(Press-News.org) Around the world, people are living longer and having fewer children, leading to a population that is older, on average, than in the past. On average, life expectancy in developed countries has risen at a pace of three months per year, and fertility has fallen below replacement rate in the majority of Europe and other developed countries.
Most academic discussion of this trend has so far focused on potential problems it creates, including challenges to pension systems, economic growth, and healthcare costs.
But according to a new study published today in the journal PLOS ONE, population aging and the compositional change that go along with it—such as increasing education levels—may turn out to have many positive impacts for society.
"In order to give a more complete picture of population aging, it is necessary to include both positive and negative effects of population aging," says IIASA researcher Elke Loichinger, who wrote the article in collaboration with researchers from the Max Planck Institute in Rostock, Germany, and the University of Washington.
The researchers chose to use Germany as a case study because the country is at an advanced stage of the demographic transition, with a current fertility rate of around 1.4 and the second oldest average population in the world (median age 44.3 years). They identified five areas in which population aging could bring net benefits, when considered in combination with other demographic factors:
Increased productivity: While population aging will likely lead to a decline in the labor force, expected increases in workers' education levels can partly compensate for this decline through higher productivity.
Aging could be good for the environment: Changes in the age structure and a declining population size are associated with reduced consumption of energy-intensive goods and lower carbon dioxide emissions.
Sharing wealth with the younger generations: As life expectancy increases, people would inherit, on average, at older ages and potentially use some of the inheritance to either fund their retirement or help their children financially as they become adults. Moreover, as families have fewer children, inheritance will be split between fewer people, so that, all else being constant, individuals would receive more on average.
Health: As people live longer, they also stay healthier longer. The results project that the average German man in 2050 will spend 80% of his lifetime in good health, compared to 63% today.
Quality of life: The study suggests that the relationship between leisure, work, and housework will change in the future, with leisure time increasing on average.
While the study focused on Germany, the researchers say that the findings are applicable across many aging societies. Loichinger says, "The particular context of another country will determine the degree of their relevance. For example, an increase in educational attainment levels can be found almost universally around the globe, and the finding that the elderly belonging to subsequent cohorts have better health has also been shown in other contexts. Depending on a country's stage in the demographic transition process, the results from the analyses of bequests and CO2 emissions are also generalizable."
The study provides a new perspective at a time when population aging is spreading to many countries around the world. Loichinger says, "The extent of population aging that is going on and expected is beyond what has ever been observed before. Since there is no precedent to this development, there is also no blueprint how to deal with it."
INFORMATION:
Reference
Kluge F, Zagheni E, Loichinger E, Vogt T. 2014. The advantages of demographic change after the wave: Fewer and older but healthier, greener, and more productive? PLOS ONE.
Academic Contact
Elke Loichinger
Guest Research Scholar
World Population
+43(0) 2236 807 486
About IIASA
IIASA is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policy makers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by scientific institutions in Africa, the Americas, Asia, Oceania, and Europe. http://www.iiasa.ac.at
The plus side of population aging
2014-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brain scans reveal 'gray matter' differences in media multitaskers
2014-09-24
Simultaneously using mobile phones, laptops and other media devices could be changing the structure of our brains, according to new University of Sussex research.
A study published today (24 September) reveals that people who frequently use several media devices at the same time have lower grey-matter density in one particular region of the brain compared to those who use just one device occasionally.
The research supports earlier studies showing connections between high media-multitasking activity and poor attention in the face of distractions, along with emotional ...
Colorado's Front Range fire severity not much different than past, say CU study
2014-09-24
The perception that Colorado's Front Range wildfires are becoming increasingly severe does not hold much water scientifically, according to a massive new study led by the University of Colorado Boulder and Humboldt State University in Arcata, Calif.
The study authors, who looked at 1.3 million acres of ponderosa pine and mixed conifer forest from Teller County west of Colorado Springs through Larimer County west and north of Fort Collins, reconstructed the timing and severity of past fires using fire-scarred trees and tree-ring data going back to the 1600s. Only 16 percent ...
New dinosaur from New Mexico has relatives in Alberta
2014-09-24
(Edmonton) A newly discovered armoured dinosaur from New Mexico has close ties to the dinosaurs of Alberta, say University of Alberta paleontologists involved in the research.
