a flu shot each year and if they don't, then women should ask for it."
A report by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and prevention presented today by the National Foundation for ...
New high-resolution satellite image analysis: 5 of 6 Syrian World Heritage sites 'exhibit significant damage'
2014-09-18
SEPTEMBER 18 —In war-torn Syria, five of six World Heritage sites now "exhibit significant damage" and some structures have been "reduced to rubble," according to new high-resolution satellite image analysis by the nonprofit, nonpartisan American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS).
The AAAS analysis, offering the first comprehensive look at the extent of damage to Syria's priceless cultural heritage sites, was completed in partnership with the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology's Penn Cultural Heritage Center (PennCHC) and ...
NASA marks Polo for a hurricane
2014-09-18
Hurricane Polo still appears rounded in imagery from NOAA's GOES-West satellite, but forecasters at the National Hurricane Center expect that to change.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured data on Hurricane Polo on Sept. 18 at 10:15 a.m. EDT. An image using that data was created by the NASA/NOAA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The image showed thunderstorms wrapping tightly around the center of the storm while one broken band of thunderstorms extended to the northwest, while the other appeared on the eastern side of the center ...
New Dartmouth smartphone app reveals users' mental health, performance, behavior
2014-09-18
Dartmouth researchers and their colleagues have built the first smartphone app that automatically reveals students' mental health, academic performance and behavioral trends. In other words, your smartphone knows your state of mind -- even if you don't -- and how that affects you.
The StudentLife app, which compares students' happiness, stress, depression and loneliness to their academic performance, also may be used in the general population – for example, to monitor mental health, trigger intervention and improve productivity in workplace employees.
"The StudentLife ...
Fall foliage season may be later, but longer on warmer Earth
2014-09-18
The fall foliage season that prompts millions of Americans to undertake jaunts into the countryside each year could come much later and possibly last a little longer within a century, according to new research.
Climate change could postpone fall leaf peeping in some areas of the United States as summer temperatures linger later into the year, Princeton University researchers report in the journal Global Ecology and Biogeography. For instance, the paper birch — a popular foliage tree that is the state tree of New Hampshire — could change color one to three weeks later ...
Want to link genes to complex traits? Start with more diversity
2014-09-18
Life is rarely simple. From crop yields to disease risks, the biological characteristics people care most about are usually those considered "complex traits." Just as for height—the textbook example of a complex trait—attributes like risk for a particular human disease are shaped by multiple genetic and environmental influences, making it challenging to find the genes involved. To track down such genes, geneticists typically mate two individuals that differ in key ways—for example, a large mouse and a small mouse—and then study their descendents, looking for genes that ...