(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill. – University of Illinois scientists have found compounds that boost liver detoxification enzymes nearly fivefold, and they've found them in a pretty unlikely place—the crushed seeds left after oil extraction from an oilseed crop used in jet fuel.
"The bioactive compounds in Camelina sativa seed, also known as Gold of Pleasure, are a mixture of phytochemicals that work together synergistically far better than they do alone. The seed meal is a promising nutritional supplement because its bioactive ingredients increase the liver's ability to clear foreign chemicals and oxidative products. And that gives it potential anti-cancer benefit," said Elizabeth Jeffery, a U of I professor of nutritional toxicology.
Oilseed crops, including rapeseed, canola, and camelina, contain some of the same bioactive ingredients—namely, glucosinolates and flavonoids—found in broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables and in nearly the same quantities, she noted.
Because the oil from oilseed crops makes an environmentally friendly biofuel, scientists have been hoping to find a green use for the protein-rich seed meal left after oil extraction. Animal feed was the obvious choice, but there were a couple of problems. Some rapeseed glucosinolates are toxic, and producers have balked at paying Canada for canola seed, the low-glucosinolate rapeseed that country had developed.
Jeffery thought Camelina sativa was worth a look so she began to work with USDA scientist Mark Berhow. In the first study of camelina's bioactive properties, Berhow isolated four major components—three glucosinolates and the flavonoid quercetin—from its defatted seed meal.
Back at Jeffery's U of I lab, researchers began to test these components on mouse liver cells both individually and together. They found that all four major camelina bioactives induced the detoxifying liver enzyme NQO1 when they were used alone. However, when a particular glucosinolate, GSL9, was paired with the flavonoid quercetin, there was a synergistic effect.
"When these two bioactives were combined, induction of the detoxifying liver enzyme increased nearly fivefold," said Nilanjan Das, a postdoctoral student in Jeffery's lab.
In all the experiments, the scientists used sulforaphane, the cancer-protective component of broccoli, as a control because it is known to induce NQO1, the detoxifying enzyme. Like camelina seed meal, broccoli contains the flavonoid quercetin, so they decided to look for synergy between sulforaphane and quercetin.
"As had been the case with camelina's GSL9 and quercetin, the combined effect of quercetin and sulforaphane—in proportions found naturally in broccoli—was far greater than when either was used alone. This demonstrates to us the importance of eating whole foods. Thanks to synergy among its bioactive components, whole broccoli appears to be more powerful than purified sulforaphane that you might buy at a vitamin store or on the Internet," Das said.
Nilanjan Das, Mark A. Berhow, Donato Angelina, and Elizabeth H. Jeffery are co-authors of "Camelina sativa Defatted Seed Meal Contains Both Alkyl Sulfinyl Glucosinolates and Quertecin that Synergize Bioactivity." The article is available pre-publication online in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. Funding was provided by USDA.
INFORMATION:
New way to detox? 'Gold of Pleasure' oilseed boosts liver detoxification enzymes
2014-09-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Alberta researchers explain 38-year-old mystery of the heart
2014-09-29
In a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, researchers at the University of Alberta's Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry have explained how the function of a key protein in the heart changes in heart failure.
Heart disease is the number-one killer in the developed world. The end stage of heart disease is heart failure, in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to satisfy the body's needs. Patients become progressively short of breath as the condition worsens, and they also begin to accumulate fluid in the legs and lungs, making it ...
Good working relationships between clients, bankers can reduce defaults
2014-09-29
You've probably seen advertising campaigns in which banks describe how much their customer relationships matter to them. While such messaging might have been cooked up at an ad agency, it turns out there is some truth underlying these slogans.
As a newly published study co-authored by an MIT professor shows, strong working relationships between bankers and clients reduce the likelihood of loan delinquencies and defaults, at least in the context of an emerging economy.
Using propriety data from a large bank in Chile, the study finds that when loan officers go on leave, ...
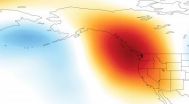
Causes of California drought linked to climate change
2014-09-29
The atmospheric conditions associated with the unprecedented drought currently afflicting California are "very likely" linked to human-caused climate change, Stanford scientists say.
