The fat suit study
The larger your friends the larger your appetite
2014-10-02
(Press-News.org) Have you ever ordered more food at a restaurant than you intended? There are elements of dining rooms that actually prime you to eat more food. One such element is the weight of those dining with or near you. This new Cornell University study found that the body type of your dining partner, or that of those dining nearby, may actually influence how much you serve yourself and how much you eat!
The study investigated the impact the presence of an overweight diner on healthy and unhealthy food choices and found you are more likely to serve and eat more unhealthy foods and less healthy foods when eating with or near someone who is overweight. These findings support a theory that when eating with or near an overweight person, you may be less likely to adhere to your own health goals. "This finding emphasizes the importance of pre-committing to meal choices before entering the restaurant," says lead author Mitsuru Shimizu, Assistant Professor of Psychology at Southern Illinois University, Edwardsville. "If you go into the restaurant knowing what you will order you're less likely to be negatively influenced by all of the things that nudge you to eat more."
The study published in Appetite was co-authored by Katie Johnson of Mayo Medical School and Brian Wansink, PhD director of Cornell University's Food and Brand Lab and author of the new book: Slim by Design: Mindless Eating Solutions for Everyday Life. The researchers recruited 82 undergraduate college students to eat a spaghetti and salad lunch. They also enlisted an actress to wear a prosthesis that added 50 pounds to her normally average weight. Each of the 82 participants was randomly assigned to one of four scenarios: the actress served herself healthfully (more salad and less pasta) while wearing the prosthesis, she served herself the same healthy meal without the prosthesis, she served herself less healthfully (more pasta and less salad) while wearing the prosthesis, or she served herself the same less healthy meal without the prosthesis. Participants in each scenario viewed the actress serving herself and then served themselves pasta and salad. Researchers found that when the actress wore the prosthesis, and appeared overweight, the other participants served and ate 31.6% more pasta regardless of whether she served herself mostly pasta or mostly salad. When she wore the prosthesis and served herself more salad, the other participants actually served and ate 43.5% less salad.
These findings demonstrate that people may serve and eat larger portions of unhealthy foods and smaller portions of healthy foods when eating with an overweight person because they are less in tune with their own health goals. Luckily, this phenomenon is easy to avoid by simply assessing your level of hunger before going to the restaurant and planning your meal accordingly. Wansink recommends, "Look up the menu beforehand and select a meal that suits your dietary goals. Or, if you're going to a buffet, pre-commit to selecting modest portions of healthy foods and with that goal in mind, those around you will have less of a negative influence over what you eat."
INFORMATION:
For more information visit: http://foodpsychology.cornell.edu/op/the_fat_suit_study
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-02
This news release is available in German, Spanish, French and Japanese.
High rates of anxiety and depression amongst patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) have led many researchers to believe there could be a causal relationship between psychological factors and IBS symptoms. Now, scientists in Germany have found clear evidence that patients with IBS process pain signals from the gut abnormally, and that disturbed brain responses to pain are particularly pronounced in patients with more depression symptoms.1
At the 22nd United European Gastroenterology ...
2014-10-02
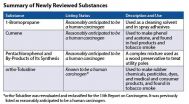
Four substances have been added in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 13th Report on Carcinogens, a science-based document that identifies chemical, biological, and physical agents that are considered cancer hazards for people living in the United States. The new report includes 243 listings.
Ortho-toluidine, used to make rubber chemicals, pesticides, and dyes, has been reevaluated and is now listed as a known human carcinogen. Three substances have been added as reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens. These include 1-bromopropane, used as a cleaning ...
2014-10-02
When asked to describe a forest or a meadow, most people would probably begin with the plants, the species diversity, or the color of the foliage. They probably wouldn't pay much attention to the animals living in the soil.
But a new Yale-led study shows the critical importance of earthworms, beetles, and other tiny creatures to the structure of grasslands and the valuable ecosystem services they provide.
During a 3-year study, researchers found that removing these small animals from the soil of a replicated Scottish sheep meadow altered the plant species that grew ...
2014-10-02
LOS ANGELES – (Oct. 2, 2014) – Surveying patients with traumatic brain injuries, a group of Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute (LA BioMed) researchers reported today that they found those who tested positive for THC, the active ingredient in marijuana, were more likely to survive than those who tested negative for the illicit substance.
The findings, published in the October edition of The American Surgeon, suggest THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, may help protect the brain in cases of traumatic brain injury, the researchers said. The study included 446 patients who ...
2014-10-02
New Rochelle, NY, October 2, 2014–Women who have a history of violent sexual abuse may suffer emotional distress during a routine pelvic examination. Healthcare providers would benefit from greater awareness of symptoms predictive of examination-related distress in this patient population, according to a study published in Violence and Gender, a new peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Violence and Gender website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/vio.2014.0016 until November 2, 2014.
In the ...
2014-10-02
VIDEO:
Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania and the University of California, Santa Barbara, have now shown how giant clams use iridescent structures to thrive, operating as exceedingly efficient, living greenhouses...
Click here for more information.
Evolution in extreme environments has produced life forms with amazing abilities and traits. Beneath the waves, many creatures sport iridescent structures that rival what materials scientists can make in the laboratory.
A ...
2014-10-02
PHILADELPHIA, PA – Physicians have long speculated at the hard-to-treat nature of joint infection. In an article published in Journal of Infectious Diseases, Thomas Jefferson University scientists, in collaboration with scientists at the National Institutes of Health, come one step closer to understanding why these infections are so tough to tackle. The results could help explain the joint pain caused by different infections, including Lyme disease and why they're so resistant to antibiotic treatment.
"Biofilm formation has been suspected to play a key role during septic ...
2014-10-02
New research suggests treatment in Australia and New Zealand for patients with sepsis is the best in the world.
The large-scale six-year study, led by the Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre at Monash University, divided 1600 patients into two groups, who were admitted to emergency care with early stage sepsis from across more than 40 hospitals.
The first group of 796 patients received Early Goal Directed Therapy (EGDT), an aggressive treatment not currently used in Australia and New Zealand, which inserts a catheter into the jugular vein to monitor ...
2014-10-02
Published today in PLOS ONE, the study is the first in the world to show that it is possible to predict abstract judgments from brain waves, even though people were not conscious of making such judgments.
The study also increases our understanding of impulsive behaviours and how to regulate it.
It found that researchers could predict from participants' brain activity how exciting they found a particular image to be, and whether a particular image made them think more about the future or the present.
This is true even though the brain activity was recorded before ...
2014-10-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Dov Sax of Brown University and Jason Fridley of Syracuse University aren't proposing a novel idea to explain species invasiveness. In fact, Charles Darwin articulated it first. What's new about Sax and Fridley's "Evolutionary Imbalance Hypothesis" (EIH) is that they've tested it using quantifiable evidence and report in Global Ecology and Biogeography that the EIH works well.
The EIH idea is this: Species from regions with deep and diverse evolutionary histories are more likely to become successful invaders in regions with less deep, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The fat suit study
The larger your friends the larger your appetite