(Press-News.org) Silver nanoparticles are well known for their anti-bacteria properties[1-4]. One of the main routes by which they may act as an anti-bacteria agent, is through attaching themselves to the thiol group present on the cellular membrane surface and hence disrupting the membrane's function[5]. Hence, it is crucial to gain a greater understanding of this complex silver-thiol interaction to determine silver nanoparticles' role in biological systems. With thiols, silver nanoparticles have been proposed to form various types of compounds with different structures[6-8]. One of the plausible reaction routes suggested for organothiols is[6,7]:
4 RSH + 4 Ag + O2 4 AgSR + 2 H2O (1)
It has been shown through scanning electron microscopy that AgSR remained on the surface, forming a shell[6]. Battocchio et al. suggested a shell of more than one species of silver thiolates – a mix of AgSR and Ag2S-like complexes were formed when aromatic organothiols were added during silver nanoparticle synthesis[8]. From the above, it known that the interaction between silver nanoparticles and thiol is complicated. Therefore, in this study, we presented a comparative view of silver-thiol interaction for MH and cysteine through voltammetric and spectroscopy experiments.
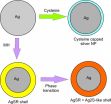
Cyclic voltammograms were performed in the presence of MH or cysteine to ascertain the changes in the ease and extent of oxidation of silver nanoparticles to silver(I) ions. The UV-vis spectra of silver nanoparticles were recorded to examine the changes in the nanoparticles' surface properties in the presence of thiols. From the experimental data, it was concluded that MH interacts with silver nanoparticles to give a sparingly soluble silver(I) thiolate complex AgSRm (Rm = -(CH2)6OH) on the surface. It was also inferred that the AgSRm complex on the nanoparticle surface undergoes a phase transition to give a mixture of AgSRm and Ag2S-like complexes due to the presence of two signals in both electrochemical voltammograms and UV-vis spectrums[8]. In contrast, when silver nanoparticles were exposed to cysteine, the citrate capping agent on the silver nanoparticles was replaced by cysteine to give cysteine capped nanoparticles. As cysteine capped nanoparticles form, the electrochemical data displayed a decrease in oxidative peak charge but the UV-vis spectra showed a constant signal. Therefore, cysteine capped nanoparticles were suggested to have either inactivated the silver surface or else promoted detachment from the electrode surface. Figure 1 shows schematically the route which silver nanoparticles interact with MH and cysteine.
It may be concluded that no general mechanism for the interactions of thiol with silver nanoparticles exist and that each thiol must be treated individually.
INFORMATION:
See the article:
Her Shuang Toh, Christopher Batchelor-McAuley, Kristina Tschulik and
Richard G. Compton.
Chemical interactions between silver nanoparticles and thiols: a comparison of mercaptohexanol against cysteine
Science China Chemistry, September 2014, Volume 57, Issue 9, pp 1199-1210. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11426-014-5141-8
References
[1]R. K. Kunkalekar, M. M. Naik, S. K. Dubey, A. V. Salker, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 873-877.
[2]Y. Park, H. J. Noh, L. Han, H.-S. Kim, Y.-J. Kim, J. S. Choi, C.-K. Kim, Y. S. Kim, S. Cho, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7087-7095.
[3]M. Sureshkumar, D. Y. Siswanto, C.-K. Lee, J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6948.
[4]C. Marambio-Jones, E. M. V. Hoek, J.Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531-1551.
[5]A. Lapresta-Fernández, A. Fernández, J. Blasco, TrAC, 2012, 32, 40-59.
[6]S. M. Ansar, G. S. Perera, P. Gomez, G. Salomon, E. S. Vasquez, I. W. Chu, S. Zou, C. U. Pittman, K. B. Walters, D. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 27146-27154.
[7]A. Andrieux-Ledier, B. Tremblay, A. Courty, Langmuir 2013, 29, 13140-13145.
[8]C. Battocchio, C. Meneghini, I. Fratoddi, I. Venditti, M. V. Russo, G. Aquilanti, C. Maurizio, F. Bondino, R. Matassa, M. Rossi, S. Mobilio, G. Polzonetti, J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19571-19578.
Chemical interactions between silver nanoparticles and thiols: A comparison of mercaptohexanol again
2014-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gender equality leads to more Olympic medals for men and women
2014-09-30
Gender equality boosts a country's Olympic medal count for both women and men, shows a new study from the University of British Columbia.
Drawing data from the World Economic Forum's 2013 Global Gender Gap Report, researchers compared a country's tendency toward sexual equality with its medal counts from the London 2012 Olympic Games and the Sochi 2014 Olympic Winter Games.
Countries with greater parity – particularly for measures of educational equality – had more women and men reach the podium.