From 76 to 66 million years ago, Alberta was home to at least five species of ankylosaurid dinosaurs, the group that includes club-tailed giants like Ankylosaurus. But fewer ankylosaurids are known from the southern parts of North America. The new species, Ziapelta sanjuanensis, was discovered in 2011 in the Bisti/De-na-zin Wilderness area of New Mexico by a team from the New Mexico Museum of Natural ...
A way to kill chemo-resistant ovarian cancer cells: Cut down its protector
2014-09-24
Ottawa, Canada – September 24, 2014 – Ovarian cancer is the most deadly gynecological cancer, claiming the lives of more than 50% of women who are diagnosed with the disease. A study involving Ottawa and Taiwan researchers, published today in the influential Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), provides new insight into why ovarian cancer is often resistant to chemotherapy, as well as a potential way to improve its diagnosis and treatment.
It is estimated that 2,700 Canadian women will be diagnosed with ovarian cancer in 2014 and that 1,750 Canadian ...
Star Trekish, rafting scientists make bold discovery on Fraser River
2014-09-24
A Simon Fraser University-led team behind a new discovery has "…had the vision to go, like Star Trek, where no one has gone before: to a steep and violent bedrock canyon, with surprising results."
That comment comes from a reviewer about a truly groundbreaking study just published in the journal Nature.
Scientists studying river flow in bedrock canyons for the first time have discovered that previous conceptions of flow and incision in bedrock-rivers are wrong.
SFU geography professor Jeremy Venditti led the team of SFU, University of Ottawa and University of British ...
Bacterial 'communication system' could be used to stop and kill cancer cells, MU study finds
2014-09-24
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Cancer, while always dangerous, truly becomes life-threatening when cancer cells begin to spread to different areas throughout the body. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have discovered that a molecule used as a communication system by bacteria can be manipulated to prevent cancer cells from spreading. Senthil Kumar, an assistant research professor and assistant director of the Comparative Oncology and Epigenetics Laboratory at the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, says this communication system can be used to "tell" cancer cells how to act, ...
Study: Biochar alters water flow to improve sand and clay
2014-09-24
As more gardeners and farmers add ground charcoal, or biochar, to soil to both boost crop yields and counter global climate change, a new study by researchers at Rice University and Colorado College could help settle the debate about one of biochar's biggest benefits -- the seemingly contradictory ability to make clay soils drain faster and sandy soils drain slower.
The study, available online this week in the journal PLOS ONE, offers the first detailed explanation for the hydrological mystery.
"Understanding the controls on water movement through biochar-amended soils ...
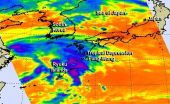
NASA sees the end of post-depression Fung-Wong
2014-09-24
Tropical Depression Fung-Wong looked more like a cold front on infrared satellite imagery from NASA than it did a low pressure area with a circulation.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression Fung-Wong on Sept. 23 at 12:23 a.m. EDT. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard Aqua gathered infrared temperature data on the storm's clouds. The data was false-colored at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California and showed that the storm resembled a frontal system more than a depression. The center of circulation was southwest ...
How a single, genetic change causes retinal tumors in young children
2014-09-24
Retinoblastoma is a childhood retinal tumor usually affecting children one to two years of age. Although rare, it is the most common malignant tumor of the eye in children. Left untreated, retinoblastoma can be fatal or result in blindness. It has also played a special role in understanding cancer, because retinoblastomas have been found to develop in response to the mutation of a single gene – the RB1 gene—demonstrating that some cells are only a step away from developing into a life-threatening malignancy.
David E. Cobrinik, MD, PhD, of The Vision Center at Children's ...
New milestone in the search for water on distant planets
2014-09-24
Astronomers have found water vapor in the atmosphere of a planet about four times bigger than Earth, in the constellation Cygnus about 124 light years - or nearly 729 trillion miles - from our home planet. In the quest to learn about planets beyond our solar system, this discovery marks the smallest planet for which scientists have been able to identify some chemical components of its atmosphere.
The researchers' findings were published Sept. 25, 2014 in the journal Nature. The team was led by University of Maryland Astronomy Professor Drake Deming, an expert in the study ...