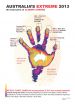
(Press-News.org) Australia's hottest year on record in 2013 along with the accompanying droughts, heat waves and record-breaking seasons of that year was virtually impossible without the influence of human-caused global warming.
New research from ARC Centre of Excellence for Climate System Science (ARCCSS) researchers and colleagues, over five different Australian papers in a special edition of the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society (BAMS), has highlighted the powerful influence of global warming on Australia's climate.
"We often talk about the fingerprint of human-caused climate change when we look at extreme weather patterns," said Prof David Karoly, an ARCCSS researcher with the University of Melbourne.
"This research across four different papers goes well beyond that. If we were climate detectives then Australia's hottest year on record in 2013 wasn't just a smudged fingerprint at the scene of the crime, it was a clear and unequivocal handprint showing the impact of human caused global warming."
In 2013, heat records fell like dominoes. Australia had its hottest day on record, its hottest month on record, its hottest summer on record, its hottest spring on record and then rounded it off with the hottest year on record.
According to the research papers presented in BAMS, the impact of climate change significantly increased the chances of record heat events in 2013. Looking back over the observational record the researchers found global warming over Australia (see attached graphic):
doubled the chance of the most intense heat waves,
tripled the likelihood of heatwave events,
made extreme summer temperature across Australia five time more likely
increased the chance of hot dry drought-like conditions seven times
made hot spring temperatures across Australia 30 times more likely.
But perhaps most importantly, it showed the record hot year of 2013 across Australia was virtually impossible without the influence of human-caused global warming. At its most conservative, the science showed the heat of 2013 was made 2000 times more likely by global warming.
"When it comes to what helped cause our hottest year on record, human-caused climate change is no longer a prime suspect, it is the guilty party," said ARCCSS Australian National University researcher Dr Sophie Lewis.
"Too often we talk about climate change impacts as if they are far in the future. This research shows they are here, now."
The extreme year of 2013 is just the latest peak in a trend over the observational record that has seen increasing bushfire days, the record-breaking warming of oceans around Australia, the movement of tropical species into temperate zones and the shifting of rain bearing storm tracks further south and away from some of our most important agricultural zones.
"The most striking aspect of the extreme heat of 2013 and its impacts is that this is only at the very beginning of the time when we are expected to experience the first impacts of human-caused climate change," said Dr Sarah Perkins an ARCCSS researcher with the University of New South Wales.
"If we continue to put carbon into our atmosphere at the currently accelerating rate, years like 2013 will quickly be considered normal and the impacts of future extremes will be well beyond anything modern society has experienced."
INFORMATION:https://www.climatescience.org.au/content/782-climate-detectives-reveal-handprint-human-caused-climate-change-australia#overlay-context=media/1699 END
Climate detectives reveal handprint of human caused climate change in Australia
Australia's hottest year on record was almost impossible without man-made climate change
2014-09-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rising prevalence of sleep apnea in US threatens public health
2014-09-29
DARIEN, IL – Public health and safety are threatened by the increasing prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea, which now afflicts at least 25 million adults in the U.S., according to the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project. Several new studies highlight the destructive nature of obstructive sleep apnea, a chronic disease that increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, stroke and depression.
"Obstructive sleep apnea is destroying the health of millions of Americans, and the problem has only gotten worse over the last two decades," said ...
Targeted combination therapy halts disease, extends life in advanced melanoma patients
2014-09-29
A world-first study in today's New England Journal of Medicine heralds the efficacy of a targeted combination drug therapy after reporting major declines in the risk of disease progression and death in people with metastatic melanoma.
The multi-centre, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial compared oral dabrafenib (150 mg twice daily) and oral trametinib (2 mg once daily) combination therapy with oral dabrafenib (150 mg twice daily) and placebo.
All trial patients had inoperable stage 3C or 4 metastatic melanoma that had a BRAF gene mutation V600E or V600K. Among ...
Investigating the 'underground' habitat of Listeria bacteria
2014-09-29
The literature describes Listeria as ubiquitous bacteria with widespread occurrence. Yet they only become a problem for humans and animals when they contaminate food processing facilities, multiply, and enter the food chain in high concentrations. An infection with Listeria monocytogenes can even be fatal for humans or animals with weakened immune systems.
