(Press-News.org) A major medical discovery by scientists at The University of Nottingham could lead to the development of an entirely new type of painkiller.
A drug resulting from the research, published in the journal Neurobiology of Disease, would offer new hope to sufferers of chronic pain conditions such as traumatic nerve injury, for which few effective painkillers are currently available.
The work, led by Dr Lucy Donaldson in the University's School of Life Sciences, in collaboration with David Bates, Professor of Oncology in the University's Cancer Biology Unit, focuses on a signal protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
VEGF controls the re-growth of blood vessels in tissues which have been damaged by injury. It is a widely targeted compound for cancer, eye disease and other illnesses in which abnormal blood vessel growth occurs.
Drugs are used to inhibit the VEGF in cancer, which can otherwise lead to the formation of new blood vessels that provide oxygen and nutrients to tumours.
Professor Bates and colleagues had previously discovered in 2002 that VEGF comes in two forms and acts like a switch — one which turns on the growth of blood vessels and another that blocks growth.
However, this latest research has shown for the first time that these two forms of VEGF not only act on blood vessels but also differently affect the sensory nerves that control pain.
The academics discovered that the VEGF that promotes blood vessel growth causes pain, while the other, which inhibits blood vessel growth, prevents pain.
The study has centred on understanding how these two types of VEGF work and why the body makes one form rather than the other.
The academics have been able to switch from the pain stimulating form to the pain inhibiting VEGF in animal models in the laboratory and are now investigating compounds to replicate this in humans. It is thought these compounds could form the basis for new drugs to be tested in humans in clinical trials.
INFORMATION:
The research has been funded by the Wellcome Trust, Diabetes UK, the British Heart Foundation and the Richard Bright VEGF Research Fund.
Medical discovery first step on path to new painkillers
2014-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Stealth' nanoparticles could improve cancer vaccines
2014-10-01
Cancer vaccines have recently emerged as a promising approach for killing tumor cells before they spread. But so far, most clinical candidates haven't worked that well. Now, scientists have developed a new way to deliver vaccines that successfully stifled tumor growth when tested in laboratory mice. And the key, they report in the journal ACS Nano, is in the vaccine's unique stealthy nanoparticles.
Hiroshi Shiku, Naozumi Harada and colleagues explain that most cancer vaccine candidates are designed to flag down immune cells, called macrophages and dendritic cells, that ...
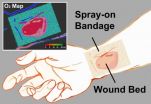
'Smart' bandage emits phosphorescent glow for healing below
2014-10-01
WASHINGTON, Oct. 1—Inspired by a desire to help wounded soldiers, an international, multidisciplinary team of researchers led by Assistant Professor Conor L. Evans at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Harvard Medical School (HMS) has created a paint-on, see-through, "smart" bandage that glows to indicate a wound's tissue oxygenation concentration. Because oxygen plays a critical role in healing, mapping these levels in severe wounds and burns can help to significantly improve the success of surgeries to restore limbs and physical ...
New drug-delivery capsule may replace injections
2014-10-01
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Given a choice, most patients would prefer to take a drug orally instead of getting an injection. Unfortunately, many drugs, especially those made from large proteins, cannot be given as a pill because they get broken down in the stomach before they can be absorbed.
To help overcome that obstacle, researchers at MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have devised a novel drug capsule coated with tiny needles that can inject drugs directly into the lining of the stomach after the capsule is swallowed. In animal studies, the team found that the capsule ...
Public feels more negative toward drug addicts than mentally ill
2014-10-01
People are significantly more likely to have negative attitudes toward those suffering from drug addiction than those with mental illness, and don't support insurance, housing, and employment policies that benefit those dependent on drugs, new Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health research suggests.
A report on the findings, which appears in the October issue of the journal Psychiatric Services, suggests that society seems not to know whether to regard substance abuse as a treatable medical condition akin to diabetes or heart disease, or as a personal failing ...
Dog waste contaminates our waterways: A new test could reveal how big the problem is
2014-10-01
Americans love their dogs, but they don't always love to pick up after them. And that's a problem. Dog feces left on the ground wash into waterways, sometimes carrying bacteria — including antibiotic-resistant strains — that can make people sick. Now scientists have developed a new genetic test to figure out how much dogs are contributing to this health concern, according to a report in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Orin C. Shanks, Hyatt C. Green and colleagues explain that our waterways are susceptible to many sources of fecal contamination, including ...
Deconstruction of avant-garde cuisine could lead to even more fanciful dishes
2014-10-01
One of the most iconic forms of avant-garde cuisine, also known as molecular gastronomy, involves the presentation of flavorful, edible liquids — like cocktails or olive oil — packaged into spheres. Now a team of scientists, in collaboration with world-renowned chef Ferran Adriá, is getting to the bottom of what makes these delectable morsels possible. Their findings appear in ACS' The Journal of Physical Chemistry B.
Christophe Chipot, Wensheng Cai and colleagues explain that the technique of "spherification" was invented 70 years ago but was popularized in avant-garde ...
ZEB1, Oscar for leading role in fat storage
2014-10-01
And the winner is ... ZEB1! There are many actors involved in the process of adipogenesis, used by the body to store the fat that it absorbs from food. Up to now there had been some uncertainty as to how it was regulated. Yet, understanding this mechanism is of crucial importance to prevent the diseases related to fat accumulation in adipose tissue.
A research team led by Carine Gubelmann and Petra Schwalie at EPFL's Laboratory of Systems Biology and Genetics, directed by Bart Deplancke, joined forces with Christian Wolfrum's researchers from ETH Zurich, to decode the ...
Research confirms controversial Darwin theory of 'jump dispersal'
2014-10-01
KNOXVILLE—More than one hundred and fifty years ago, Charles Darwin hypothesized that species could cross oceans and other vast distances on vegetation rafts, icebergs, or in the case of plant seeds, in the plumage of birds.
Though many were skeptical of Darwin's "jump dispersal" idea, a new study suggests that Darwin might have been correct.
A new computational method, published in the journal Systematic Biology, tested two competing theories about how species came to live where they do and found strong evidence for jump dispersal, especially for island species.
The ...
Nature collides with James Bond: Newly discovered ant species hides in plain sight
2014-10-01
WASHINGTON—Researchers plan and plot every considerable aspect of their work, but sometimes it's something unexpected and seemingly insignificant that leads to the real discovery. That was the case for Scott Powell, assistant professor of biology at the George Washington University.
While conducting field research on turtle ants in the savannah region of Brazil, Dr. Powell noticed something peculiar: a species of ant infiltrating the region of a host ant, Crematogaster ampla. The C. ampla is known for its hyper-aggressiveness, but did not attack the invading species, ...
Chapman University research on meat in pet foods shows not all brands follow regulations
2014-10-01
ORANGE, Calif. – Researchers in Chapman University's Food Science Program have just published a study on pet food mislabeling. The study focused on commercial pet foods marketed for dogs and cats to identify meat species present as well as any instances of mislabeling. Of the 52 products tested, 31 were labeled correctly, 20 were potentially mislabeled, and one contained a non-specific meat ingredient that could not be verified.
"Although regulations exist for pet foods, increases in international trade and globalization of the food supply have amplified the potential ...