(Press-News.org) Thermal energy storage is a common strategy in energy production systems in which the period of production does not coincide with that of consumption. This happens with the production of hot water by means of solar thermal panels, for example; here, hot water is produced during sunlight hours when demand is lower. It is also the case in residential cogeneration, where heat and electrical power are simultaneously generated but not so demand. In both cases, storing the heat allows production to be decoupled from demand, thus making the integration of these technologies into buildings more flexible. Here, it is normal for periods of energy production not to coincide with those when it is consumed.
Water tanks have been traditionally used to store heat. "They work well," explained Álvaro Campos, a researcher on the project, "and water is very cheap, but large volumes are needed to achieve significant heat storage, which restricts their integration into homes, where the availability of space is very limited."
The UPV/EHU research group ENEDI has developed a prototype with 50% less volume and more flexible in terms of design; it has a prismatic shape, is easy to integrate into buildings and offers optimum use of space. What is more, its modular nature allows the design to be easily changed.
The system is based on the use of latent heat from the solid-liquid phase change of materials known as PCMs (Phase Change Materials). "When we heat these materials they have the capacity, once they reach their phase change temperature, to start changing their state; and by keeping the temperature practically constant, they allow a very high quantity of energy to be stored; that way, we can achieve much greater energy density with smaller heat losses into the atmosphere," explained Campos.
The device uses a commercial paraffin that melts at around 60 ºC. "It is very stable and has a long service life," pointed out Campos. The paraffin is encapsulated inside aluminium plates which are arranged in such a way that channels are formed between them. The thermal loading and unloading process is carried out by making water circulate through these channels, so the hot water yields heat to the plates during the loading process and melts the encapsulated material; conversely, cold water is made to circulate through the channels so that the stored heat is recovered and the paraffin solidifies. Campos' proposal solves one of the problems of PCMs which, owing to their low thermal conductivity, tend to take a very long time to yield the heat they have accumulated. "Our design is based on very thin metal plates which allow the heat to be extracted at a speed similar to that of water tanks," he concluded.
According to Campos, one of the most attractive aspects of the system lies in its compact, modular nature. Water tanks need to be cylindrical and slim (tall and thin) if they are to function optimally. "We can achieve much more compact, prismatic shapes that can be fitted into any corner, even inside a false ceiling," he remarked. "All this makes our proposal more than just an alternative to the water tank, because it offers the possibility of fitting a device for storing thermal energy in places and in applications where, owing to a lack of space, the fitting of a water tank may not be feasible," added Campos.
Right now, work is being done to build a full-scale prototype that will be integrated into an experimental facility of the Quality Control in Building Lab (LCCE) of the Government of the Basque Autonomous Community, "to study how the equipment responds under actual operating conditions".
Campos is optimistic about the competitiveness of the device. "We have something that could offer sufficient technical advantages as it is an attractive proposal irrespective of the final price." The group is already working on other potential PCMs that allow greater storage capacity and are cheaper; they include fatty acids and other organic materials.
INFORMATION:
Additional Information
Alvaro Campos-Celador is a Doctor of Engineering, researcher and lecturer at the UPV/EHU-University of the Basque Country and member of the university's consolidated research group ENEDI (Energy in Building). The team is led by Jose María Sala-Lizarraga, Professor of Thermodynamics in the UPV/EHU's Department of Thermal Machines and Engines at the Faculty of Engineering in Bilbao. The research was mainly conducted at the UPV/EHU's University School of Mining and Public Works Engineering and at the Quality Control in Building Lab of the Government of the Basque Autonomous Community, where the Thermal Area is currently being led by ENEDI. This research is registered within the microTES project (ENE2012-38633-C03), in which the University of Oviedo and the University of La Rioja are also participating.
References
A. Campos-Celador, G. Diarce, J. Terés-Zubiaga, T. Bandos, A. García-Romero, L.M. López, J.M. Sala, Design of a Finned Plate Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage System for Domestic Applications, Energy Procedia, 48 (2014) 300-308
Campos-Celador, G. Diarce, I. González-Pino, J.M. Sala, Development and comparative analysis of the modeling of an innovative finned-plate latent heat thermal energy storage system, Energy, 58 (2013) 438-447.
Patents
As a result of this research, an international patent is currently being applied for:
Modular latent thermal storage unit (WO 2014016456 A1)
Inventors: Álvaro Campos Celador, José María Sala Lizarraga, Luis Alfonso del Portillo Valdés. http://www.google.com/patents/WO2014016456A1?cl=es
Paraffins to cut energy consumption in homes
UPV/EHU-University of the Basque Country researchers develop a compact heat storage prototype that can be easily fitted in buildings
2014-09-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advancing the understanding of an understudied food allergy disorder
2014-09-23
Investigators at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have published the first study to extensively characterize eosinophilic gastritis (EG). The study, published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, found that EG is a systemic disorder that has high levels of eosinophils in the blood and gastrointestinal tract, involves a series of allergy-associated-immune mechanisms and has a gene expression pattern (transcriptome) that is distinct from that of a related disorder, eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders are chronic ...