In a new study, a team led by Stanford climate scientist Noah Diffenbaugh used a novel combination of computer simulations and statistical techniques to show that a persistent region of high atmospheric pressure hovering over the Pacific Ocean that diverted storms away from California was much more likely to form in the presence of modern greenhouse gas concentrations.
The research, published ...
Decision to reintroduce aprotinin in cardiac surgery may put patients at risk
2014-09-29
Cardiac surgery patients may be at risk because of the decision by Health Canada and the European Medicines Agency to reintroduce the use of aprotinin after its withdrawal from the worldwide market in 2007, assert the authors of a previous major trial that found a substantially increased risk of death associated with the drug. In an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal), the authors refute three major criticisms of the trial made by the regulatory bodies.
Aprotinin, used to control bleeding in cardiac surgery, was withdrawn worldwide in 2007 after the ...
Revolutionary hamstring tester will keep more players on the field
2014-09-29
Elite sporting stars can assess and reduce their risk of a hamstring injury thanks to a breakthrough made by QUT researchers.
The discovery could be worth a fortune to football codes, with hamstring strain injuries accounting for most non-contact injuries in Australian rules football, football and rugby union, as well as track events like sprinting.
Using an innovative field device, a research team led by Dr Anthony Shield, from QUT's School - Exercise and Nutrition Sciences, and former QUT PhD student, Dr David Opar, now at the Australian Catholic University, measured ...
Drug for kidney injury after cardiac surgery does not reduce need for dialysis
2014-09-29
Among patients with acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery, infusion with the antihypertensive agent fenoldopam, compared with placebo, did not reduce the need for renal replacement therapy (dialysis) or risk of death at 30 days, but was associated with an increased rate of abnormally low blood pressure, according to a study published in JAMA. The study is being posted early online to coincide with its presentation at the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine annual congress.
More than 1 million patients undergo cardiac surgery every year in the United States ...
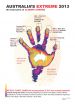
Climate detectives reveal handprint of human caused climate change in Australia
2014-09-29
Australia's hottest year on record in 2013 along with the accompanying droughts, heat waves and record-breaking seasons of that year was virtually impossible without the influence of human-caused global warming.
New research from ARC Centre of Excellence for Climate System Science (ARCCSS) researchers and colleagues, over five different Australian papers in a special edition of the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society (BAMS), has highlighted the powerful influence of global warming on Australia's climate.
"We often talk about the fingerprint of human-caused ...
Rising prevalence of sleep apnea in US threatens public health
2014-09-29
DARIEN, IL – Public health and safety are threatened by the increasing prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea, which now afflicts at least 25 million adults in the U.S., according to the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project. Several new studies highlight the destructive nature of obstructive sleep apnea, a chronic disease that increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, stroke and depression.
"Obstructive sleep apnea is destroying the health of millions of Americans, and the problem has only gotten worse over the last two decades," said ...
Targeted combination therapy halts disease, extends life in advanced melanoma patients
2014-09-29
A world-first study in today's New England Journal of Medicine heralds the efficacy of a targeted combination drug therapy after reporting major declines in the risk of disease progression and death in people with metastatic melanoma.
The multi-centre, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial compared oral dabrafenib (150 mg twice daily) and oral trametinib (2 mg once daily) combination therapy with oral dabrafenib (150 mg twice daily) and placebo.
All trial patients had inoperable stage 3C or 4 metastatic melanoma that had a BRAF gene mutation V600E or V600K. Among ...
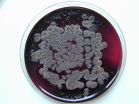
Investigating the 'underground' habitat of Listeria bacteria
2014-09-29
The literature describes Listeria as ubiquitous bacteria with widespread occurrence. Yet they only become a problem for humans and animals when they contaminate food processing facilities, multiply, and enter the food chain in high concentrations. An infection with Listeria monocytogenes can even be fatal for humans or animals with weakened immune systems.
Listeria in soil or water are not dangerous
"Listeria in soil or water represent a relatively low risk to humans," explains study director Beatrix Stessl. "The concentrations are too low. The aim of our study was ...