Listeria in soil or water are not dangerous
"Listeria in soil or water represent a relatively low risk to humans," explains study director Beatrix Stessl. "The concentrations are too low. The aim of our study was ...
Trial shows trastuzumab should remain as standard of care for HER2-positive breast cancer
2014-09-29
JACKSONVILLE, Fla., Sept. 29, 2014 — Analysis of more than 8,000 women who participated in the world's largest study of two treatments for HER2-positive breast cancer reinforces other findings from the clinical trial showing that trastuzumab (Herceptin) should remain the standard of care for this cancer, says a Mayo Clinic researcher.
This study, being presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2014 Congress in Madrid, reveals that when used as a single HER2-targeted therapy in addition to standard chemotherapy, trastuzumab offers a better outcome than ...
Tooth serves as evidence of 220 million-year-old attack
2014-09-29
At the beginning of the age of dinosaurs, gigantic reptiles—distant relatives of modern crocodiles—ruled the earth. Some lived on land and others in water and it was thought they didn't much interact. But a tooth found by a University of Tennessee, Knoxville, researcher in the thigh of one of these ancient animals is challenging this belief.
Stephanie Drumheller, an earth and planetary sciences lecturer, and her Virginia Tech colleagues Michelle Stocker and Sterling Nesbitt examined 220-million-year-old bite marks in the thigh bones of an old reptile and found evidence ...
A molecular mechanism involved in cellular proliferation characterized
2014-09-29
Researchers from Guillermo Montoya's team at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), in collaboration with Isabelle Vernos' Group from the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), have uncovered the molecular interaction between TACC3 and chTOG, key proteins in forming the internal cellular framework that enables and sustains cell division. Published today in Nature Communications, the observations may help to optimise current oncological therapies specifically designed to fight against this framework, named by the scientific community as microtubules.
KEY MOLECULES ...
New method to motivate students to reduce energy consumption
2014-09-29
The research found that a combination of a real-time feedback system together with a human energy delegate in eight halls of residence resulted in a reduction of 37% in energy consumption when compared to normal consumption. The savings were 1360.49 kWh, which is equivalent to a reduction of 713.71 kg of CO2 over four weeks.
In contrast, another eight halls, exposed only to the real-time feedback and a weekly email alert, resulted in saw a 3.5% reduction in energy consumption.
Student's energy-use behaviour is complex as they cannot easily identify how much electricity ...
Dolphins are attracted to magnets
2014-09-29
Dolphins are indeed sensitive to magnetic stimuli, as they behave differently when swimming near magnetized objects. So says Dorothee Kremers and her colleagues at Ethos unit of the Université de Rennes in France, in a study in Springer's journal Naturwissenschaften – The Science of Nature. Their research, conducted in the delphinarium of Planète Sauvage in France, provides experimental behavioral proof that these marine animals are magnetoreceptive.
Magnetoreception implies the ability to perceive a magnetic field. It is supposed to play an important role in how some ...
Human trafficking, an invisible problem
2014-09-29
This news release is available in Spanish. This study compares the existing legislation on this subject in European countries and analyzes both the level of protection afforded to the victims and the measures taken to avoid this crime; in addition, it proposes of code of best practices that favors the enactment of new European guidelines aimed at ending this activity. Specifically, it shows that one of the first obstacles to change is that the magnitude of the problem is not known, points out one of the authors of the report, Begoña Marugán Pintos, of the department ...
Evolutionary biology: It's not just for textbooks anymore
2014-09-29
Solving global challenges in food security, emerging diseases and biodiversity loss requires evolutionary thinking, argues a new study published online in Science Express that was co-authored by Bruce Tabashnik of the University of Arizona College of Agriculture and Life Sciences.
For the first time, an international team of nine scientists has reviewed progress in addressing a broad set of challenges in agriculture, medicine and environmental management using approaches that consider evolutionary histories and the likelihood of rapid adaptation to human activities.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
[Press-News.org] Climate detectives reveal handprint of human caused climate change in AustraliaAustralia's hottest year on record was almost impossible without man-made climate change