Gene mutation discovered in blood disorder
2014-09-23
An international team of scientists has identified a gene mutation that causes aplastic anemia, a serious blood disorder in which the bone marrow fails to produce normal amounts of blood cells. Studying a family in which three generations had blood disorders, the researchers discovered a defect in a gene that regulates telomeres, chromosomal structures with crucial roles in normal cell function.
"Identifying this causal defect may help suggest future molecular-based treatments that bypass the gene defect and restore blood cell production," said study co-leader Hakon Hakonarson, ...
NASA sees Tropical Depression Fung-Wong becoming more frontal
2014-09-23
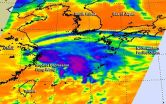
Tropical Depression Fung-Wong skirted the coast of mainland China and is moving through the East China Sea. NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data that showed strongest thunderstorms were stretched out as the storm continues to look more frontal in nature.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Fung-Wong on Sept. 22 at 1:23 p.m. EDT, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument read cloud top temperatures. AIRS detected strongest, highest storms, those with the coldest cloud tops stretched out from northwest to southeast giving the depression ...
New research suggests sleep apnea screening before surgery
2014-09-23
Scheduled for surgery? New research suggests that you may want to get screened and treated for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) before going under the knife. According to a first-of-its-kind study in the October issue of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®), patients with OSA who are diagnosed and treated for the condition prior to surgery are less likely to develop serious cardiovascular complications such as cardiac arrest or shock.
"OSA is a common disorder that affects millions and is associated with an increased ...
Recreating the stripe patterns found in animals by engineering synthetic gene networks
2014-09-23
VIDEO:
Researchers at the CRG try to understand how networks of genes work together to create specific patterns like stripes.
They have gone beyond studying individual networks and have created computational and...
Click here for more information.
Pattern formation is essential in the development of animals and plants. The central problem in pattern formation is how can genetic information be translated in a reliable manner to give specific spatial patterns of cellular differentiation. ...
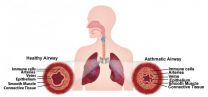
Airway muscle-on-a-chip mimics asthma
2014-09-23
The majority of drugs used to treat asthma today are the same ones that were used 50 years ago. New drugs are urgently needed to treat this chronic respiratory disease, which causes nearly 25 million people in the United States alone to wheeze, cough, and find it difficult at best to take a deep breath.
But finding new treatments is tough: asthma is a patient-specific disease, so what works for one person doesn't necessarily work for another, and the animal models traditionally used to test new drug candidates often fail to mimic human responses – costing tremendous ...
Eating five a day may keep the blues away
2014-09-23
Fruit and vegetable consumption could be as good for your mental as your physical health, new research suggests.
The research, conducted by the University of Warwick's Medical School using data from the Health Survey for England, and published by BMJ Open focused on mental wellbeing and found that high and low mental wellbeing were consistently associated with an individual's fruit and vegetable consumption.
33.5% of respondents with high mental wellbeing ate five or more portions of fruit and vegetables a day, compared with only 6.8% who ate less than one portion. ...
Southampton scientists grow a new challenger to graphene
2014-09-23
A team of researchers from the University of Southampton's Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) has developed a new way to fabricate a potential challenger to graphene.
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms in a honeycomb lattice, is increasingly being used in new electronic and mechanical applications, such as transistors, switches and light sources, thanks to the unprecedented properties it offers: very low electrical resistance, high thermal conductivity and mechanically stretchable yet harder than diamond.
Now, ORC researchers have developed molybdenum di-sulphide ...
Search for better biofuels microbes leads to the human gut
2014-09-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists have scoured cow rumens and termite guts for microbes that can efficiently break down plant cell walls for the production of next-generation biofuels, but some of the best microbial candidates actually may reside in the human lower intestine, researchers report.
Their study, reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is the first to use biochemical approaches to confirm the hypothesis that microbes in the human gut can digest fiber, breaking it down into simple sugars in order to ferment them into nutrients that nourish ...
Results of the 1st EORTC Cancer Survivorship Summit
2014-09-23
A special issue of the European Journal of Cancer presents detailed reports on the wide range of research presented during the 1st EORTC Cancer Survivorship Summit held this past January in Brussels, Belgium.
Early diagnosis, targeted therapeutics, and more personalized multimodal treatments has boosted survival rates of patients with cancer and led to a large and rapidly increasing number of cancer survivors. Despite this good news, cancer survivors are often confronted with a broad spectrum of late adverse treatment effects and some must also deal with societal discrimination ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
[Press-News.org] Paraffins to cut energy consumption in homesUPV/EHU-University of the Basque Country researchers develop a compact heat storage prototype that can be easily fitted in buildings