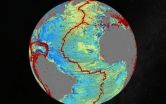
(Press-News.org) Scientists have created a new map of the world's seafloor, offering a more vivid picture of the structures that make up the deepest, least-explored parts of the ocean.
The feat was accomplished by accessing two untapped streams of satellite data.
Thousands of previously uncharted mountains rising from the seafloor, called seamounts, have emerged through the map, along with new clues about the formation of the continents.
Combined with existing data and improved remote sensing instruments, the map, described today in the journal Science, gives scientists new tools to investigate ocean spreading centers and little-studied remote ocean basins.
Earthquakes were also mapped. In addition, the researchers discovered that seamounts and earthquakes are often linked. Most seamounts were once active volcanoes, and so are usually found near tectonically active plate boundaries, mid-ocean ridges and subducting zones.
The new map is twice as accurate as the previous version produced nearly 20 years ago, say the researchers, who are affiliated with California's Scripps Institution of Oceanography (SIO) and other institutions.
"The team has developed and proved a powerful new tool for high-resolution exploration of regional seafloor structure and geophysical processes," says Don Rice, program director in the National Science Foundation's Division of Ocean Sciences, which funded the research.
"This capability will allow us to revisit unsolved questions and to pinpoint where to focus future exploratory work."
Developed using a scientific model that captures gravity measurements of the ocean seafloor, the map extracts data from the European Space Agency's (ESA) CryoSat-2 satellite.
CryoSat-2 primarily captures polar ice data but also operates continuously over the oceans. Data also came from Jason-1, NASA's satellite that was redirected to map gravity fields during the last year of its 12-year mission.
"The kinds of things you can see very clearly are the abyssal hills, the most common landform on the planet," says David Sandwell, lead author of the paper and a geophysicist at SIO.
The paper's co-authors say that the map provides a window into the tectonics of the deep oceans.
The map also provides a foundation for the upcoming new version of Google's ocean maps; it will fill large voids between shipboard depth profiles.
Previously unseen features include newly exposed continental connections across South America and Africa and new evidence for seafloor spreading ridges in the Gulf of Mexico. The ridges were active 150 million years ago and are now buried by mile-thick layers of sediment.
"One of the most important uses will be to improve the estimates of seafloor depth in the 80 percent of the oceans that remain uncharted or [where the sea floor] is buried beneath thick sediment," the authors state.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the paper include R. Dietmar Muller of the University of Sydney, Walter Smith of the NOAA Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry Emmanuel Garcia of SIO and Richard Francis of ESA.
The study also was supported by the U.S. Office of Naval Research, the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency and ConocoPhillips.
Zoonosis—transmission of infections from other vertebrates to humans—causes regular and sometimes serious disease outbreaks. Bats are a well-known vertebrate reservoir of viruses like rabies and Ebola. Recent discovery of sequences in bats that are resemble influenza virus genes raised the question of whether bat flu viruses exist and could pose a threat to humans. A study published on October 2nd in PLOS Pathogens addresses this question based on detailed molecular and virological characterization.
Because no infectious virus particles were isolated from the bat samples ...
Scientists at the University of California, Santa Cruz, using a new wildlife tracking collar they developed, were able to continuously monitor the movements of mountain lions in the wild and determine how much energy the big cats use to stalk, pounce, and overpower their prey.
The research team's findings, published October 3 in Science, help explain why most cats use a "stalk and pounce" hunting strategy. The new "SMART" wildlife collar--equipped with GPS, accelerometers, and other high-tech features--tells researchers not just where an animal is but what it is doing ...
VIDEO:
This is a video interview with Jens Nielsen.
With a simple mutation, yeast can grow in higher than normal temperatures. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology demonstrate this in an article...
Click here for more information.
With a simple mutation, yeast can grow in higher than normal temperatures. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology demonstrate this in an article to be published in the scientific journal Science. The findings may result in ethanol ...
Wild cheetah populations have declined precipitously in the past century: from an estimated 100,000 in 1900 to only around 10,000 today. A new study from researchers in Europe, South Africa and at North Carolina State University suggests that the energy cheetahs spend looking for prey, rather than their high-speed hunting tactics or food stolen by other predators, may be to blame for their dwindling numbers.
Cheetahs are high-speed hunters, but are not the strongest predators in their ecosystems. Often, hyenas and lions will take advantage of this, stealing the cheetah's ...
VIDEO:
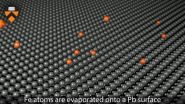
Princeton University researchers first deposited iron atoms onto a lead surface to create an atomically thin wire. They then used a scanning-tunneling microscope to create a magnetic field and to...
Click here for more information.
Princeton University scientists have observed an exotic particle that behaves simultaneously like matter and antimatter, a feat of math and engineering that could yield powerful computers based on quantum mechanics.
Using a two-story-tall microscope ...
The HIV pandemic with us today is almost certain to have begun its global spread from Kinshasa, the capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), according to a new study.
An international team, led by Oxford University and University of Leuven scientists, has reconstructed the genetic history of the HIV-1 group M pandemic, the event that saw HIV spread across the African continent and around the world, and concluded that it originated in Kinshasa. The team's analysis suggests that the common ancestor of group M is highly likely to have emerged in Kinshasa around ...
Accessing two previously untapped streams of satellite data, scientists at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego and their colleagues have created a new map of the world's seafloor, creating a much more vivid picture of the structures that make up the deepest, least-explored parts of the ocean. Thousands of previously uncharted mountains rising from the seafloor and new clues about the formation of the continents have emerged through the new map, which is twice as accurate as the previous version produced nearly 20 years ago.
Developed using a scientific ...
A new study led by Queen's University Belfast into how cheetahs burn energy suggests that human activity, rather than larger predators, may force them to expend more energy and thus be the major cause of their decline.
Wild cheetahs are down to under 10,000 from 100,000 a century ago with conventional wisdom blaming bigger predators for monopolising available food as their habitat becomes restricted. The traditional thinking has been that cheetahs no longer have sufficient access to prey to fuel their enormous energy output when engaging in super-fast chases.
But, ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Yeast are commonly used to transform corn and other plant materials into biofuels such as ethanol. However, large concentrations of ethanol can be toxic to yeast, which has limited the production capacity of many yeast strains used in industry.
"Toxicity is probably the single most important problem in cost-effective biofuels production," says Gregory Stephanopoulos, the Willard Henry Dow Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT.
Now Stephanopoulos and colleagues at MIT and the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research have identified a new way to ...
How can we tell when someone has fallen asleep? To answer this question, scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital have developed a new statistical method and behavioural task to track the dynamic process of falling asleep.
Dr Michael Prerau, Dr Patrick Purdon, and their colleagues used the evolution of brain activity, behaviour, and other physiological signals during the sleep onset process to automatically track the continuous changes in wakefulness experienced as a subject falls asleep.
The study, publishing today in PLOS Computational Biology, suggests that it ...