(Press-News.org) Drilling in Pennsylvania's Marcellus Shale region led to a rapid increase in both the number of hotels and hotel industry jobs, but Penn State researchers report that the faltering occupancy rate may signal that there are now too many hotel rooms.
"Demand is still high in many of the counties in the Marcellus Shale region, but the occupancy rate is starting to come down," said Daniel Mount, an associate professor in hospitality management. "The case could be made that this is a sign that hotels were overbuilt."
Marcellus drilling operations generated approximately $685 million in hotel revenues and added an extra 1,600 new hotel jobs since 2006, according to the researchers, who report their findings in the International Council on Hotel, Restaurant, and Institutional Education Penn State Research Reports. However, the latest figures show that demand for rooms may be decreasing. For example, in 2012, demand was flat and occupancy was down 4.1 percent.
If demand continues to decrease, the older, non-franchised hotels may be the most vulnerable to bankruptcy and closure, according to Mount. Of the 14 hotels that closed between 2006 and 2012, nine did not have a national franchise. The average age of the 14 closed hotels was more than 38 years old.
"The overall economic benefit of the drilling boom is still good for hoteliers, but it's just not the bonanza that it used to be," said Mount. "It may be that the newer hotels and the hotel chains are in a better position to withstand the lower demand, in which case, it will be the older, independent hotels that go out of business."
The flat rate contrasts with the explosive growth of hotel construction during the early stages of the drilling boom. Hotel developers built 65 hotels in the drilling region, which is a far greater number than national trends would suggest for hotel development, said Mount, who worked with Timothy Kelsey, professor of agricultural economics and co-director of the Center for Economic and Community Development and Kathryn Brasier, associate professor of rural sociology.
Alternative housing may explain some of the lower demand, as well, said Mount. Some companies that originally assigned workers to hotel rooms may now be housing them at alternative sites, such as apartment complexes or mobile homes, further reducing demand for hotel space.
Other workforce patterns, such as hiring more local workers and gains in workforce efficiencies, may also be contributing factors to the decreased demand in hotel rooms, said Brasier.
A drop in the price of natural gas and decrease in future drilling may also affect demand for rooms, the researchers suggest. Recently, as natural gas prices fell, the total number of wells drilled decreased from 1,968 in 2011 to 1,362 in 2012.
The researchers used the most recent data available from the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection on hotel development and drilling activity in the five major drilling regions -- northeast, north central, central, west central and southwest -- of Pennsylvania. They then compared data on hotel performance -- total demand, average daily rate and total rooms revenue -- with national figures.
INFORMATION: END
Marcellus drilling boom may have led to too many hotel rooms
2014-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Survey: Fortune 500 employees can expect to pay more for health insurance
2014-09-18
Employees working for Fortune 500 companies can expect to pay higher employee contributions for their health insurance, according to a survey of chief human resource officers about the impact of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (also known as PPACA or Obamacare) conducted by the Darla Moore School of Business at the University of South Carolina this past May/June.
Patrick Wright, a professor in strategic human resource management, directs the annual the HR@Moore Survey of Chief HR Officers. The survey is distributed to more than 560 CHROs of Fortune 500 ...
Agricultural fires in the Ukraine
2014-09-18
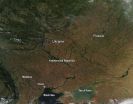
Numerous fires (marked with red dots) are burning in Eastern Europe, likely as a result of regional agricultural practices. The body of water at the lower left of this true-color Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) image is the Sea of Azov. The Sea is bordered by Ukraine to the northwest, west and southwest and by Russia to the northeast, east, and southeast. To its left is the Black Sea.
The location, widespread nature, and number of fires suggest that these fires were deliberately set to manage land. Farmers often use fire to return nutrients to the ...
Professional recommendations against routine prostate cancer screening have little effect
2014-09-18
DETROIT – The effect of guidelines recommending that elderly men should not be routinely screened for prostate cancer "has been minimal at best," according to a new study led by researchers at Henry Ford Hospital.
The study, published as a research letter online in JAMA Internal Medicine, focused on the use of PSA – prostate-specific antigen – to test for prostate cancer.
"We found that the effect of the guidelines recommending against the routine screening of elderly men in particular has been minimal at best," says Jesse Sammon, D.O., a researcher at Henry Ford's Vattikuti ...
New insights on an ancient plague could improve treatments for infections
2014-09-18
DURHAM, N.C. – Dangerous new pathogens such as the Ebola virus invoke scary scenarios of deadly epidemics, but even ancient scourges such as the bubonic plague are still providing researchers with new insights on how the body responds to infections.
In a study published online Sept. 18, 2014, in the journal Immunity, researchers at Duke Medicine and Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School Singapore detail how the Yersinia pestis bacteria that cause bubonic plague hitchhike on immune cells in the lymph nodes and eventually ride into the lungs and the blood stream, where the infection ...
Sensing neuronal activity with light
2014-09-18
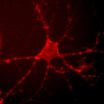
For years, neuroscientists have been trying to develop tools that would allow them to clearly view the brain's circuitry in action—from the first moment a neuron fires to the resulting behavior in a whole organism. To get this complete picture, neuroscientists are working to develop a range of new tools to study the brain. Researchers at Caltech have developed one such tool that provides a new way of mapping neural networks in a living organism.
The work—a collaboration between Viviana Gradinaru (BS '05), assistant professor of biology and biological engineering, and ...
No sedative necessary: Scientists discover new 'sleep node' in the brain
2014-09-18
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A sleep-promoting circuit located deep in the primitive brainstem has revealed how we fall into deep sleep. Discovered by researchers at Harvard School of Medicine and the University at Buffalo School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, this is only the second "sleep node" identified in the mammalian brain whose activity appears to be both necessary and sufficient to produce deep sleep.
Published online in August in Nature Neuroscience, the study demonstrates that fully half of all of the brain's sleep-promoting activity originates from the parafacial ...
Miranda: An icy moon deformed by tidal heating
2014-09-18
Boulder, Colo., USA – Miranda, a small, icy moon of Uranus, is one of the most visually striking and enigmatic bodies in the solar system. Despite its relatively small size, Miranda appears to have experienced an episode of intense resurfacing that resulted in the formation of at least three remarkable and unique surface features -- polygonal-shaped regions called coronae.
These coronae are visible in Miranda's southern hemisphere, and each one is at least 200 km across. Arden corona, the largest, has ridges and troughs with up to 2 km of relief. Elsinore corona has ...
Research milestone in CCHF virus could help identify new treatments
2014-09-18
SAN ANTONIO, September 18, 2014 – New research into the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV), a tick-borne virus which causes a severe hemorrhagic disease in humans similar to that caused by Ebolavirus, has identified new cellular factors essential for CCHFV infection. This discovery has the potential to lead to novel targets for therapeutic interventions against the pathogen.
The research, reported in a paper published today in the journal PLoS Pathogens and conducted by scientists at the Texas Biomedical Research Institute and their colleagues, represents ...
Microplastic pollution discovered in St. Lawrence River sediments
2014-09-18
A team of researchers from McGill University and the Quebec government have discovered microplastics (in the form of polyethylene 'microbeads', END ...
A new quality control pathway in the cell
2014-09-18
Proteins are important building blocks in our cells and each cell contains millions of different protein molecules. They are involved in everything from structural to regulatory aspects in the cell. Proteins are constructed as linear molecules but they only become functional once they are folded into specific three-dimensional structures. Several factors, like mutations, stress and age, can interfere with this folding process and induce protein misfolding. Accumulated misfolded proteins are toxic and to prevent this, cells have developed quality control systems just like ...