"Our study makes apparent that gender equality has a tendency to lift ...
New learning mechanism for individual nerve cells
2014-09-30
The traditional view is that learning is based on the strengthening or weakening of the contacts between the nerve cells in the brain. However, this has been challenged by new research findings from Lund University in Sweden. These indicate that there is also a third mechanism – a kind of clock function that gives individual nerve cells the ability to time their reactions.
"This means a dramatic increase in the brain's learning capacity. The cells we have studied control the blink reflex, but there are many cells of the same type that control entirely different processes. ...
Erectile dysfunction drugs could affect vision of genetically susceptible users
2014-09-30
Sildenafil, the active ingredient in the erectile dysfunction drug Viagra®, could cause unusual visual responses in people who carry a common mutation for eye disease and may have long-term detrimental effects on their vision, UNSW Australia researchers warn.
Sildenafil can inhibit an enzyme which is important for transmitting light signals from the retina to the brain, and it is already known from clinical trials of Viagra® that its use in high doses can cause transient disturbances in the vision of some healthy people.
"Side effects can include sensitivity to bright ...
First mapping that reveals the molecular pathway for MDSC cancer progression
2014-09-30
Scientists from InSilico Medicine and its partners successfully established a visual mapping of the molecular pathway cancer progression originating from myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSC). The damage and immune suppression the cells cause are not fully understood, however this is a major stepping stone in creating necessary transparency. Highly cited MetaCoreTM was the primary interactome analysis tool used for mapping, providing these promising results.
"MDSCs are elicited by tumor-derived factors from precursors present in hematopoietic organs such as the bone ...
Benzodiazepine sedatives linked to higher rates of mortality compared to propofol
2014-09-30
AUDIO:
Sedation is commonly used in the intensive care unit (ICU) to make patients that require mechanical ventilation more comfortable, and less anxious. What many don't realize is that sedation can...
Click here for more information.
Sedation is frequently required for mechanically ventilated intensive care unit (ICU) patients to reduce anxiety, provide comfort, and assist in providing optimal respiratory support. It is estimated that each year, there are nearly 1 million U.S. ...
How to make a 'perfect' solar absorber
2014-09-30
CAMBRIDGE, Mass--The key to creating a material that would be ideal for converting solar energy to heat is tuning the material's spectrum of absorption just right: It should absorb virtually all wavelengths of light that reach Earth's surface from the sun — but not much of the rest of the spectrum, since that would increase the energy that is reradiated by the material, and thus lost to the conversion process.
Now researchers at MIT say they have accomplished the development of a material that comes very close to the "ideal" for solar absorption. The material is a two-dimensional ...
UConn scientists discover how to beat monk parakeets at their own game
2014-09-30
In a study published this week in the online journal PeerJ, University of Connecticut researchers announce they have found a way to prevent Monk Parakeets (Myiopsitta monarchus), an invasive species of parrot, from building huge nests that create power outages and public hazards on utility poles by blocking their access to the electric lines that are the gateway to their nest sites.
The nests, which are built out of sticks and twigs, can weigh up to 200 pounds or more. The damage they cause can cost electric utility companies millions of dollars annually.
But, the brightly ...
Selectively rewiring the brain's circuitry to treat depression
2014-09-30
Philadelphia, PA, September 30, 2014 – On Star Trek, it is easy to take for granted the incredible ability of futuristic doctors to wave small devices over the heads of both humans and aliens, diagnose their problems through evaluating changes in brain activity or chemistry, and then treat behavior problems by selectively stimulating relevant brain circuits.
While that day is a long way off, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex does treat symptoms of depression in humans by placing a relatively small device on a person's scalp ...
New material steals oxygen from the air
2014-09-30
Researchers from the University of Southern Denmark have synthesized crystalline materials that can bind and store oxygen in high concentrations. Just one spoon of the substance is enough to absorb all the oxygen in a room. The stored oxygen can be released again when and where it is needed.
We do fine with the 21 per cent oxygen in the air around us. But sometimes we need oxygen in higher concentrations; for example lung patients must carry heavy oxygen tanks, cars using fuel cells need a regulated oxygen supply. Perhaps one day in the future even sunlight-driven "reversible" ...
Low-birth-weight children are particularly vulnerable to environmental influences
2014-09-30
Low birth weight children are more vulnerable to environmental influences than infants born with normal weight. When brought up with a great deal of sensitivity, they will be able to catch up in school, but on average they will not become better students than normal birth weight children. This result, provided by an international psychologist team, has confirmed the so-called diathesis-stress model of development for low birth weight populations. The researchers report their findings in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
Theories on how environmental factors ...